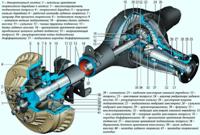
The rear suspension of the car is dependent, it includes a guide device, elastic elements and devices that dampen body vibrations.
The rear axle beam is pivotally connected to the body by means of torque rods - two lower 3 (Fig. 1) and two upper 9 longitudinal and one transverse rod 1.
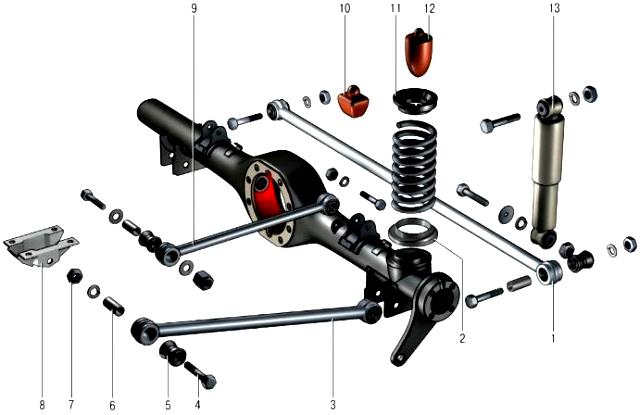
Longitudinal rods transmit pushing and braking forces from the drive wheels through the rear axle beam to the body.
The cross bar keeps the body from lateral displacements.
The reaction rods are attached to the body brackets and the rear axle beam through rubber-metal hinges, which are structurally the same and differ only in size.
The hinge consists of a rubber bushing 5 installed in the eye of the rod, a spacer sleeve 6 that passes through the hole of the rubber bushing, a thrust washer and a rod fastening bolt.
The elastic elements of the suspension consist of coiled coil springs, two main buffers 12 of the compression stroke and an additional compression buffer 10.
The spring installed in the suspension rests with its upper end on the support cup through the rubber insulating gasket 11, which is placed in the stamped steel cup of the body.
The lower end of the spring rests on the cup of the rear axle beam through the insulating gasket 2.
The main buffers 12 are installed inside the springs and secured with a mushroom-shaped retainer in the holes of the upper supports.
Additional buffer 10 is mounted on a bracket bolted to the bottom of the body.
The extinguishing device consists of two hydraulic shock absorbers.

Rear suspension at the bottom rear of the car
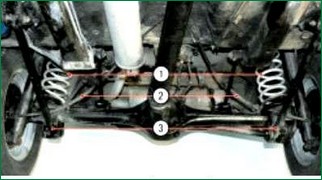
Checking the technical condition of the rear suspension on a car
Check the condition of the rear suspension from below the vehicle mounted on a lift or pit.
Suspensions on rubber parts are not allowed:
- – signs of rubber aging;
- - mechanical damage.
On rubber-metal hinges, signs of aging, cracks, one-sided bulging of the rubber mass are not allowed.
Replace defective parts.
Check for mechanical damage (deformations, cracks, etc.) of the suspension elements, especially the suspension rods and the cross rod bracket on the body.
When checking, carefully inspect:

Rubber bushings of the lower hinges
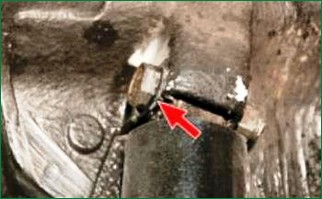
Pillows of the upper hinges of shock absorbers.
Shock absorbers.
Liquid drips and "sweating" are not allowed.

Rubber bushings of the hinge of fastening of the transverse rod to the rear axle beam

Hinge for fastening the transverse rod to the bracket on the body

Hinges for attaching the upper longitudinal bars to the rear axle,

Hinges for fastening the lower longitudinal bars to the rear axle,

Hinges for fastening the upper longitudinal bars to the body

Hinges for fastening the lower longitudinal bars to the brackets on the body
Inspect the additional compression buffer.
Compression buffer.
Possible malfunctions of the rear suspension, and solutions
- Cause of malfunction
Remedy
Noise and knock in the suspension when the car is moving
- Faulty shock absorbers
Replace or repair shock absorbers
- The shock absorbers are loose or the bushings of the shock absorber eyes are worn out
Tighten the shock absorber mounting bolts and nuts, replace worn or damaged parts
- Settlement or breakage of a spring
Replace springs as a set
- Knocking from the “breakdown” of the suspension due to the destruction of the compression stroke buffer or overloading the rear suspension
Replace damaged buffers, unload the car's rear suspension
Frequent "breakdowns" of the rear suspension
- The rear axle of the car is overloaded
Unload the rear axle
- Settlement or breakage of a spring
Replace springs as a set
- Shock absorbers do not work
Replace or repair shock absorbers
Moving the car away from straight ahead
- Different air pressure in tires
Set your tires to the correct pressure
- Settlement or breakage of one of the suspension springs
Replace springs as a set
- Displacement of the rear axle due to deformation of the rear suspension bars
Straighten or replace rods