Precautions with airbag (SRS) Mazda 3
Incorrect handling of the airbag module can lead to sudden deployment of the airbag and injury to the operator
Be sure to read the safety rules when performing these works.
Mazda 3 is equipped with a passive safety system that includes a driver's airbag, a front passenger's airbag, a side airbag and a side curtain airbag.
If the sequence of operations is violated, the passive safety system may unexpectedly work, resulting in an accident.
If a mistake was made during the maintenance of the passive safety system, the system may not perform its functions in a collision.
Before performing maintenance (including removing or installing components, checking or replacing them), read the following items carefully and then follow the steps in the repair manual.
You can start working 90 seconds after the ignition key is turned to the "LOCK" position and the cable is disconnected from the negative (-) battery terminal.
(The SRS is equipped with a back-up power source, so if you start work earlier than 90 seconds after disconnecting the cable from the negative (-) battery terminal, the SRS may operate.).
Do not expose the airbag modules in the horn button, instrument panel, or airbag sensors to direct hot air or flames.
Symptoms of a passive restraint system are difficult to confirm, which is why diagnostic codes are the most important source of information when troubleshooting.
Even in minor collisions where the SRS fails, check the airbag modules and sensors.
Before repairing, remove the airbag sensor to avoid damaging it.
Never use parts of the passive safety system from another car.
Replace parts with new ones.
Do not disassemble or repair airbag modules and sensors for reuse.
If airbag modules and sensors have been dropped, cracked, dented, or otherwise defective in their housings, brackets, or connectors, replace them with new ones.
Use a high impedance volt/ohmmeter (at least 10 kΩ/V) when troubleshooting the system's electrical circuits.
The elements of the passive safety system are provided with information labels. Follow the directions on these labels.
After finishing work on the passive safety system, check its warning lamp.
Disconnecting the cable from the negative (-) battery terminal will de-energize the clock and audio system memory.
Before starting work, write down the contents of the audio system's memory.
After completing all the operations, restore the audio system settings and set the time on the clock.
To prevent memory erasure in storage systems, never use an external backup power supply.
The system (SRS) of the car combines in a complex frontal 1 and 6 (Fig. 1), as well as side 2 and 5 airbags for the driver and passenger in the front seat, window (curtains) 3 safety (depending on configuration) and 4 front seat belt pretensioners
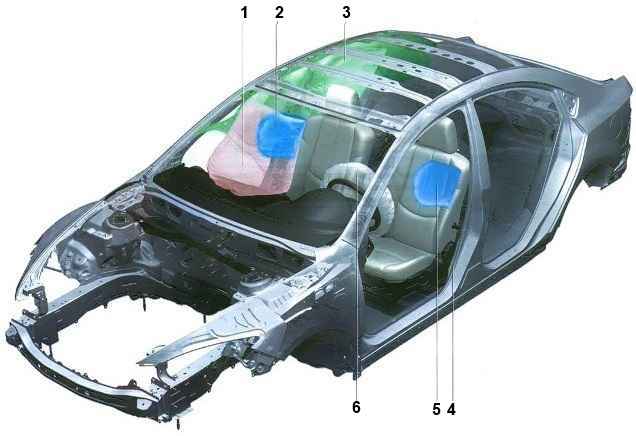

The system includes:

- - the driver's airbag module, located in the steering wheel hub and consisting of a folded airbag shell and a domed gas generator;

- - the front passenger airbag module (depending on the configuration), installed in the instrument panel on the passenger side and consisting of a folded airbag shell and a pipe barrel gas generator
Different from the driver's airbag in shape and volume
When installing a child seat in the front passenger seat, the passenger airbag must be deactivated

The switch is located in the upper left corner of the glove box.
The airbag can be switched off with the car key

When the front passenger airbag is deactivated, the deactivation indicator in the center console panel will illuminate

- - driver and front passenger side airbag modules located in the outer side parts of the front seat backs;

- - window cushion modules (installed on request) located above the windows of the front and rear doors, under the upholstery of the ceiling, and consisting of a folded cushion and a gas generator

- - an electronic control unit (ECU) with shock sensors (accelerometers), installed under the center console
The ECU incorporates micromechanical sensors that measure the longitudinal and lateral acceleration/deceleration of the vehicle in a collision
The electronic unit evaluates the impact by comparing the values it receives from the frontal impact sensor and internal electronic sensors with a set value
If the deceleration signal due to a frontal or side impact exceeds a predetermined value, the ECU will trigger the seat belt pretensioners and deploy the airbags
If the vehicle's battery is destroyed during the crash, the ECU's voltage holding circuit will still be able to activate the airbags for some time after the impact;

- - pretensioners of the front seat belts (mounted in the inertial coils of the front belts) with force limiters of their tension
Pretensioners provide a timely response to an emergency deceleration of the car, pulling the driver and passengers to the seatbacks, preventing them from further moving forward by inertia and getting injured from a deployed airbag
The seat belt pretensioner mechanism always deploys before the airbag
- - headrests installed on the backs of the driver's and passengers' seats prevent damage to the cervical vertebrae of people sitting in the car in case of a strong rear impact and airbag deployment
- - signaling devices of the passive safety system
If the ECU detects a system problem, the airbag warning light will illuminate
The seat belt warning light comes on when the vehicle speed exceeds 10 km/h and stays on for five minutes or until the seat belt is fastened.