The clutch is located between the engine and the gearbox and is designed to disconnect and connect the flywheel mounted on the engine crankshaft and the gearbox input shaft
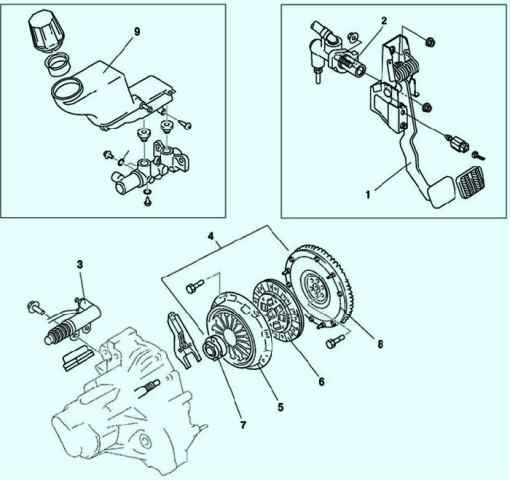
On vehicles equipped with a manual transmission, a diaphragm-type dry single-plate clutch is used (Fig. 1).
Clutch release drive - hydraulic.
The clutch consists of a basket (pressure plate assembly) and a driven plate.
The basket is a steel casing in which a pressure diaphragm spring and a pressure plate are installed.
A diaphragm-type pressure spring presses the disk from the side of the casing.
The clutch basket is attached to the flywheel with six bolts. A driven disk is installed between the pressure plate and the flywheel.
Friction linings are riveted to both sides of the driven disk.
To dampen torsional vibrations when the clutch is engaged, a damper with four coil springs is built into the driven disc.
The hub of the driven disk is splined into gear with the input shaft of the gearbox.
The clutch release hydraulic actuator consists of a main and a clutch release cylinder connected by a pipeline.
The hydraulic clutch uses brake fluid.
Basic data for control and adjustment
Clutch pedal travel 135 mm
Clutch pedal travel for disengaging the clutch 90-110 mm
Thickness of driven disc 7.65 mm
Permissible wear of the petals of the diaphragm spring, no more than 0.6 mm
Permissible wear of the clutch drive disc, no more than 0.5 mm
Permissible runout of the lining of the driven disk, no more than 0.7 mm
The minimum distance between the working surface of the lining of the driven disk and the rivets of their fastening is 0.3 mm
Type of working fluid Dot-3, Dot-4
Tightening torques for threaded connections
Clutch release slave cylinder bolts 18-25 Nm
Bolts for fastening the basket (pressure plate) to the flywheel 17-26 Nm
Checking the technical condition of the clutch
Clutch life depends on operating conditions and driving style.
Operation of the vehicle with a maximum load or off-road, towing a trailer, incomplete disengagement of the clutch when starting off, accelerating and driving, as well as holding the clutch pedal depressed for a long time while the engine is running, significantly reduce the life of the clutch parts.
The clutch in the engaged state (when the pedal is released) should not “slip” and transmit torque from the engine to the transmission without loss, and when the clutch pedal is depressed, completely disconnect the transmission from the engine. Clutch engagement should be smooth - without jerks.
Execution sequence
With the engine off, press the clutch pedal several times.
We make sure that there are no jams in the clutch release mechanism, that there are no squeaks, knocks and other extraneous noises.
Starting the engine. If a howling sound is heard from the clutch housing, which increases when the clutch pedal is depressed, the clutch release bearing is most likely worn
With the engine running, press the clutch pedal all the way and shift into gear.
Switching on should be easy, without crackling or crunching.
If a crackling sound is heard when shifting into gear, and disengagement is difficult, then the clutch is not fully disengaged.
Pumping the hydraulic clutch release, article - bleeding the Mazda 3 clutch.
If there is no air in the drive, the malfunction may be caused by the failure of the clutch master cylinder (it is better to contact a specialized service station to replace it), the clutch slave cylinder, wear or loss of elasticity of the clutch diaphragm spring.
We check the absence of brake fluid leakage on the cuff of the clutch slave cylinder and at the point where the pipeline is connected to it (this is accompanied by a gradual decrease in the fluid level in the master brake cylinder reservoir).

If there is edema, which means that the tightness of the clutch release cylinder is broken, and it must be replaced or the pipeline must be replaced along with the seal
With the engine running and the first gear engaged, gradually releasing the clutch pedal, we check the smooth engagement of the clutch, the absence of jerks or extraneous sounds at the moment of starting off.
Jerking and chattering at the moment of engagement of the clutch can be caused by oiling or warping of the clutch discs or the destruction of the vibration damper
In motion, in third or fourth gear, we sharply press the gas pedal.
If the speed of the crankshaft increases quickly, and the car accelerates sluggishly, then the clutch will slip.
This is also evidenced by the appearance in the cabin of the smell of burning, emitted by highly heated friction linings of the driven disk. To eliminate this malfunction, it is necessary to replace the clutch
If the above symptoms of malfunctions are not detected during clutch diagnostics, the clutch is in a technically sound condition.










