Rear suspension independent, multi-link spring (two transverse and one trailing arm on each side), with telescopic shock absorber struts, coil springs and anti-roll bar
The main element of the rear suspension is a telescopic shock absorber strut 3, which combines the functions of the telescopic element of the guide mechanism and the damping element of the vertical vibrations of the wheel relative to the body
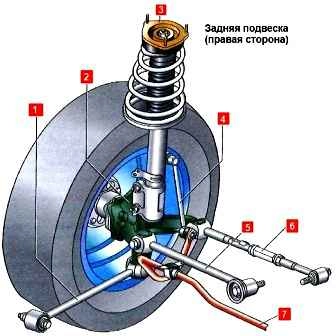
A coil spring, a compression buffer and an upper support are assembled on the shock absorber strut, through which the load is transferred to the car body.
Shock absorber strut is connected to wader 2 with two bolts
Transverse; levers 5 and 6 are attached to the fist and to the rear suspension crossbar using silent blocks
The trailing arm 1 connects the fist to the body through silent blocks
The rear suspension cross member is attached to the body side members.
The anti-roll bar 7 with rubber bushings installed on it is connected to the body with two brackets, and with the shock absorber struts of the rear suspension - stabilizer struts 4
Rear wheel hubs mounted on double row angular contact ball bearings
Bearing housings are bolted to knuckles
The camber angle of the rear wheels is set by design and is not adjustable in operation
At the camber angle, you can only control the condition of the rear suspension
Toe-in of the rear wheels is adjusted by changing the length of the rear wishbones with adjusting clutches
Possible malfunctions of the rear suspension and solutions
Noise and knock in the suspension when the car is moving:
- - shock strut is faulty - replace the shock strut;
- - weakening of the shock strut attachment or wear of the suspension strut lug bushing - tighten the bolt and nut of the lower shock strut mounting or replace the bushings;
- - settling or breakage of the spring - replace the spring;
- - failure of the wheel hub bearing - replace the bearing
Moving the car away from straight ahead:
- - uneven tire pressure - set normal tire pressure;
- - wheel tires have different wear or tread pattern - change tires;
- - the camber angle is violated - eliminate the cause of the violation of the camber angle and adjust the wheel alignment angles;
- - sediment or breakage of one of the springs - replace the springs;
- - deformation of the trailing arms - replace the trailing arms;
- - wear of trailing arm silent blocks - replace trailing arms
Increased tire tread wear:
- - air pressure in tires is not correct - set normal tire pressure;
- - wheel alignment parameters are violated - eliminate the causes of wheel alignment violation and adjust the rear wheel alignment angles;
- - car overload - do not overload the car;
- - wheels out of balance - balance the wheels