The energy-absorbing mechanism (Fig. 2) is mainly composed of a bottom bracket, an energy-absorbing plate, a tear-off bracket, a deformable main shaft, and a deformable intermediate shaft
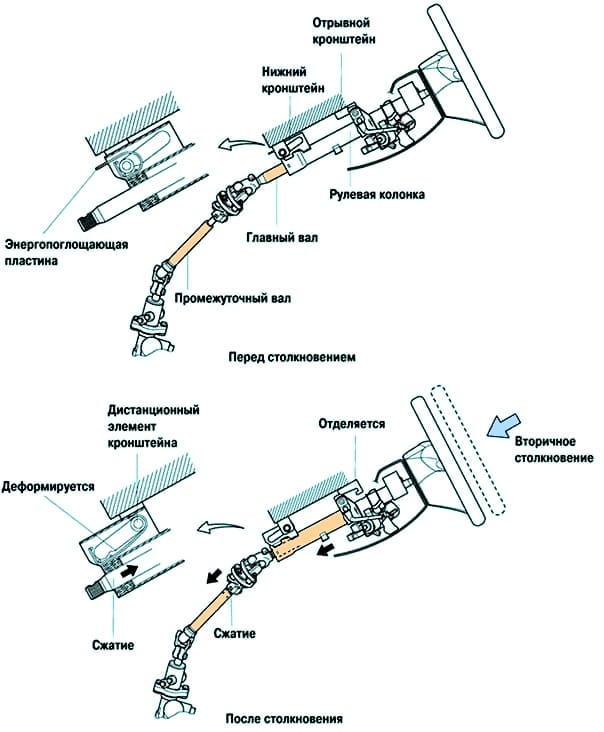
When an impact is transmitted to the steering wheel in a frontal collision (secondary impact), the bottom bracket and bracket spacer, and the tilt bracket and column tilt lever lock bolt are separated, causing the steering column to move forward.
At the same time, the bottom bracket energy absorbing plate is deformed by the bracket spacer and helps absorb the impact energy of the secondary collision.
In addition, the amount of movement of the entire steering column is absorbed by the compression of the main and intermediate shaft.
Precautions for working with the passive restraint system (SRS)
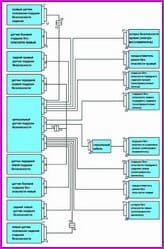
Fig. 2. Scheme of connections of the passive safety system
The Camry is equipped with a passive safety system that includes a driver airbag, a front passenger airbag, a side airbag and a side curtain airbag.
Failure to follow the sequence of maintenance work can lead to unexpected activation of the passive safety system during maintenance with the possibility of an accident.
Further, if a mistake was made during the maintenance of the passive safety system, then the passive safety system may not perform its functions in a collision.
Before performing maintenance (including removing or installing components, checking or replacing them), read the following items carefully and then follow the steps in the repair manual.
You can start working 90 seconds after the ignition key is turned to the "LOCK" position and the cable is disconnected from the negative (-) battery terminal.
The passive safety system is equipped with a backup power source, so if you start work earlier than 90 seconds after disconnecting the wire from the negative (-) battery terminal, the passive safety system may work.
Do not expose airbag modules in the horn button, instrument panels, etc., or airbag sensors, to direct hot air or flames.
Signs of a passive restraint system malfunction are difficult to confirm, thus diagnostic codes are the most important source of information when troubleshooting.
When troubleshooting the SRS, always check the diagnostic codes before disconnecting the battery.
Even in minor collisions where the SRS fails, the airbag modules and sensors must be checked.
Before repairing, remove the airbag sensor if there is a possibility that the sensor may be impacted during the repair.
Never use parts of the passive safety system from another car.
When replacing parts, replace them with new ones. Never disassemble or repair airbag modules and sensors for reuse.
If airbag modules and sensors have been dropped or have cracks, dents, or other defects in their housings, brackets, or connectors, replace them with new ones.
Use a high impedance volt/ohmmeter (at least 10 kΩ/V) when troubleshooting the system's electrical circuits.
The elements of the passive safety system are provided with information labels. Follow the directions on these labels.
After the work on the restraint system is finished, check the warning lamp of the restraint system.
Disconnecting the cable from the negative (-) battery terminal will de-energize the clock and audio system memory.
Before starting work, write down the contents of the audio system's memory.
After completing the work, restore the audio system settings and set the time on the clock.
To prevent memory erasure in storage systems, never use an external source of resizing power supply.
All SRS connectors have a distinctive yellow color.
In order to ensure high reliability, the connectors of the passive safety system have a special design and functions.
The pins of these connectors are gold plated for high reliability and durability.