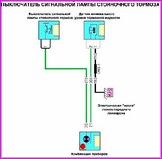
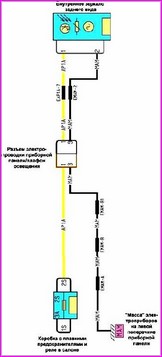
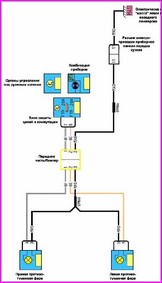
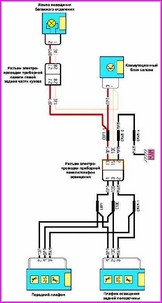
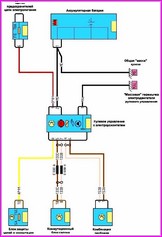
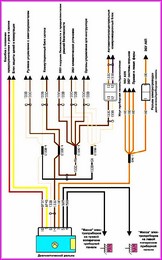
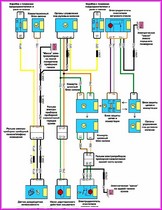
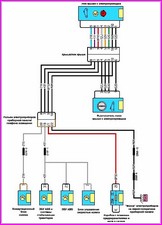
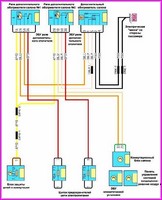
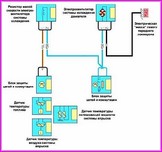
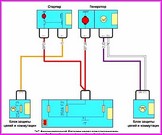
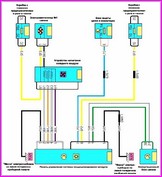
Before you begin troubleshooting any electrical circuit, carefully study the relevant diagram to understand its function as clearly as possible
The circle of troubleshooting is usually narrowed by gradually identifying and eliminating normally functioning elements of the same circuit.
If several elements or circuits fail at the same time, the most likely cause of the failure is a blown fuse or a broken contact with “ground (different circuits in many cases can be closed to one fuse or ground terminal).
Electrical equipment failures are often due to the simplest causes, such as corrosion of connector contacts, fuse failure, fuse blown, or relay damage.
Visually check the condition of all fuses, wiring, and connectors in the circuit before proceeding to a more detailed check of the health of its components.
When using diagnostic tools for troubleshooting, carefully plan (in accordance with the attached electrical diagrams) where and in what sequence the device should be connected in the loop for the most effective troubleshooting.
The main diagnostic tools include an electrical circuit tester or voltmeter (you can also use a 12-volt test lamp with a set of connecting wires), an open circuit indicator (probe) that includes a lamp, its own power supply and a set of connecting wires.
In addition, you should always have a set of wires in the car for starting the engine from an external source (the battery of another car), equipped with crocodile clips and preferably an electrical circuit breaker.
They can be used for shunting and connecting various elements of electrical equipment when diagnosing a circuit.
As already mentioned, before starting to check the circuit using diagnostic equipment, determine the connection points from the diagrams.
Parking brake warning light switch.
Interior rearview mirror.
Fog lights
Interior and luggage compartment lights
Electric Power Steering
Diagnostic connector
Front and rear wipers and washers
Power sunroof
Carry out any work on the electrical equipment of the car only with the battery disconnected.
Disconnect or connect the battery only when the ignition is off.
When checking the circuits of electrical equipment, it is forbidden to short the wires to ground, check the health of the circuits for a spark, as this can lead to failure of electrical equipment elements.
It is forbidden to use fuses that are not provided for by the design of the car or designed for a higher current, and also to use wire instead of fuses.
When replacing fuses, do not use screwdrivers, as this can lead to a short circuit in electrical circuits.
It is forbidden to disconnect the battery while the engine is running in order to avoid damage to the voltage regulator and elements of the car's electronic equipment.
When carrying out electric welding on a car, it is necessary to disconnect the wires from the terminals of the battery, generator and controller.
Regularly clean the battery terminals and cable lugs from oxides and dirt.
When recharging the battery with the charger, disconnect the wires from the battery terminals.
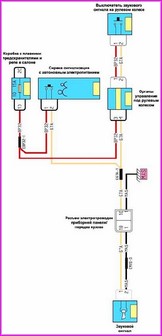
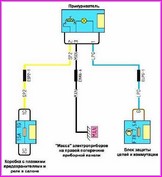
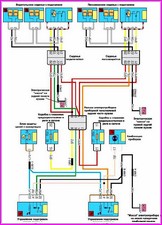
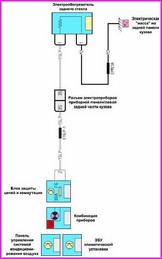
A typical electrical circuit may include a main electrical element, various switches, relays, electric motors, fuses, fuses or circuit breakers related to this element, wiring and connectors used to connect the main element to the battery and body ground .
Beep
Cigarette lighter
Heated seats
Electrically heated rear window
Additional heater in the passenger compartment
Automatic air conditioning
Generator and starter
Basic heating