The brake mechanism of the rear wheel is drum, with automatic adjustment of the gap between the pads and drums
The automatic gap adjustment device is located in the working cylinder.
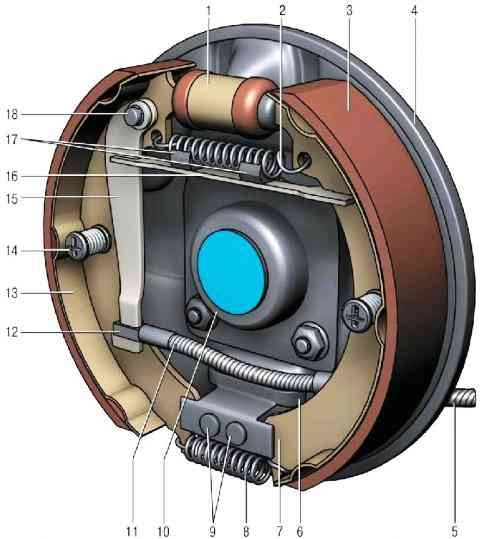
1 - working cylinder; 2 - upper coupling spring; 3 - overlay pads; 4 - brake shield; 5 - rear cable; 6 - inner plate; 7 - front brake shoe; 8 - lower coupling spring of the shoes; 9 - rivets; 10 - oil deflector; 11 - rear hummock spring; 12 - tip of the rear cable; 13 - rear brake shoe; 14 - support column pads; 15 - expanding lever of the parking brake drive; 16 - spacer bar for pads; 17 - rubber pads; 18 - the finger of the lever of the manual drive of the pads
In figure 2, the working cylinder of the rear wheel
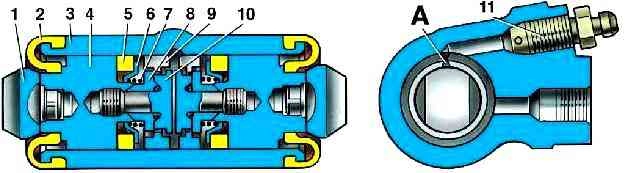
1 - pad stop; 2 - protective cap; 3 - cylinder body: 4 - piston: 5 - seal: 6 - support plate: 7 - spring; 8 - crackers; 9 - thrust ring: 10 - thrust screw; 11 - fitting: A - slot on the thrust ring
Its main element is a split thrust ring 9 (Fig. 2) mounted on the piston 4 between the collar of the thrust screw 10 and two crackers 8 with a gap of 1.25–1.65 mm.
Thrust rings 9 are inserted into the cylinder with an interference fit, providing a shear force of the ring along the cylinder mirror of at least 343 N (35 kgf), which exceeds the force on the piston from the coupling springs 2 and 8 (see Fig. 1) of the brake shoes.
When, due to the wear of the linings, a gap of 1.25–1.65 mm is completely selected, the collar on the thrust screw 10 (see Fig. 1) is pressed against the collar of the ring 9, as a result of which the thrust ring is shifted after the piston by the amount of wear .
When braking stops, the pistons are shifted by the force of the coupling springs until the crackers stop against the collar of the thrust ring.
Thus, the optimal clearance between the pads and the drum is automatically maintained.