Mazda 3 Manual Transmission Features
The gearbox converts the torque transmitted from the engine in magnitude and direction
This is necessary to ensure optimal speed and patency of the car, high efficiency of the engine and reversing the car.
In addition, the gearbox separates the engine and transmission when the car is stopped and parked, as well as when it coasts with the engine running.
All manual transmission models are equipped with a five-speed gearbox combined with a differential and final drive.
Torque from the engine is transmitted through the gearbox and final drive to the differential, which in turn distributes it between the drive shafts.
The five-speed manual transmission is equipped with a synchronization mechanism for all gears.
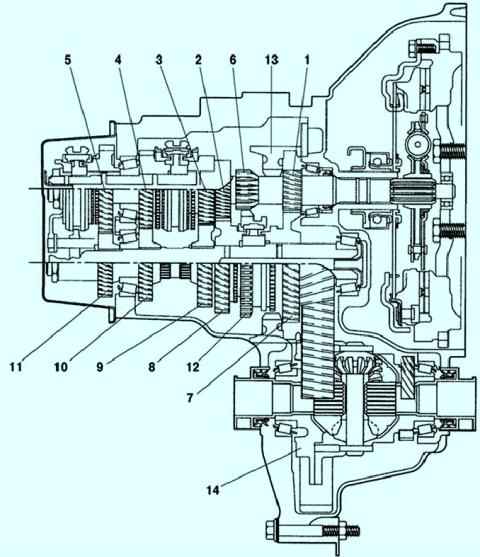
Possible malfunctions of a manual transmission and solutions
Vibration and noise in the gearbox:
- loosening or damage to the engine and gearbox mounts
Tighten fasteners or replace supports
- wear or damage to gears and bearings
Repair the gearbox
- the wrong brand of oil was filled in
Fill with the correct brand of oil
- insufficient oil level
Top up the oil to the correct level
- Violation of engine idle adjustment
Adjust engine idle
Difficult shifting and grinding noise when shifting:
- malfunction of the gearshift cables
Replace shift cables
- the wrong brand of oil was filled in
Fill with the correct brand of oil
- loose fit or wear of blocking rings and synchronizer cones
Repair the gearbox
- weakening of the synchronizer springs
Repair the gearbox
- incomplete engagement of the clutch
Repair the clutch release actuator and bleed the clutch system
Spontaneous disengagement of gears:
- wear of the shift forks or breakage of the springs of the clamps
Repair the gearbox
- increased clearance of the synchronizer clutch on the hub
Repair the gearbox
Oil leak:
- destruction or damage to oil seals or o-rings
Replace seals or O-rings