Carburetor "Ozone" model DAAZ 2107 - emulsion type, two-chamber, with a falling flow
It has one balanced float chamber, two main metering systems, an enrichment device (econostat) in the second chamber, an autonomous idling system with a forced idle economizer (EPKhK), transitional systems of the first and second chambers, a diaphragm accelerator pump with a spray in the first chamber, a spool device for removing crankcase gases into the throttle space, a pneumatic actuator for the throttle valve of the second chamber.
The control of the air damper of the first chamber is manual, with a cable drive.
After starting the engine, the damper is automatically opened by a diaphragm-type starting device under the action of vacuum in the intake pipeline.
The carburetor is equipped with a vacuum tap to control the vacuum ignition timing controller.
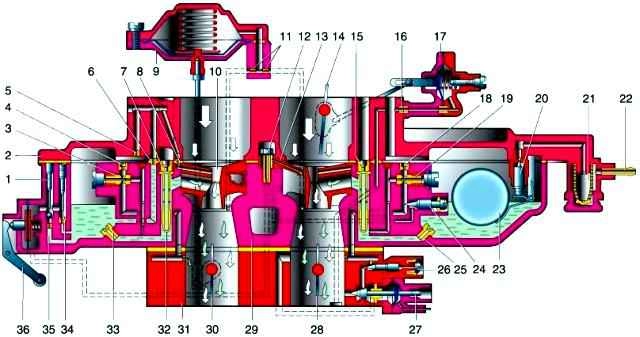
Fuel enters the carburetor through a strainer and needle valve. The valve is mechanically connected to the float and maintains the specified fuel level in the float chamber.
From the float chamber, fuel enters through the main fuel jets (of the first and second chambers) into the emulsion wells and emulsion tubes, where it mixes with air entering through the main air jets.
The air-fuel emulsion enters through the atomizers into the carburetor diffusers.
The idle system and forced idle economizer are combined into one common system.
The idle system takes fuel from the emulsion well of the first chamber.
Fuel passes through the idle jet and mixes with the air entering through the idle air jet and the openings of the transition system of the first chamber.
The resulting emulsion is fed through two channels (one has a calibrated hole - a jet, and the other has an adjusting screw - a quality screw) is fed to the hole blocked by the economizer needle, where it is additionally mixed with air and then enters the inlet pipeline through the emulsion hole.
The amount of the mixture is changed by the adjusting screw, which acts on the economizer needle, and the composition of the mixture is adjusted by the quality screw.
When the throttle valves are partially opened (before the main metering system is switched on), the air-fuel mixture enters the chambers through vias - two in each chamber.
Econostat provides fuel directly from the float chamber to the econostat atomizer, which is located in the diffuser of the second chamber.
The econostat starts working at maximum power modes, further enriching the working mixture.
Accelerator pump - diaphragm type, mechanically driven from the throttle valve axis of the first chamber.
When the throttle is suddenly opened, a portion of fuel is injected through the sprayer into the first chamber of the carburetor, enriching the mixture.
The pump is equipped with ball valves.
One check valve is located in the channel connecting the float chamber with the cavity of the accelerator pump.
It opens when the pump cavity is filled with fuel and closes when fuel is injected by the diaphragm.
Another valve is located in the atomizere.
It opens under the pressure of the injected fuel and closes under the weight of the ball as soon as the fuel supply stops.
When pumping, excess fuel flows through the drain channel with a jet back into the float chamber.
The performance of the pump depends on the profile of the cam, the diameter of the hole in the bypass jet, the profile and length of the adjusting needle in the channel of the bypass jet.
The accelerator pump cannot be adjusted during operation.
Calibration data for carburetor DAAZ 2107-1107010
Parameters of the first carburetor chamber
Diameters, mm:
- - diffuser - 22;
- - mixing chamber - 28;
- - main fuel jet - 1.12;
- main air jet - 1.5;
- idling fuel jet / transition system - 0.5;
- idling air jet / transition system - 1.7;
- air jet launcher - 0.7;
- throttle pneumatic jet - 1.5;
- accelerator pump atomizer holes - 0.4;
- accelerator pump bypass jet - 0.4;
- supply of the accelerating pump for 10 full strokes, cm 3 - 7±25;
- marking of the mixture sprayer - 3.5;
- marking the emulsion tube F15;
Parameters of the second carburetor chamber
Diameters, mm:
- - diffuser - 25;
- - mixing chamber - 36;
- - main fuel jet - 1.5;
- main air jet - 1.5;
- idling fuel jet / transition system - 0.6;
- idling air jet / transition system - 0.7;
- econostat fuel jet - 1.5;
- econostat air jet - 1.2;
- emulsion jet econostat - 1.5;
- throttle pneumatic jet - 1.5;
- supply of the accelerating pump for 10 full strokes, cm 3 - 7±25;
- marking of the mixture sprayer - 3.5;
- marking the emulsion tube F15;
Gap between float and carburetor cover with gasket, mm - 6.5±0.25;
Gaps at the dampers for adjusting the trigger, mm:
- air - 5.5±0.25;
- throttle - 0.7-0.8
The starter consists of the choke, choke lever, telescopic rod, throttle actuator rod, diaphragm mechanism and throttle actuator.
When the choke handle is pulled out from the driver's seat, it closes, and the throttle valve of the first chamber opens slightly by 0.7–0.8 mm (starting gap).
At the first flashes in the cylinders, the vacuum behind the throttle is transmitted to the diaphragm, which opens the air damper through the rod and the rod.
The maximum amount of opening of the damper is adjusted by the diaphragm stop screw located under the plug screw.