Insufficient belt tension impairs the circulation of fluid in the cooling system, which leads to engine overheating
In addition, recharging the battery worsens and the belt itself wears out more.
Too much tension can damage the water pump and alternator bearings.
Check the tension of the water pump and generator drive belt from above in the engine compartment.
You will need: a key "13", mounting blade.

The tension is characterized by the amount of deflection of the belt between the pump and crankshaft pulleys (deflection B) (Fig. 1) or the generator and pump pulleys (deflection A)
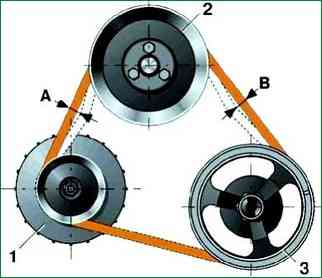
when applying a force of 98.1 N (10 kgf) in the middle of the distance between the pulleys.
Deflection A should be 10-15 mm, deflection B - 12-17 mm.
It is more convenient to check deflection A.
To check the tension, you can use a spring balance scale by hooking a branch of the belt with a hook and pulling it up.
Adjust the belt tension on the vehicle mounted on a lift or a pit.
Adjustment is carried out by moving the generator relative to the engine.
Remove the oil sump guard and engine mudguard.

Loosen the nut securing the alternator to the tension bar by about one turn

Loosen the bottom fastening nut of the alternator.

Move the alternator away from the engine to increase belt tension.
When moving the alternator to increase belt tension, apply force only to the alternator housing. by placing a mounting spatula between the body and the engine.

To reduce belt tension, move the alternator towards the engine by hand.

Without changing the position of the generator, tighten the nut securing the generator to the tension bar and the nut of the lower generator mount.
Tightening torques:
- nuts for fastening the generator to the tension bar 28.08-45.3 Nm (2.9-4.6 kgcm);
- alternator lower mounting nuts 57.3-72 Nm (5.95-7.35 kgcm).
Install the oil sump guard and engine mudguard in the reverse order of removal.
To replace the belt, unscrew the crankshaft position sensor screw and remove the sensor from the bracket socket without disconnecting the wires.
Remove the power steering pump drive belt.
Follow steps 2 and 3 provided for adjusting the belt tension and move the alternator against the engine until it stops.

Remove the belt first from the pump pulley, then from the alternator pulleys and the crankshaft.
Place the new belt first on the crankshaft pulley, then on alternator pulley and then on the pump pulley.
If the new belt is tight on the pump pulley, and the generator is shifted all the way to the engine, carefully turn the pump pulley by hand or slowly turn the crankshaft until the belt is completely put on the pulley.
Ask an assistant to turn the crankshaft.
Follow steps 2-6 for adjusting the belt tension.
Reinstall the crankshaft position sensor.
As an option, one V-ribbed belt can be installed on the car, which serves as the drive for all auxiliary units (water pump, generator and power steering pump).
In this case, the generator is installed to the left of the engine at the top.
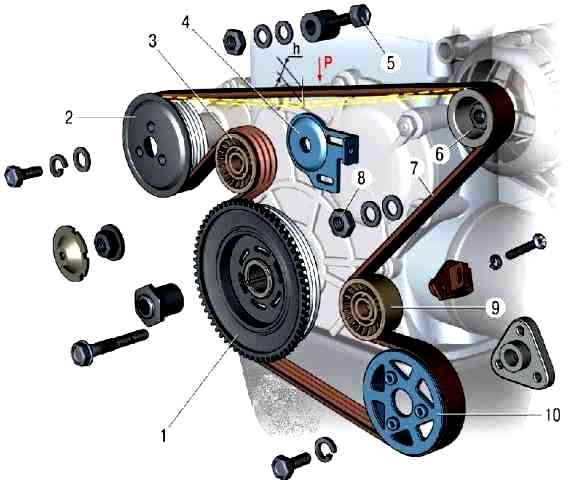
Scheme for checking the tension of the auxiliary drive V-ribbed belt
In this case, the belt tension is checked by its deflection between the pulleys of the generator and the water pump.
Under normal belt tension, the deflection "h" (figure) under the action of a concentrated load "P" of 75 N (7.6 kgf) should be equal to (12 ± 1) mm.
Regulate the belt tension by moving the tension roller 3, rotating the bolt 5 of the tensioner with the nuts 8 of the fastening bracket 4 of the tensioner loosened.
After adjusting, turn the engine crankshaft two turns and check the belt tension again.










