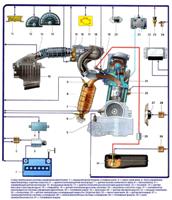
Removal and installation of the cylinder head can be found in the article - Replacing the cylinder head gasket of the VAZ-2126 engine
We also look at related articles:
You will need: a tool for compressing valve springs, a tool for pressing out and a mandrel for pressing valve stem seals, socket wrenches "8", "10", "13", keys "19", "21", hexagon "10", screwdriver, tweezers.
Remove the cylinder head from the engine

Install the head of the block with the camshafts up, placing wooden shims under it so as not to damage the valves.

Unscrew the socket head 13 three nuts securing the left support of the power unit

Remove the support

With a 10 wrench, remove the two bolts securing the fuel pipe bracket

Remove bracket

Unscrew the two bolts of the phase sensor with a 10 wrench

Remove the phase sensor

Unscrew the 21 oil pressure warning light sensor from the camshaft bearing housing with a key 21

Unscrew the coolant temperature sensor from the thermostat with a 19 wrench

Unscrew the key to 21 coolant temperature gauge sensor from the rear end of the block head

Unscrew the two nuts securing the thermostat with a 13 wrench

Remove thermostat

Remove the gasket underneath

Turn out the spark plugs with a candle wrench so as not to accidentally damage them
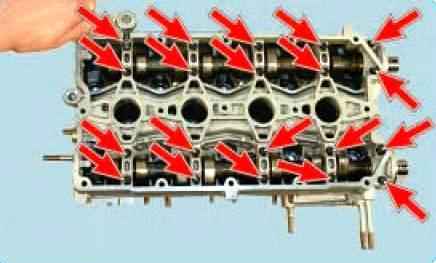
Turn out with a socket head 8 twenty bolts securing the camshaft bearing housing

Remove the housing

Remove the camshafts from the cylinder head bearings and remove the oil seals from their front ends

Remove the plugs from the rear end of the block head

Remove the valve lifters from the cylinder head holes
Clean the combustion chambers from soot.
Inspect the block head.
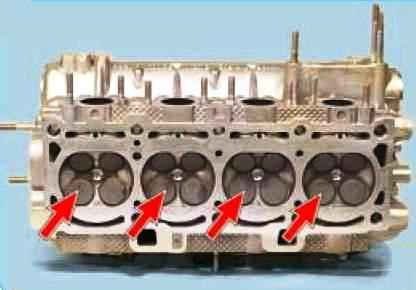
If it has cracks or burn marks in the combustion chambers, replace the head.
Remove burrs and nicks on the block head plane.
Check the flatness of the surface adjacent to the cylinder block.

To do this, place the ruler with an edge on the surface of the head, first in the middle along, and then diagonally, and measure the gap between the surface of the head and the ruler with a feeler gauge.
If the gap is greater than 0.1 mm, the mating surface can be sanded.

Similarly, check the flatness of the mating surfaces of the block head under the intake manifold

Check flatness under the collector. The flatness of these surfaces should not exceed 0.1 mm

To check the tightness of the block head, plug the hole in the head under the thermostat socket.
This can be done, for example, by installing a blank pad of thick cardboard under the socket and tightening its fastening nuts.
Reinstall the coolant temperature sensor if it was removed.

Pour kerosene into the channels of the water jacket.
If the level of kerosene decreases during exposure for 15-20 minutes, then there are cracks in the head and it must be replaced.
After checking, do not forget to remove the cardboard lining and remove the plugs.
Check the condition of the bearing surfaces for the camshaft journals on the block head and bearing housing.
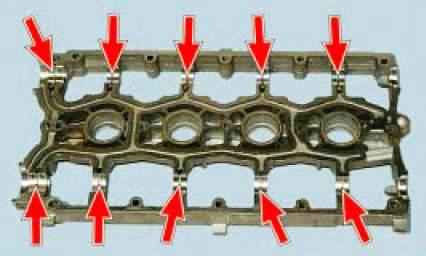
If at least one of them has signs of wear, scuffing or deep scratches, replace the head and bearing housing
Flush the oil channels.
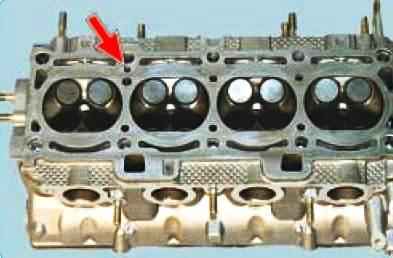
To do this, plug the vertical oil channel from the side of the combustion chamber (the channel is located between the 3rd and 4th cylinders).
Pour gasoline into the oil channel of the block head.
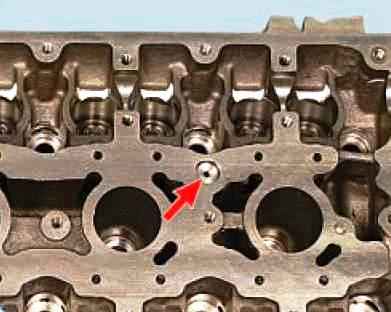
Pour gasoline into the channel of the camshaft bearing housing and soak for 15 - 20 minutes.

Pour out the gasoline, remove the plug and finally flush the channels with gasoline using a blower.

To check the tightness of the valves, screw in the candles and pour kerosene into the combustion chambers.
If kerosene does not leak from the combustion chambers into the channels within 3 minutes, the valves are tight.
If not, lap the valves or replace the valves.
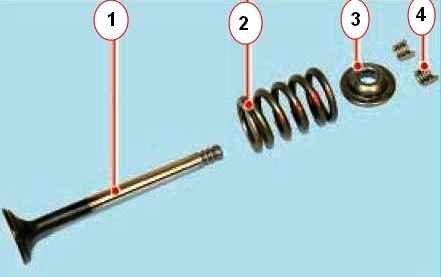
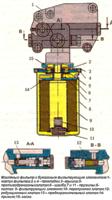
To replace or grind the valves, remove the following parts from the cylinder head: 1 - valve; 2 - spring; 3 - plate, 4 - crackers.
Place a suitable stop under the valve to be removed.

Install the valve spring compressor by screwing the camshaft bearing cap bolt into one of the holes in the head of the block and hooking the tool onto this bolt.
Compress the valve spring with the tool.

Remove the two crackers from the upper spring plate using tweezers or a magnetized screwdriver.
Then remove the fixture.
If the force of moving the lever of the device increases significantly, and the crackers do not come out of the valve groove, apply a light blow with a hammer on the spring plate to release the crackers.

Remove the spring plate.

Remove the spring

Push and remove the valve from the block head

Press the valve stem seal onto the valve guide with a tool or pliers
Remove carbon deposits from the valve with a suitable tool. Then pay attention Inspect the valve carefully.
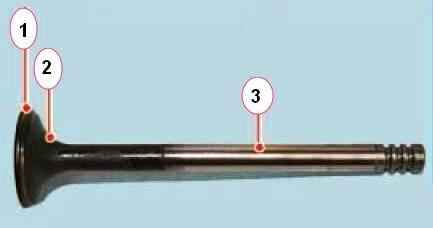
Replace valves with the following defects: deep scratches and scratches on the working chamfer 1, cracks, deformation of the stem 3, warping of the plate 2, traces of burnout.
Shallow risks and scratches on the working chamfer can be removed by lapping the valves.
If damage to the working chamfer of the valves cannot be removed by grinding, you can grind the chamfer on a special machine.

Check the condition of the valve seats.
The seat bevels must be free of wear, pitting, corrosion, etc.
Valve seats can be replaced.
More significant defects in valve seats are eliminated by grinding.
Saddles can be manually ground with a set of cutters.

First, chamfer “a” is processed at an angle of 15˚, then chamfer “b” at an angle of 20˚ and chamfer “c” at an angle of 45˚.
After grinding, it is necessary to grind the valves

Check the condition of the valve springs. Replace bent, broken or cracked springs.
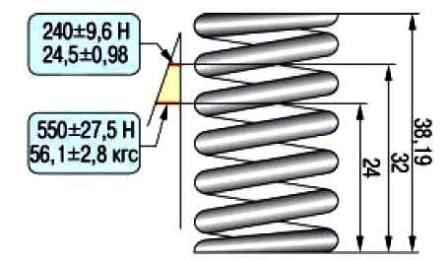
To check the elasticity of the outer spring, measure its height in the free state, and then under two different loads.
If the spring does not meet the required parameters, replace it.

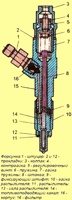
Inspect the valve lifters.
If there are scratches or other defects, replace the hydraulic pushers.
Measure the outer diameters of the tappets, replace the worn tappets.
On working surfaces 2 there should be no scuffs, nicks, scratches, signs of stepped or uneven wear, metal rubbing.
Hydraulic pushers with such defects must be replaced. On surfaces 2, concentric run-in marks with camshaft cams are allowed.
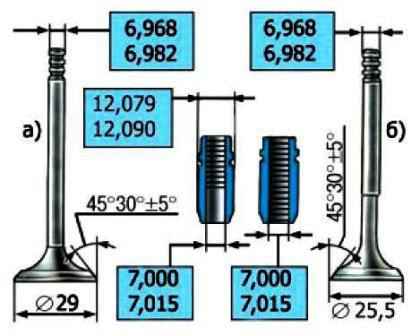
Check clearances between guide bushings and valves.
Clearance is calculated as the difference between the diameter of the hole in the sleeve and the diameter of the valve stem.
Gaps between valve and guide sleeve, mm:
- - nominal for inlet and outlet valves - 0.018-0.047
- - maximum allowable for intake and exhaust valves - 0.3
If the gap has not reached the maximum allowable, you can try to eliminate it by replacing the valve. If this fails or the clearance exceeds the limit, replace the guide bush.
To do this, press out the defective bushing from the side of the combustion chamber with a mandrel, having previously measured the height of the protrusion of the upper part of the bushing above the surface of the block head.
Cool the new bushing (for example, with carbon dioxide, lubricate it with oil, insert it into a special mandrel and press it in from the camshaft side so that the height of the protrusion of the upper part of the bushing corresponds to the measured value.

Ream the hole in the bushing using a reamer to 7.0 - 7.015 mm for the intake and exhaust valves.
If an old valve is being installed, deburr the cracker grooves. After that, it is necessary to grind the valve to the seat.
Install the valves in the block head in accordance with the previously made markings, after lubricating the rods with engine oil.
Install the valve stem seals.
Install the camshafts and camshaft bearing housing.
Install all the parts and assemblies removed during its disassembly on the head of the block.