- Mazda 3 Clutch Master Cylinder Replacement
- Mazda 3 engine start
- Mazda 3 Gearshift Replacement
- Removal and installation of the pallet Mazda 3
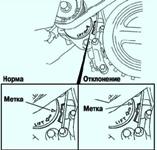
- Checking camshaft marks on Mazda 3
- Dismantling manual transmission Mazda 3
- Mazda 3 drive belt
- Mazda 3 wheel alignment
- Windows car Mazda 3
- Removal and installation of the Mazda 3 engine
- Mazda 3 fuel pump module
- Mazda 3 pump replacement
- Replacing and checking the vacuum on the Mazda 3
- Fuses and relays for Mazda 3
- Mazda 3 door glass replacement
- Repair of the front pillar Mazda 3
- Mazda 3 Rear Suspension Spring Replacement
- Mazda 3 car generator
- Mazda 3 Clutch Bleeding
- Mazda 3 windshield washer repair
- Mazda 3 speed sensor replacement check
- Features of Mazda-3 brakes
- Cruise control of Mazda 3
- Mazda 3 Airbags
- Refueling the Mazda 3 air conditioner
- Diagrams of car systems Mazda 3
- Immobilizer Mazda 3
- Mazda 3 valve clearance adjustment
- Removal and installation of the Mazda 3 cylinder head
- Mazda 3 automatic transmission control
- Mazda 3 Timing Chain Replacement
- Checking fluid levels in Mazda 3