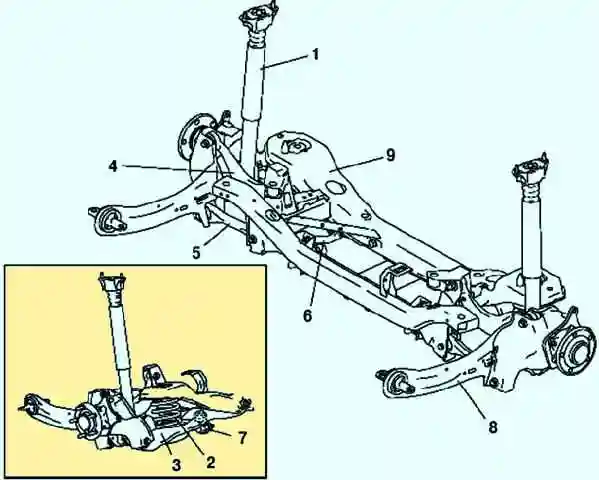
In the rear suspension (Fig. 1) assemblies of struts and leaf springs are used
The upper end of each rack is attached to the car body.
The lower ends of the struts are attached to the axle housing.
The knuckle is held in position by a pair of lower arms on each side, as well as a longitudinal balancer mounted between the body and the knuckle.
Checking Mazda 3 Rear Suspension Parts
We install the car on a lift or a viewing ditch
Inspecting suspension parts
Check the condition of rubber-metal hinges, rubber cushions, condition of suspension springs
Rubber-metal hinges and rubber pads must be replaced in case of ruptures and one-sided bulging of the rubber, as well as when cutting their end surfaces
Not allowed on rubber-metal hinges:
- - signs of aging, cracks;
- - one-sided swelling of the rubber array
Checking the absence of mechanical damage to the suspension elements
Inspecting the rubber bushings of the upper and lower shock absorber mounts and shock absorbers
Shock absorbers must not drip or sweat
Checking the rubber-metal hinges (silent blocks) of the trailing arms of the rear suspension
Using a mounting spatula, we check for backlash in the internal silent blocks of the rear lower arms and rear fists
Checking the inner and outer silent blocks of the front lower arms
We also check the inner and outer silent blocks of the upper rear suspension arms
Swinging up and down the anti-roll bar, we check for the absence of backlash of the stabilizer strut and the rubber pads of the bar
Checking the springs and compression buffers
Pay attention to the exhaust system. Extraneous knocks emitted by her are often mistaken for a knock in the rear suspension
Possible malfunctions of the rear suspension and solutions
Noise and knocks in the suspension when the car is moving
- shock absorber is faulty
Replace shock absorber
- shock absorber loosening
Tighten the shock absorber mounting bolts
- wear of silent blocks of suspension arms
Replace levers or silent blocks
- spring settling or breakage
Replace the spring
- wheel bearing failure
Replace bearing
Moving the car away from straight ahead
- uneven tire pressure
Set the correct tire pressure
- broken camber
Find the cause of the camber error and adjust the rear wheel alignment
- wheel tires have different wear or tread pattern
Change tires
- settling or breakage of one of the springs
Replace the spring
- deformation of trailing arms
Replace trailing arms
- wear of trailing arm silent blocks
Replace trailing arms
Increased or uneven tire tread wear
- the air pressure in the tires is not correct
Set the correct tire pressure
- wheel settings are violated
Remove wheel misalignment and adjust wheel alignment
- vehicle overload
Do not overload your vehicle
- wheel balance is broken
Balance the wheels