Checking and adjusting the wheel alignment is necessary to ensure good vehicle stability and handling, as well as uniform tire wear during its operation
Checking and adjusting the wheel alignment angles is performed on special stands according to the instructions for their operation.
Check the wheel alignment angles on the car without load, with a half-filled fuel tank, normal air pressure in the tires, in the absence of excessive play in the suspension units.
After installing the car on the stand, just before checking the corners, "squeeze" the car's suspension, applying two or three times a force of 392-490 N (40-50 kgf), directed from top to bottom, first to the rear bumper, and then to the front .
The wheels of the car must be parallel to the longitudinal axis of the car.
When checking and adjusting the front wheel alignment, first check the caster angle, then the camber angle, and lastly the toe-in.
The angle of longitudinal inclination of the axis of rotation of the front wheel is formed by a vertical and a line passing through the middle of the upper support of the telescopic strut and the center of the sphere of the ball bearing mounted on the lower arm.
Adjusting the angle of the longitudinal inclination of the axis of rotation is not provided for by the design of the car.
The camber angle of the front wheels is characterized by the deviation of the mean plane of rotation of the wheel from the vertical.
Adjusting the camber angle of the front tracks is not provided for by the design of the car.
Toe-in of the front wheels is the angle between the plane of rotation of the wheel and the longitudinal axis of the vehicle.
Toe-in of the front wheels is regulated by changing the length of the steering rods,
Adjusting the angles of camber and convergence of the rear wheels is not provided for by the design of the car.
A discrepancy between the actual values measured on the vehicle and the reference values indicated below may be caused by wear and deformation of the suspension parts, as well as deformation of the body.
If deviations are found in the parameters of the rear suspension caused by deformation of its elements and the body, it is necessary to find the cause of the deviations and eliminate it by replacing the failed parts.
Replacing or repairing suspension parts may result in wheel alignment changes, so checking wheel alignment is a must.
Wheel alignment
Pitch Angle
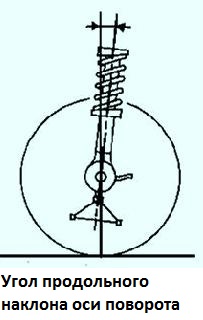
- - front wheel swivel axis 2 °42 "± 30"
Camber Angle:
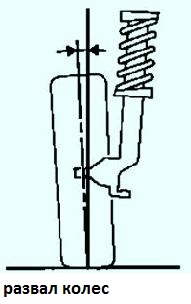
- - front wheels - 0°10‘ ± 30‘
- - rear wheels -0°51‘± 15‘
Convergence:
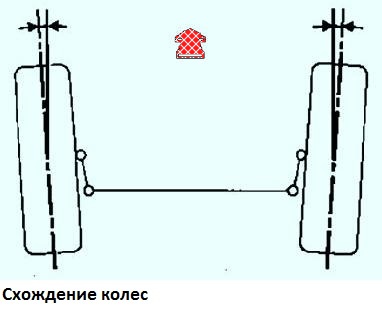
- - front wheels - 0°10" ± 10"
- - rear wheels +0°44" ± 15"
Maximum difference between right and left wheel alignment angles....1°











