Manual transmission vehicles are equipped with a dry single plate clutch with a central diaphragm spring
The pressure plate is mounted in a stamped steel casing, bolted to the engine flywheel

The driven disc is mounted on the splines of the input shaft of the gearbox and is clamped by a diaphragm spring between the flywheel and the pressure plate
The clutch release bearing is mounted on the guide sleeve.
The bearing is moved by the clutch release fork.
The clutch release fork is actuated by the clutch slave cylinder rod
The hydraulic clutch release consists of a master cylinder, a hydraulic accumulator, a slave cylinder, a pipeline and a clutch pedal
The hydraulic clutch release uses brake fluid
Possible clutch failures and solutions
Incomplete clutch disengagement (clutch leads):
Clutch pedal full travel reduced - adjust clutch actuator;
Warping of the driven disk (end runout more than 0.5 mm) - straighten the disk or replace with a new one;
Irregularities on the surfaces of the friction linings of the driven disk - replace the linings, check the end runout of the disk;
Weakening of rivets or breakage of the friction linings of the driven disk - replace the linings, check the end runout of the disk;
Seizure of the driven disk hub on the splines of the input shaft of the gearbox - clean the splines, coat with LSTs-15 grease.
If the cause of jamming is crushing or wear of the splines, then replace the input shaft or the driven disk;
Air in the hydraulic drive system - bleed the system;
Leakage of fluid from the hydraulic drive system through connections or damaged pipelines - tighten connections, replace damaged parts, bleed the hydraulic drive system;
Loose pressure spring rivets - replace clutch cover with pressure plate assembly;
Distorted or warped pressure plate - replace clutch basket
Incomplete clutch engagement (clutch slips):
Clutch pedal free play - adjust clutch actuator;
Increased wear or burning of the friction linings of the driven disc - replace the friction linings or the driven disc assembly;
Oiling the friction linings of the driven disk, the surfaces of the flywheel and the pressure plate - thoroughly rinse the oiled surfaces with white spirit, eliminate the causes of oiling of the disks;
Clutch actuator damaged or sticking - repair causing sticking
Clutch jerks:
Seizure of the driven disk hub on the splines of the input shaft - clean the splines, lubricate with LSTs-15 grease.
If the cause of jamming is crushing or wear of splines, then if necessary, replace the input shaft or driven disk;
Oiling the friction linings of the driven disk, the surfaces of the flywheel and the pressure plate - thoroughly rinse the oiled surfaces with white spirit, eliminate the causes of oiling of the disks;
Increased wear on the friction linings of the driven disc - replace the linings with new ones, check for disc damage
Loosening of the rivets of the friction linings of the driven disk - replace the faulty rivets, and, if necessary, the linings;
Surface damage or buckling of pressure plate - replace clutch cover with pressure plate assembly
Increased noise when disengaging the clutch:
Worn, damaged or leaking lubricant from clutch release bearing - replace bearing
Increased clutch noise:
Breakage or decrease in elasticity of the springs of the damper of the driven disk - replace the driven disk assembly;
Clutch release fork retaining spring breakage, loss of elasticity or jumping off - replace the clutch release fork;
Breakage of the plates connecting the pressure plate to the casing - replace the clutch casing with the pressure plate assembly
Checking and adjusting the travel of the clutch release pedal
In case of abnormal clutch operation, check the clutch pedal stroke
Without pressing the pedal, we measure the distance between the pedal pad and the body floor mat
Without changing the position of the ruler, press the pedal all the way and again measure the distance between the pedal pad and the mat
The difference between the two measurements should be 158 cm.
Significant deviation of the stroke from the specified value, accompanied by abnormal operation of the clutch (slipping, driving, jerking at the moment of starting off) indicate damage to the clutch or its drive.
With slight deviations of the stroke from the specified value, but with the clutch working properly, it can be operated
Checking pedal free play
To do this, press the pedal until there is a noticeable resistance to its movement. The measured value should be within 5-15 mm.
If the free play of the pedal is greater than the specified value, the clutch may not be clearly disengaged (the clutch "leads").
If there is too little or no free play, the clutch does not fully engage (the clutch “slips”)
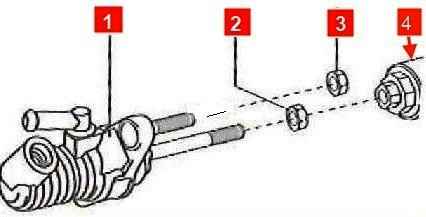
Holding the adjusting assembly of the pusher fork of the master cylinder the clutch release drive 4 with a wrench, loosen the tightening of the lock nut 2 with the wrench
Holding the locknut with a wrench, rotate the master cylinder rod in the desired direction until 5-15 mm of pedal free play is obtained. After that, tighten the locknut of the adjusting unit
Checking the moment the clutch is engaged when the pedal is released.
With the engine idling, press the pedal all the way, turn on the first gear and slowly release the pedal, trying to determine at what distance the pedal pad from the floor the car starts to move.
If the clutch and its engagement drive are in the normal state, this distance should be 25 mm.
If the pedal travel before engaging the clutch is less or greater than the specified value, check the following:
- -free travel of the clutch pedal, adjust it if necessary;
- - the full travel of the clutch pedal. With a greater than permissible stroke, we check the condition of the clutch release drive
- - the presence of air in the clutch release hydraulic drive. If necessary, pump the hydraulic drive;
- - the state of the pressure and driven clutch discs. If necessary, we replace defective units and parts