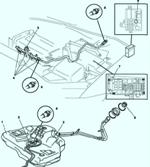
Mazda 3 Fuel System Overview
Mazda 3 (GG) vehicles are equipped with the new L-series engines. The features of the L-series engines are as follows:
- – CAN controller LAN is used
- – Uses a mechanical fuel system with no fuel return to the tank.
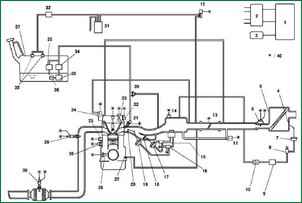
Fig.1 Scheme of the Mazda 3 fuel system management system: 1 - PCM block; 2 - ignition coil; 3 - generator; 4* – damper of the VAD system; 5 - air filter; 6 - mass air flow sensor; 7* – damper actuator of the VAD system; 8* - control solenoid valve of the VAD system; 9* – vacuum chamber; 10* - check valve of the VAD system; 11 - idle speed regulator; 12 – purge solenoid valve; 13 - throttle position sensor; 14 - absolute pressure sensor; 15* - control solenoid valve of the VIS system; 16 - control solenoid valve Variable tumble; 17* – damper actuator of the VIS system; 18* – damper of the VIS system; 19 - actuator damper system VTCS; 20 - damper of the VTCS system; 21 - fuel injector; 22* - control oil valve; 23 - camshaft position sensor; 24 - valve of the exhaust gas recirculation system; 25 - knock sensor; 26 - coolant temperature sensor; 27 - crankcase ventilation valve; 28 - crankshaft position sensor; 29 - heated oxygen concentration sensor (front); 30 - heated oxygen concentration sensor (rear); 31 - container with activated carbon (adsorber); 32 - check valve (double-sided); 33 - pressure regulator; 34 - fuel filter (high pressure); 35 - fuel pump; 36 - fuel filter (low pressure); 37 – fuel tank; 38 - gravity valve; 39 - pulsation damper; 40 - to the PCM block; Note – * : for L3 motors
- - An intake control system is used to improve engine performance in the high speed region (L3 engine).
- - The camshaft control system is used to improve engine performance (L3 engine).
- - A variable intake system is used to increase engine torque and combustion efficiency (L3 engine).
- - The fuel injection control system corrects for intake manifold absolute pressure. – The system has a non-adjustable ignition timing.
- - All fuel line connections are equipped with quick connectors.
- – The KOEO/KOER self-diagnosis function is used.
- - Changed how raw codes are stored.
- - Changed MIL mode for Type 2 drive cycle.
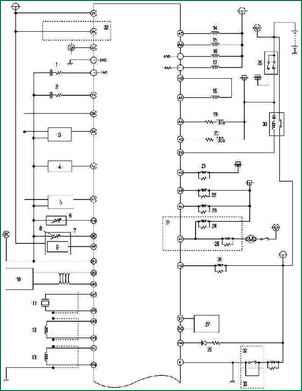
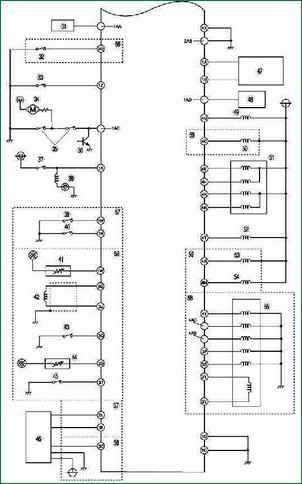
Fig. 2 Wiring diagram of the fuel system control system of a Mazda 3 car with an immobilizer (part 1) The fuel system control system of a Mazda 3 car with an immobilizer (Fig. 2a, 2b) contains the following elements: 1 – heated oxygen concentration sensor (front); 2 - oxygen concentration sensor with heating (rear); 3 - throttle position sensor; 4 - absolute pressure sensor in the intake manifold; 5 – pressure sensor; 6 - coolant temperature sensor; 7 - mass air flow / intake air temperature sensor; 8 - intake air temperature sensor; 9 - absolute pressure sensor in the intake manifold; 10 – local area network of the controller (CAN); 11 - knock sensor; 12 - crankshaft position sensor; 13 - camshaft position sensor; 14 - fuel injector No. 1; 15 - fuel injector No. 2; 16 - fuel injector No. 3; 17 - fuel injector No. 4; 18 - idle speed regulator; 19 - oxygen concentration sensor heater (front); 20 – oxygen concentration sensor heater (rear); 21 - the relay of the air conditioning system; 22 – cooling fan relay; 23 - cooling fan relay; 24 - cooling fan relay; 25 - cooling fan relay; 26 - fuel pump relay; 27 - spiral; 28 - safety lamp; 29 - ignition switch; 30 - main relay; 31 - engines L8, LF (hot area) and L3; 32 - models with automatic transmission; 33 - models with a manual transmission; 34 - generator; 35 - refrigerant pressure sensor (medium); 36 - power steering pressure sensor; 37 - fan motor; 38 - refrigerant pressure sensor (high and low); 39 – switch of the air conditioning system; 40 - brake signal switch; 41 - neutral switch; 42 - clutch switch; 43 - gearbox range switch; 44 - turbine speed sensor; 45 - HOLD switch; 46 - TFT sensor; 47 - oil pressure sensor; 48 - vehicle speed sensor; 49 - ignition coil; 50 - generator; 51 - purge solenoid valve; 52 - control solenoid valve of the VAD system; 53 - valve of the exhaust gas recirculation system; 54 - control solenoid valve Variable tumble; 55 - control solenoid valve of the VIS system; 56 - control oil valve; 57 - valve body; 58 - braking signal; 59 - engines L8, LF (hot area) and L3; 60 - model with a manual transmission; 61 - models with automatic transmission; 62 - L3 engine
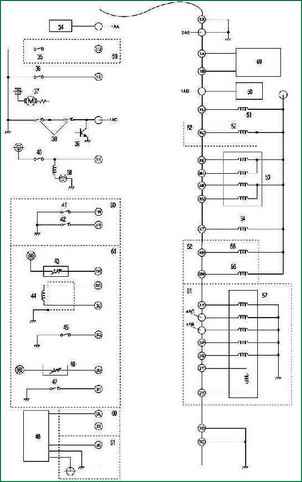
Fig. 2b. Mazda 3 fuel management system wiring diagram with immobilizer (part 2 - continued)
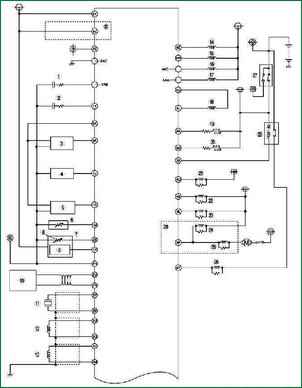
Fig. 3a. Wiring diagram of the fuel system control system of a Mazda 3 car without an immobilizer (part 1) The fuel system control system of a Mazda 3 car without an immobilizer (Fig. 3a, 3b) contains the following elements: 1 - heated oxygen concentration sensor (front); 2 - oxygen concentration sensor with heating (rear); 3 - throttle position sensor; 4 - absolute pressure sensor in the intake manifold; 5 – pressure sensor; 6 - coolant temperature sensor; 7 - mass air flow / intake air temperature sensor; 8 - intake air temperature sensor; 9 - absolute pressure sensor in the intake manifold; 10 – local area network of the controller (CAN); 11 - knock sensor; 12 - crankshaft position sensor; 13 - camshaft position sensor; 14 - fuel injector No. 1; 15 - fuel injector No. 2; 16 - fuel injector No. 3; 17 - fuel injector No. 4; 18 - idle speed regulator; 19 - oxygen concentration sensor heater (front); 20 – oxygen concentration sensor heater (rear); 21 - the relay of the air conditioning system; 22 – cooling fan relay; 23 - cooling fan relay; 24 - cooling fan relay; 25 - cooling fan relay; 26 - fuel pump relay; 27 - ignition switch; 28 - main relay; 29 - engines L8, LF (hot area) and L3; 30 - models with automatic transmission; 31 - generator; 32 - refrigerant pressure sensor (medium); 33 - power steering pressure sensor; 34 - fan motor; 35 - refrigerant pressure sensor (high and low); 36 - switch of the air conditioning system; 37 – the switch of signals of braking; 38 - braking signal; 39 - neutral switch; 40 - clutch switch; 41 - gearbox range switch; 42 – inlet/turbine speed sensor; 43 - HOLD switch; 44 - TFT sensor; 45 - oil pressure sensor; 46 - vehicle speed sensor; 47 - oil pressure sensor; 48 - vehicle speed sensor; 48 - generator; 49 - purge solenoid valve; 50 - control solenoid valve of the VAD system; 51 - valve of the exhaust gas recirculation system; 52 - control solenoid valve Variable tumble; 53 - control solenoid valve of the VIS system; 54 - control oil valve; 55 - valve body; 56 - engines L8, LF (hot area) and L3; 57 - models with a manual transmission; 58 - models with automatic transmission; 59 - L3 engine.
Fig. 3b. Mazda 3 fuel management system wiring diagram without immobilizer (part 2 - continued)