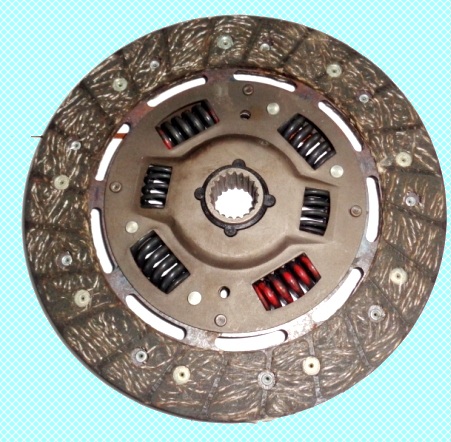
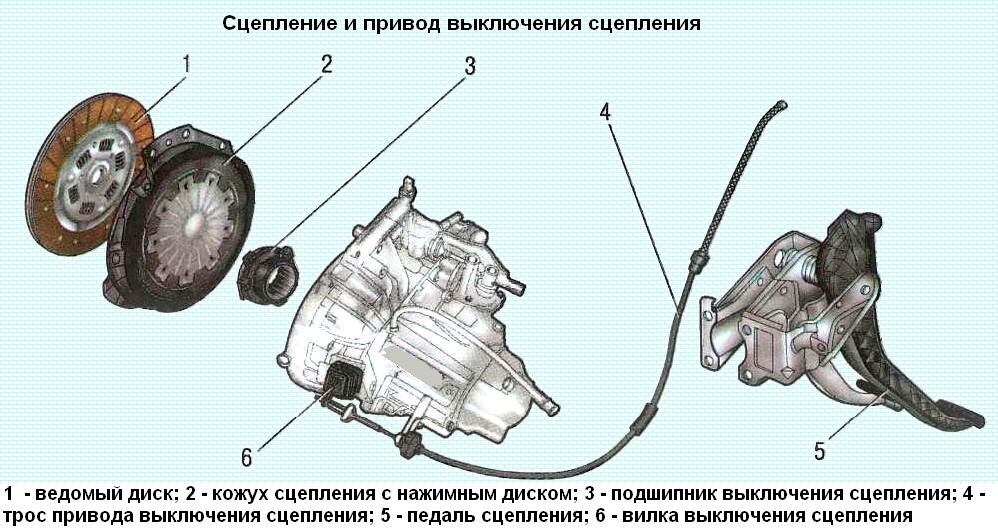
Renault Logan cars are equipped with a dry single-plate clutch with a central diaphragm spring
The clutch basket is connected with six bolts to the engine flywheel
Three pins are pressed into the flywheel to center the basket.
The clutch housing contains a diaphragm spring made of spring steel.
The diaphragm spring consists of eighteen petals, which are elastic release levers.
Due to the elasticity of the levers, the diaphragm spring creates a uniform pressure on the clutch pressure plate and contributes to smooth engagement and disengagement of the clutch.
The need to replace the basket occurs when the diaphragm spring petals are worn to a depth of more than 0.8 mm, as well as in the event of a decrease in pedal force when the clutch is disengaged, which indicates a large wear of the pressure plate surface or a diaphragm spring settlement.
Clutch drive on cars - cable, backlash-free.
The front end of the cable is attached to the clutch release fork, and the rear end is attached to the clutch pedal holder.
The front tip is threaded, used to adjust the clutch release drive.
The clutch pedal is mounted on an axle in the pedal assembly bracket. A pedal return spring is installed on the same axle.
The fork pivots on a ball joint installed in the clutch housing.
A clutch release bearing is installed between the clutch release fork and the diaphragm spring petals.
There are two hooks on the bearing sleeve, with which it hooks onto the legs of the fork.
A clutch drive scheme has been applied, in which the bearing is constantly pressed against the petals of the diaphragm spring.
The bearing moves freely along the guide sleeve pressed into the clutch housing.
Clutch disengagement is as follows.
When the clutch pedal is depressed, the cable turns the clutch release fork, which moves the bearing along the guide sleeve.
The bearing presses on the petals of the diaphragm spring.
The spring, deforming, stops pressing the pressure plate against the flywheel, while the pressure plate moves away from the flywheel, as a result of which the engine crankshaft and the gearbox input shaft can rotate independently of each other.
When the clutch pedal is released, the bearing returns to its original position, while the diaphragm spring again begins to press on the pressure plate, which, in turn, presses the driven disc against the flywheel - as a result, the transmission of torque resumes.
Driven disc 1 is mounted on the splines of the input shaft of the gearbox and is clamped by a diaphragm spring between the flywheel and the pressure plate.
Clutch release bearing 3 of a closed type, which does not require lubrication in operation, is mounted on a guide sleeve pressed into the hole in the clutch housing.
The guide sleeve is a non-separable assembly that includes an oil seal and front input shaft bearing.
The bearing is moved by fork 6, mounted on a ball bearing, screwed into the clutch housing.
The fork is inserted into the grooves of the bearing coupling without additional fastening.
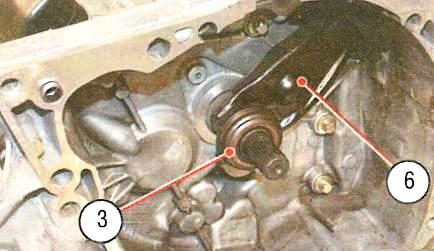
On the free shoulder of the clutch release fork, sealed in the clutch housing with a rubber boot, the cable 4 of the clutch release drive acts, the second end of which is fixed on the sector of the clutch pedal 5.
The pedal travel in operation is adjusted as the lining of the driven disk wears out with an adjusting nut mounted on the threaded end of the cable.
The clutches of engines with a working volume of 1.4 and 1.6 liters are the same in design and differ only in the diameters of the driven and pressure plates.
For a 1.4L engine the diameter is 180mm, for a 1.6L engine it is 200mm.
The working stroke of the outer shoulder of the clutch release fork is somewhat different, which for a 1.4 liter engine is 28 ~ 33 mm, for a 1.6 liter engine - 30-35 mm.
Possible clutch failures and solutions
Jerks when starting off
Clutch cable sticking - Apply engine oil to the cable. If the cable is damaged, replace it
Jamming of the driven disk hub on the splines of the input shaft of the gearbox - Clean the splines from dirt, eliminate minor damage with a file.
With a significant worn or damaged splines, replace the disc or the input shaft of the gearbox.
Before assembly, apply SHRUS-4 grease to the splines.
Distortion of the driven disc - Replace the driven disc
Weakening of the friction linings of the driven disc, severe wear or cracks on the lining - Replace the driven disc
Loss of elasticity of driven disc spring plates - Replace driven disc
Significant settlement or breakage of the springs of the damper of torsional vibrations, wear of the windows under the springs - Replace the driven disk
Scoring on the running surfaces of the flywheel or pressure plate - Replace the flywheel or clutch housing with pressure plate assembly (clutch basket)
Oiling the working surfaces of the friction linings of the driven disk - Thoroughly rinse the oiled surfaces with mineral spirits or gasoline and wipe them dry.
Replace heavily oiled driven disc. Eliminate the cause of oiling.
Rattle, knock or noise when engaging the clutch
Significant settlement or breakage of the springs of the damper of torsional vibrations, wear of the windows under the springs - Replace the driven disk
Distortion of the driven disc - Replace the driven disc
Weakening of the friction linings of the driven disc, severe wear or cracks on the lining - Replace the driven disc
Increased noise when disengaging the clutch
Worn, damaged or leaking lubricant from clutch release bearing - Replace bearing
The clutch slips (not fully engaged) when the gas pedal is pressed sharply, the engine picks up speed, but the car does not accelerate
Oiling the flywheel, pressure plate and friction linings of the clutch disc - Wash the oiled surfaces with gasoline and wipe them dry.
Replace a heavily oiled disc. Eliminate the cause of oiling.
Decreased diaphragm spring force - Replace drive disc (basket)
Severe wear or burnt friction linings of the driven disc - Replace the driven disc
Clutch actuator damage or binding - Eliminate binding. Replace drive parts if necessary.
Clutch engages (does not disengage completely) forward shifting is difficult, reverse gear shifts with noise when the gearbox is in good condition
Incorrect adjustment of the clutch drive (insufficient full pedal travel) - Adjust the drive
Clutch cable sticking - Apply engine oil to the cable. If the cable is damaged, replace it.
Loose rivets or breakage of friction linings, warping of the driven disk (end runout more than 0.5 mm) - Replace the driven disk
Heavy and uneven wear, scuffing on the working surfaces of the flywheel or clutch pressure plate - Replace the flywheel.
If the surface of the pressure plate is damaged, replace the casing with the pressure plate assembly (clutch basket)
Distorted or warped pressure plate - Replace cover with pressure plate assembly (clutch basket)
Jamming of the driven disk hub on the splines of the input shaft of the gearbox - Clean the splines from dirt, eliminate minor damage with a file.
In case of significant wear or damage to the splines, replace the driven disk or the gearbox input shaft