The cooling system ensures the correct operating temperature of the engine
It consists of a series of components such as a radiator and thermostat, plumbing lines, and a network of small, precisely fitted channels in the engine block and cylinder head
The coolant circulates in them.
So there is a water jacket, which through the hoses of the cooling system removes the heat of combustion to the radiator.
Which paths the coolant takes in the cooling system depends on the temperature of the engine.
Coolant circulation in a small circuit
After starting a cold engine, the coolant initially circulates, limited by the engine and heating.
In this so-called small circuit coolant circulation, the thermostat keeps the flow to the radiator closed.
Coolant flows directly back into the engine.
So the coolant heats up faster, and the engine warms up faster.
The radiator comes into play only after the coolant reaches a certain temperature.
The thermostat opens the flow, while the cold water from the radiator mixes with the already heated water from the circulation along the small circuit.
This gradual addition of cold water prevents the so-called cold shock of the engine.
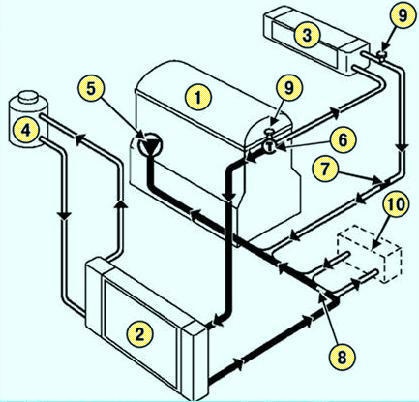
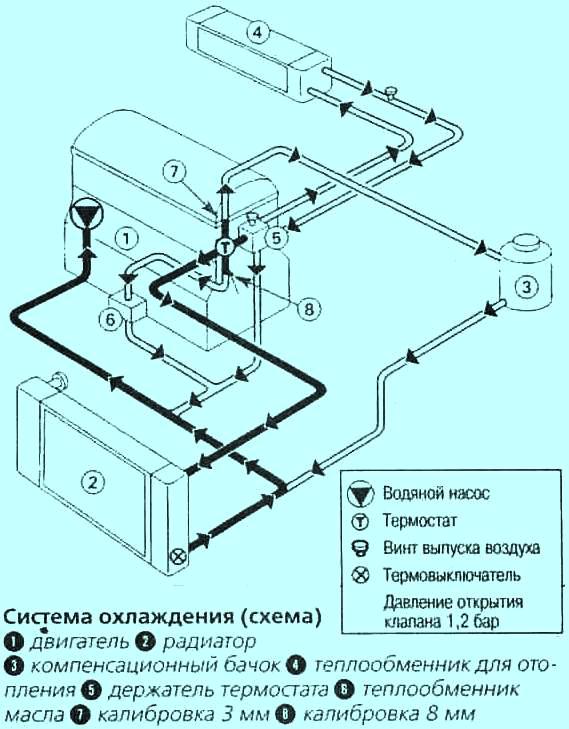
Fig. Fig. 2. Scheme of the cooling system of the car Megane 2 with engines K4J, K4M: 1 - engine; 2 - radiator of the engine cooling system; 3 - heater radiator; 4 - expansion tank; 5 - water pump; 6 - thermostat; 7 - branch pipe with a diameter of 9 mm; 8 - branch pipe with a diameter of 16 mm; 9 - plugs for air release; 10 - oil-water cooler for automatic transmission
Scheme of the cooling system with engines K4J, K4M (Fig. 2)
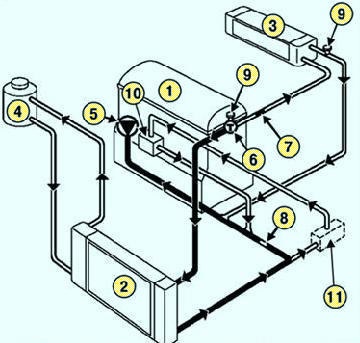
Fig. Fig. 3. Scheme of the cooling system of a Megane 2 car with an F4R engine: 1 - engine; 2 - radiator of the engine cooling system; 3 - heater radiator; 4 - expansion tank; 5 - water pump; 6 - thermostat; 7 - branch pipe with a diameter of 8.3 mm; 8 - branch pipe with a diameter of 16 mm; 9 - plugs for air release; 10 - oil-water cooler;11 - oil-water cooler for automatic transmission
Cooling at operating temperature
While the water temperature rises, the thermostat keeps the cold water supply open all the time and at the same time closes the circulation along the small circuit.
At operating temperature, coolant circulates from the lower right tank hose (in the direction of travel) to the water pump, which sends it under pressure to the engine block and cylinder head.
Most of the fluid is then directed through the open thermostat and top hose back to the radiator, while the remainder flows to the heating coil.
If the water temperature drops below the prescribed operating level while driving, the thermostat will again shut off the flow to the radiator until the coolant is warm enough.

Water distributor with built-in thermostat in fig. 4
Overpressure and engine cooling fan
The cooling system is under overpressure of approximately 1.2 bar. Because of this, the boiling point of the coolant rises from 100°C to, rounded off, 120°C.
The increased temperature enables more economical and thus energy-saving operation of the motor.
If the coolant pressure exceeds 1.2 bar when the engine is warm, the pressure relief valve on the expansion tank will take over.

It will open and release some water vapor to equalize the pressure.
Tem however, when traveling, for example, around the city, it may happen that the coolant in the system overheats.
In this case, the cooling fan should additionally cool the radiator.
All Megane engines have electrically driven cooling fans.
This small wind turbine is activated by a thermal switch in the radiator water tank as soon as the coolant flowing past exceeds a certain temperature.
It will turn off the fan again if the coolant temperature drops below a certain value.
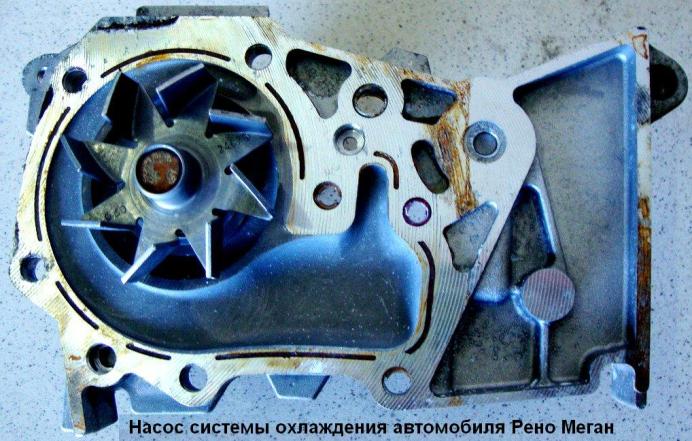
Water pump
The so-called centrifugal pump, which ensures constant circulation of the coolant.

Radiator

It consists of two plastic tanks, one of which is located on its right side and the other on its left side.
There are many thin-walled tubes between them, interconnected by a framework of plates.
This increases the airflow area to many square meters.
The radiator is mounted on the body crosshead with two attachment points (upper and lower).
Thermostat
Maintains a constant temperature.
It opens the flow at about 90°C and allows water to flow to the radiator and back into the engine.
Inside the thermostat there is a jar filled with special wax and a valve plate.
The more the coolant heats up, the more the wax liquefies.
It expands more and more and opens the valve that controls the flow of cold water from the radiator.
At operating temperature, the valve is fully open, and the path to the circulation of coolant through the small circuit is completely closed.
If the water cools, the spring will press on the valve plate and block the flow through the radiator exactly until the coolant heats up again enough.
Compensation tank

If the pressure is too high, it releases water vapor through the safety valve in the lid.
It is located in the engine compartment, on the left (towards the direction of travel) side.
Replacing a car's coolant is discussed in the article - Replacement method coolant Renault Megane 2










