The engine cooling system is liquid, closed type, with forced circulation of the liquid.
The device of the cooling system is shown in the figure
The system consists of a cooling jacket, a radiator with electric fans, an expansion tank, a water pump 1, a thermostat 3 and hoses.
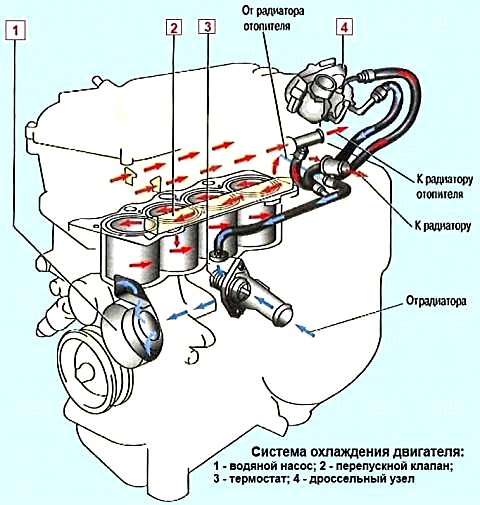
The fluid circulation in the system is created by the water pump 1.
From the pump, liquid is supplied to the engine cooling jacket, washes the cylinders and combustion chambers, and then, depending on the position of the valve, thermostat 3 returns to the pump through bypass channel 2 (at low temperatures) or through the radiator (at high temperatures).
The radiator of the interior heater and the heating channels of the throttle assembly 4 of the power system are connected to the engine cooling system.
Radiator with a vertical fluid flow, with a tubular-ribbon aluminum core and plastic tanks.
In the radiator tanks there are inlet and outlet pipes of hoses to the engine water jacket.
In the lower tank there is a heat exchanger for cooling the automatic transmission fluid and a valve for draining the coolant from the radiator.
In the upper tank of the radiator there is a filler neck with a steam hose connection connecting the radiator to the expansion tank. The neck is hermetically sealed with a stopper with two valves: inlet and outlet.

The exhaust valve opens at a pressure of 78.5-122.7 kPa (0.80-1.25 kgf / cm 2), providing an increase in the temperature at which the coolant begins to boil and preventing intense vaporization.
When a liquid cools, its volume decreases and a vacuum is created in the system.
The inlet valve in the plug opens at a vacuum of about 7 kPa (0.07 kgf / cm 2) and passes the coolant from the expansion tank to the radiator.
Healthy radiator cap valves are very important for the normal operation of the cooling system.
When problems arise (for example, boiling of the coolant), motorists pay attention only to the operation of the thermostat and forget to check the valves.
Leaking of the exhaust valve leads to a decrease in the boiling point of the coolant, and its jamming in the closed state leads to an emergency increase in pressure in the system, which can cause damage to the radiator and hoses.
The expansion tank is used to compensate for the changing volume of the coolant depending on its temperature.

It is made of translucent plastic.
The filler neck of the tank is closed with a plastic stopper, to which a steam hose is connected.
The centrifugal type water pump provides forced circulation of liquid in the cooling system.
It is located on the front surface of the cylinder block and is driven by a V-ribbed belt common to the generator, power steering pump and air conditioning compressor from the crankshaft pulley.
The pump has sealed bearings that do not need to be relubricated
The pump cannot be repaired, therefore, in case of failure (liquid leakage or damage to the bearings), it is replaced as an assembly.
Thermostat 3 with a solid temperature-sensitive filler maintains the normal operating temperature of the coolant and reduces the warm-up time of the engine.

The thermostat is installed in a housing fixed to the cylinder head.
At a coolant temperature of up to 77º C, the thermostat is completely closed and the liquid circulates through a small circuit, bypassing the radiator, which accelerates engine warm-up
At temperatures above 80º C, the thermostat starts to open, at 95º C it opens completely, ensuring fluid circulation through the radiator.
Electric fans of the cooling system (with plastic lotpaddle impellers) serve for additional airflow of the radiator, turn on and off at the signal of the electronic engine control unit.

Moreover, depending on the tension of the thermal regime and the algorithm of the air conditioner, the electric fans can rotate at low and high speed
Changing the speed of electric fans is provided by the engine control unit by changing their connection scheme from serial to parallel circuit
Electric fans assembled with a casing are fixed to the radiator of the cooling system.
The system is filled with a liquid (antifreeze) that does not freeze at ambient temperatures down to -40º C.
The type of coolant filled in the cooling system is Toyota Super Long Life Coolant (red).
It is not recommended to fill the cooling system with water, as antifreeze contains anti-corrosion, anti-foaming and anti-scale additives
Possible malfunctions of the engine cooling system and solutions
Engine is overheating
- - low level of coolant in the radiator - add coolant;
- - the thermostat is faulty (the valve is frozen in the closed position) - replace the thermostat;
- - the water pump is faulty - check the pump and replace it in case of a fault;
- - the radiator core is clogged with dirt and insects - rinse the radiator core from the outside;
- - radiator pipes, hoses and engine cooling jacket are clogged with scale and sludge - flush the cooling system and fill with fresh coolant;
- - one or both electric fans do not turn on due to an open circuit, failure of the temperature sensor, fuses, additional resistance, relay or fan motor - check and repair the electrical circuits.
If necessary, replace the fuses, resistor, relay or fan assembly;
- - damage to the valve in the radiator cap (the valve is constantly open, due to which the system is under atmospheric pressure - replace the radiator cap)
The engine overheats, cold air comes out of the heater
- - an excessive drop in coolant level due to damage to the cylinder head gasket, causing the formation of vapor locks in the engine water jacket. - Repair the coolant leak. Replace damaged cylinder head gasket;
Continuous drop in coolant level in the expansion tank
- - heatsink leaking - replace heatsink;
- - the expansion tank is leaky - replace the expansion tank;
- - coolant leaks through leaky connections of pipes and hoses - replace hose clamps;
- - water pump seal damaged - replace water pump;
- - the cylinder head bolts are not tightened enough (on a cold engine, during a long stop, coolant leaks through the joint between the cylinder head and the cylinder block, traces of coolant may appear in the engine oil) - tighten the cylinder head bolts to the required torque;
- - the heater radiator is leaky - replace the heater radiator.











