Design of wheel drives with JH3 gearbox of a car Lada Largus
A design feature of the transmission with the JH3 gearbox is the equal length approximation of the drives
Due to the same length of the drives, the equality of the moments and forces that occur on the drive wheels is ensured.
The drive of the left wheel is increased due to the internal hinge, which is made inside the gearbox housing.
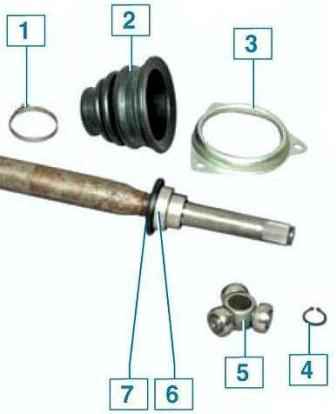
The drive of the right wheel, on the contrary, is reduced due to the splined shaft, which is made in one piece with the side gear of the differential and exits the gearbox.
A rubber damper is installed on the right wheel drive shaft.
The external and internal hinges of the drives (of the "Tripod" type) have different designs.
The hinges of the drives are covered with dirt covers.
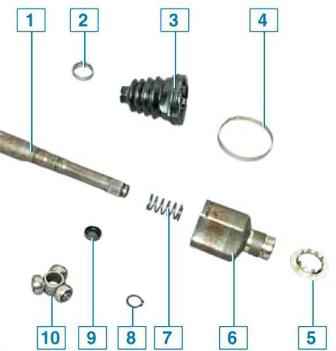
Internal hinge of the drive provides the possibility of angular movements of the suspension and compensates for the mutual movements of the suspension and the power unit by changing the length of the drive shaft.
The inner hinge is collapsible.
At the splined end of the drive shaft, on the side of the inner hinge, there is a hub with three spikes - a three-spike, on each of the spikes (trunnion) of which there is a roller with an outer spherical surface, rotating on a needle bearing.
The needle bearing is fixed against displacement along the stud axis by a locking ring, put on a retaining ring located in the stud groove.
The three-stud is fixed on the drive shaft with a retaining ring.
The mutual movements of the suspension and the power unit are compensated by the movement of the three-stud rollers in the longitudinal grooves of the internal hinge body.
The inner joints of the left and right wheel drives are not interchangeable.

The tip of the body of the inner hinge of the right wheel drive is put on the splined shaft coming out of the gearbox housing and made integral with the differential side gear (see Fig. 3).
A spring installed inside the housing of the right wheel drive inner joint ensures that the joint housing is pressed against the side gear of the differential during suspension operation.

The body of the inner hinge of the left wheel drive is located in the gearbox and is made integral with the left side gear of the differential (shown in Figure 4 with the drive removed).

A needle bearing assembly with an oil seal is installed on the left wheel drive shaft behind the three-pin inner joint.
The bearing inner race is pressed onto the drive shaft and rotates with it.
A protective cover of the inner joint is clamped to the stationary outer ring of the bearing.
The other end of the hinge cover is attached to the gearbox housing through a metal flange holder.
An oil seal installed in the outer ring of the bearing prevents oil leakage from the gearbox along the drive shaft.
The bearing seal is closed from dirt with a plastic gryase deflector mounted on the shaft.
If the mudguard of the hinge or the bearing seal is damaged, oil will leak from the gearbox.

The outer joint of the drive (Fig. 6) provides torque transmission at various angles of rotation of the drive wheels.
The external hinges of the drives of both wheels are the same, they are made non-separable and cannot be dismantled from the shafts.
The outer hinge consists of a housing in which a three-stud joint with rollers rotating on needle bearings is rigidly fixed, and a fist made integral with the drive shaft.
With mutual angular displacements of the body and the knuckle of the hinge, the rollers of the three-pin roll over in the longitudinal grooves of the knuckle.
The body of the outer hinge with a splined shank enters the splined hole of the wheel hub and is fastened with the hub bearing nut.
The outer joints of both drives and the inner joint of the right drive are greased for life.

Replenishment or replacement of lubricant, as well as any other maintenance of the wheel drive shafts during the operation of the vehicle is not required.
It is only necessary to monitor the condition of the protective covers of the hinges and the collars of their fastening, as well as the condition of the oil seal of the bearing of the inner hinge of the left drive.
A damaged boot must be replaced as soon as possible, since dirt entering the lubricant causes rapid wear of the hinge parts and failure, and damage to the rubber boot or seal of the bearing of the inner joint of the left drive will lead to oil leakage from the gearbox and to its failure out of order.
When installing a new hinge cover, the clamps of its fastening should also be replaced with new ones.
If the outer joint fails, the entire actuator assembly must be replaced, and if the inner joint of the actuator fails, only the joint can be replaced.
The bearing (complete with the oil seal) of the inner joint of the left wheel drive is supplied as spare parts along with a protective cover.