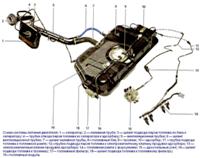
You will need: wrenches "for 10", "for 12", "for 14", heads "for 15", "for 19", a hammer
Remove the cylinder head
Remove the engine oil sump and crankcase gasket.
Remove the oil pump.

Remove the nuts 1 of the connecting rod bolts and remove the cap 2 of the connecting rod.
If the lid is tight, knock it off with gentle hammer blows.
Remove the insert from the lid.
Push the piston out of the cylinder and remove it along with the connecting rod.
Remove the bearing from the connecting rod.
If you are going to install the old liners, mark them with the cylinder number.
Remove the piston with the connecting rod from the cylinder carefully so as not to damage the cylinder mirror.
Check the marks on the connecting rod and its cap. If the marks are not visible, mark the connecting rod and cap with the cylinder number.
Remove the remaining pistons with connecting rods.
Remove the piston rings with a puller or, if it is not available, carefully straighten the rings at the locks.
Do not unbend the rings more than is required to remove them, otherwise the rings may be distorted or broken.

Remove the circlips from both sides of the piston.
Press out the piston pins with a special tool.
If a tool is not available, the piston pins can be knocked out with light hammer blows through drift 1.
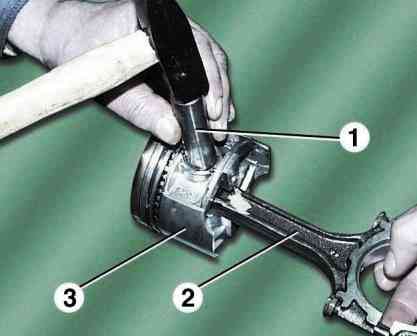
This must be done while hanging, so as not to damage the piston. Remove connecting rod 2 from piston 3.
Remove the rest of the pistons from the connecting rods.
Wash all parts in gasoline. Clean the pistons from carbon deposits.
Clean the piston ring grooves with a piece of the old piston ring from carbon deposits.
Inspect the pistons. If they have scuff marks, traces of burnout, replace the pistons.
Measure the piston diameter. If it is less than 95.4 mm, replace the piston.
The piston diameter is measured in a plane perpendicular to the piston pin axis, 8.0 mm below the piston pin axis.
The piston is installed in the cylinder with a clearance of 0.036–0.060 mm.
Pistons are divided by diameter into five size groups: A, B, C, D, E. The letter marking is stamped on the piston bottom.
When selecting a piston to a cylinder, the clearance indicated above must be ensured.
The maximum allowable clearance between the piston and the cylinder is 0.25 mm.
The clearance between the piston and cylinder can be determined by measuring the piston and cylinder. Spare parts are supplied with pistons of two repair sizes: with a diameter increased by 0.5 and 1.0 mm.
On one of the bosses for the piston pin, the inscription "409" (piston of nominal diameter), "409AP" (diameter increased by 0.5 mm) or "409BR" (diameter increased by 1.0 mm) is cast.

Measure the gap between the piston ring and the groove on the piston at several places around the circumference of the piston.
The gap should be between 0.060-0.096 mm for compression rings and 0.115-0.365 mm for the oil scraper ring.
If the clearances exceed the specified values, the rings or pistons must be replaced.
Measure the gaps in the piston ring locks.

To do this, insert the ring into the cylinder and move the piston like a mandrel so that the ring fits in the cylinder evenly, without distortion.
Measure the gap in the lock (socket) of the ring with a feeler gauge, it should be within 0.3–0.6 mm for compression rings and 0.5–1.0 mm for oil scraper discs.
If the clearance is greater than specified, replace the ring.
If the gap is smaller, you can file the ends of the ring with a file clamped in a vice, moving the ring up and down along the file.
Check the fit of the piston pin in the top end of the connecting rod.
The clearance between the pin and the bushing of the upper end of the connecting rod should be between 0.0045-0.0095 mm.
Pistons, pistons and connecting rods are divided into four size groups and marked with paint.
The finger is marked on the inner surface from one end, the connecting rod - on the rod, the piston - on the lower surface of one of the bosses or a Roman numeral is knocked out ru on the piston crown.
Lightly lubricate the piston pin with clean engine oil and insert into the upper end of the connecting rod.
The finger should enter the head from the effort of the hand evenly, without jamming.
The connecting rod must rotate on the piston pin under its own weight from a horizontal position.
In the vertical position, the pin must not extend or fall out of the connecting rod head under its own weight.
Piston pin and connecting rod must be of the same size group or adjacent groups.
Pistons with piston rings, pins and connecting rods are assembled by weight. The difference in weight for one engine should be no more than 10 g.
Inspect the connecting rod bearings. If they have scuffs, chips or other damage, replace the liners.
Install the caps on the connecting rods and measure the diameter of the hole in the bottom head of the connecting rod.
Nominal hole diameter 60 + 0.019 mm, maximum allowable - 60.03 mm.
If the measured diameter exceeds the limit, replace the connecting rod with a cap.
Measure the diameter of the hole in the connecting rod bushing.
Nominal hole diameter 22 + 0.007 -0.003 mm, maximum allowable - 22.01 mm.
If the measured diameter exceeds the limit, replace the connecting rod. The dimensions of the connecting rod and piston group are shown in the table.
Nominal and maximum allowable dimensions and fit of mating parts of the connecting rod and piston group of the ZMZ-409.10 engine
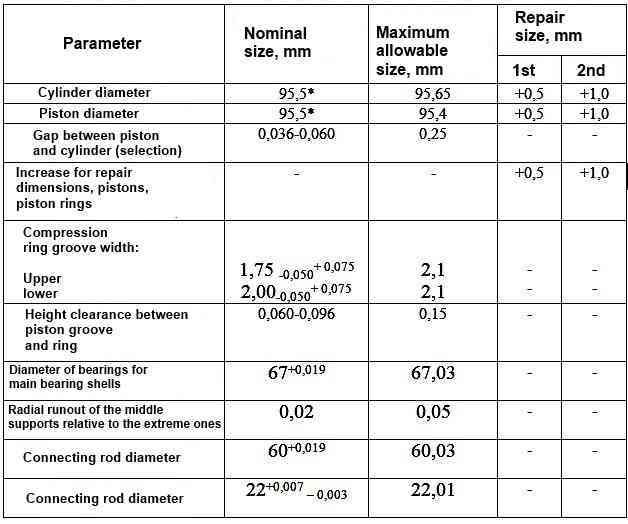
*Tolerance 0.06 mm divided into 5 groups (through 0.012 mm)
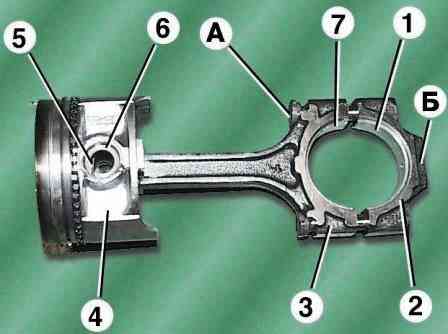
Assemble piston 4 with connecting rod 3. Preheat piston to 60-80°C.
Then, quickly insert the connecting rod into the piston so that the inscription "Front" on the piston and the protrusion "A" on the connecting rod are on the same side, and press the piston pin 6 with a maximum interference of 0.0025 mm.
Install retaining rings 5.
Put the piston rings onto the piston using a puller.
The upper compression ring is marked with the inscription "Top", the ring must be installed on the piston with this inscription to the piston bottom.
A groove is made on the inner side of the lower compression ring, the ring must be installed with this groove upwards to the piston bottom.
Insert the bushing 7 into the lower head of the connecting rod - the locking lug ("lock") on the bushing should fit into the recess in the lower head of the piston.
Insert insert 1 into connecting rod cover 2 - the locking lug (“lock”) of the insert should fit into the recess in the cover.
Lubricate the cylinder, piston 4, crankshaft journal and bearings 1 and 7 with clean engine oil.
Orient the piston rings so that the compression ring locks are at an angle of 180° to each other, the oil scraper ring disc locks are also at an angle of 180° to each other and 90° to the compression ring locks, the oil scraper ring expander lock is under 45° angle to the lock of one of the oil scraper discs.
Turn the crankshaft so that the connecting rod journal of the cylinder in which the piston is installed is at BDC.
Insert the piston with the connecting rod into the cylinder so that the inscription "Front" on the piston boss faces the front of the engine (towards the camshaft drive).
In order not to damage the cylinder mirror, we recommend putting bushings made of soft material (for example, cuttings of rubber or plastic hoses) on the connecting rod bolts.
Using a special mandrel, crimp the piston rings and lightly push the piston into the cylinder with a hammer handle, while the mandrel must be firmly pressed against the block, otherwise the piston rings may be broken.
Move the piston down so that the lower head of the connecting rod sits on the connecting rod journal of the crankshaft, remove the hose trimmings from the connecting rod bolts.
Install the connecting rod cap 2 onto the connecting rod bolts so that the ledge "B" on the connecting rod cap is on the same side as the projection "A" on the bottom head of the connecting rod; the cylinder numbers stamped on the connecting rod and the cover were located on one side, and the “locks” of the liners were opposite each other.

Install the nuts of the connecting rod bolts and tighten them to 68–75 Nm (6.8–7.5 kgf m).
Install other pistons with connecting rods in the same way.
Turn the crankshaft several times, it should rotate easily, without jamming.
Set Repair the oil pump, oil sump and cylinder head.