Automatic transmission checks are carried out to determine the malfunction of the gearbox elements
Checking transmission switch continuity
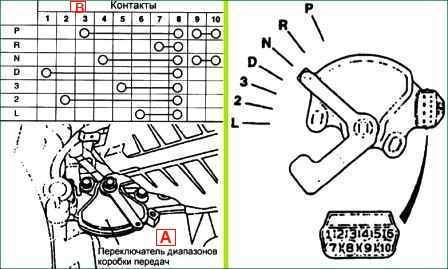
Disconnect the connector and use a tester to check the conductivity of the gearbox range switch at various positions of the selector lever
Checking the conductivity of the sport mode switch (F4A42-2 2.0 and 2.5 l)
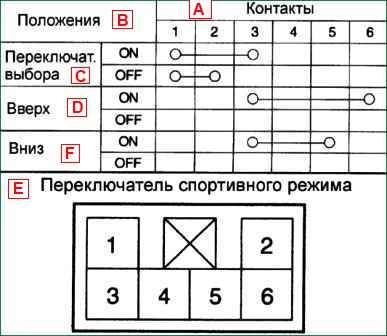
Disconnect the connector and check the continuity of the sport mode switch
Transmission range switch and control cable adjustment
Set the selector lever to the neutral position "N"
From the gearbox side, loosen the nut that secures the control cable to the lever to release the cable and control lever
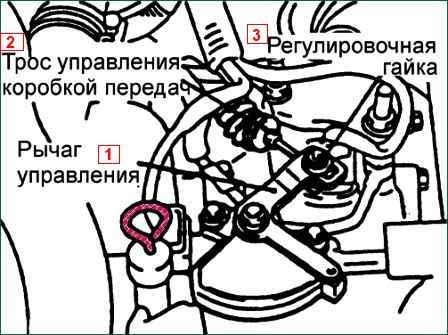
Setting the selector lever to the neutral position
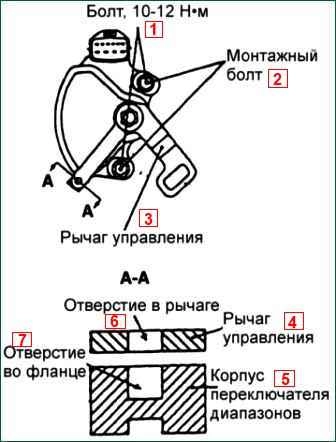
Weaken the mounting bolts of the gearbox range switch housing
Then turn the gear range switch housing so that the hole at the end of the control lever and the hole in the projection of the gear range switch housing are aligned
We tighten the mounting bolts of the gearbox range switch housing with the tightening torque given in the specification
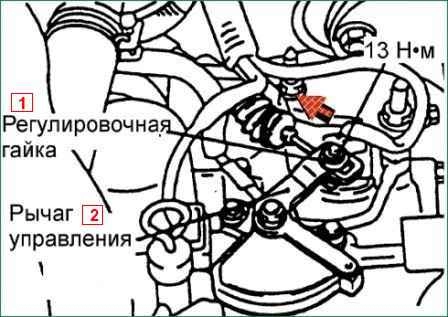
Gently press the transmission control cable in the direction of the arrow and tighten the adjusting nut
Checking that the selector lever is in the "N" position
Checking the operation and functioning of the switch for each position of the selector lever
Checking automatic transmission components
- Check throttle position sensor
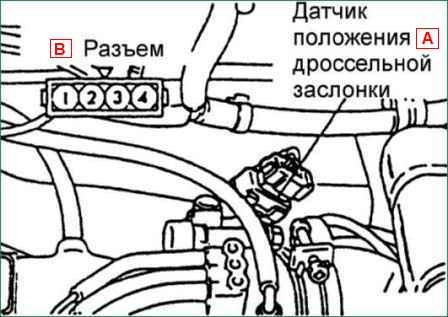
Disconnect the connector from the throttle position sensor.
Measure the resistance between terminals 1 and 4 of the throttle position sensor connector.
Resistance: 3.5-6.5 kΩ
Measure the resistance between terminals 2 and 4 of the throttle position sensor connector.
Normal state:
If the throttle valve is slowly opened from the home position to the fully open position, the resistance should change smoothly in accordance with the throttle valve opening angle.
If the resistance is different or does not change smoothly, replace the throttle position sensor.
- Checking the oil temperature sensor
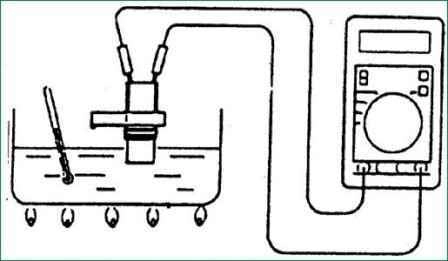
Remove the oil temperature sensor.
Measure the resistance between terminals 1 and 2 of the sensor connector.
Resistance:
- 16.7-20.5 kΩ at 0° C
- 0.57-0.69 kΩ at 100° C
- Vehicle speed sensor test
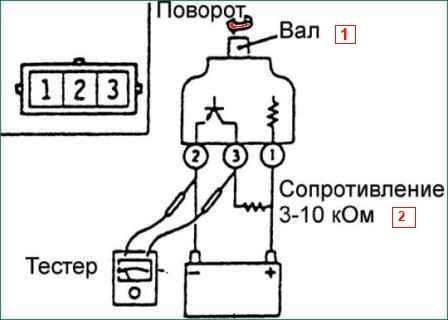
Remove the vehicle speed sensor and connect a 3-10 kΩ resistor as shown.
Rotate the vehicle speed sensor shaft and check that there is voltage between terminals 2 and 3 (1 revolution = 4 pulses).
- Check control relay A / T
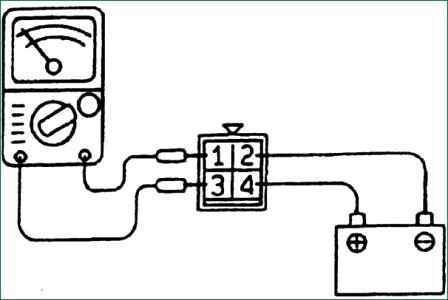
Remove control relay A / T.
Connect terminal (2) of the A/T control relay to the negative (-) battery terminal and terminal (4) of the control relay to the positive (+) battery terminal.
Check continuity between terminal (1) and terminal (3) of the A/T control relay when the jumpers are connected and disconnected from the battery.
When connecting jumpers between the relay terminals, there must be conductivity.
When disconnecting the jumpers between the relay terminals, there must be no conduction.
If the test fails, replace the relay.
- Checking the solenoid valve
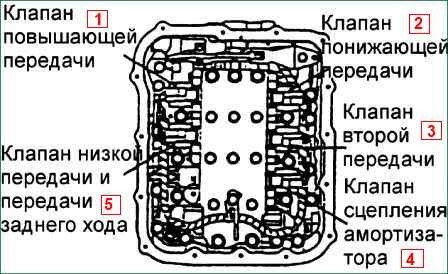
Remove the valve body cover.
Disconnect the connectors from each solenoid valve.
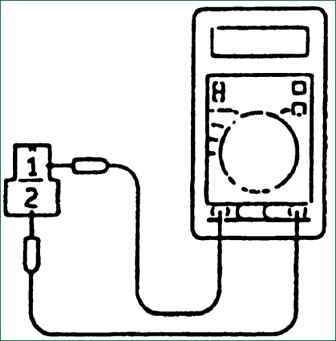
Measure the resistance between terminals 1 and 2 of each solenoid valve.
Resistance :
Shock Clutch Solenoid Valve: 2.7-3.4 ohms at 20°C
Low and reverse solenoid valve: 2.7-3.4 ohms at 20°C
Second gear solenoid valve: 2.7-3.4 ohms at 20°C
Back Solenoid Valve: 2.7-3.4 ohms at 20°C
Overdrive solenoid valve: 2.7-3.4 ohms at 20°C
If the valve resistance is different, replace the solenoid valve.
Testing the joint operation of an automatic transmission and an engine on a stationary vehicle (stall test)
Testing is performed to determine the maximum engine speed when the selector lever is in the D or R position, as well as to check the operation of the torque converter, starter and one-way clutch, as well as the performance of clutches and brakes.
No one should stand in front of or behind the vehicle while testing.
Before testing, check the levels of all operating fluids and, if necessary, bring them to normal.
- - The transmission fluid temperature should be between 80-100°C.
- - Coolant temperature 80–100°C.
- - Install the wedges under the rear wheels.
- - Apply the parking brake and depress the brake pedal.
- - Start the engine.
- - Move the selector lever to position D. Press the brake pedal all the way down with your left foot, and gently press the accelerator pedal with your right foot.
When the engine speed no longer increases, read the tachometer and release the accelerator pedal.
To exclude damage to the gearbox, test for 8 seconds.
If more than one test is required with the engine running, move the selector lever to position N and leave the engine running at idle until the transmission fluid has cooled.
Running the engine at idle speed cools the transmission fluid and prevents deterioration.
Engine speed when testing the combination of automatic transmission and engine on a stationary vehicle ( stall test ): 2000–2900 min-1
(6) Test in selector lever position R in the same way.
Engine speed when testing the combined operation of the automatic transmission and the engine on a stationary vehicle (stall test): 2000–2900 min-1
- Engine RPM is above specification in positions D and R.
- - Low pressure in the pipeline.
- - Slippage of the brake bands in low gear and reverse gear.
- Engine speed above specification only in position D.
- - Downshift clutch slip.
- If the engine speed is above specification only in position R.
- - Reverse clutch slippage.
- If the engine speed is below specification in position D and R.
- - Torque converter damage.
- - Insufficient engine power