Engines installed on Renault Megan 2 cars are equipped with an electronic engine management system with distributed fuel injection
This system ensures that the latest emissions and fumes regulations are met while maintaining high driving performance and low fuel consumption.
The control device in the system is the electronic control unit (ECU).
Based on the information received from the sensors, the ECU calculates the parameters for fuel injection control and ignition timing control.
In addition, in accordance with the embedded algorithm, the ECU controls the operation of the electric motor of the fan of the engine cooling system and the electromagnetic clutch for turning on the air conditioning compressor, performs the function of self-diagnostics of the system elements and notifies the driver of any malfunctions.
If individual sensors and actuators fail, the ECU turns on emergency modes that ensure engine performance.
The amount of fuel supplied by the injectors is determined by the duration of the electrical signal from the ECU.
The electronic unit monitors data on the state of the engine, calculates the need for fuel and determines the required duration of fuel supply by the injectors (signal duration).
To increase the amount of fuel supplied, the duration of the signal increases, and to decrease the amount of fuel, it decreases.
The engine management system, along with the electronic control unit, includes sensors, actuators, connectors and fuses.
The electronic control unit (ECU, controller) is connected by electrical wires to all sensors of the system.
Receiving information from them, the block performs calculations in accordance with the parameters and control algorithm stored in the memory of the programmable read-only memory (PROM), and controls the system's executive devices.
The program variant recorded in the PROM memory is indicated by the number assigned to this ECU modification.
The control unit detects a fault, identifies and remembers its code, even if the fault is unstable and disappears (for example, due to poor contact).
The engine control system malfunction indicator in the instrument cluster goes out 10 seconds after the failed unit is restored.
After repair, the fault code stored in the memory of the control unit must be erased.
To do this, turn off the power supply of the unit for 10 s (remove the fuse of the power supply circuit of the electronic control unit or disconnect the wire from the “minus battery” terminal).
The unit supplies DC voltage of 5 and 12 V to various sensors and switches of the control system.
Because the electrical resistance of the power circuits is high, the test lamp connected to the system outputs does not light up.
To determine the supply voltage at the computer terminals, use a voltmeter with an internal resistance of at least 10 MΩ.
The electronic control unit controls the immobilizer system.
The ECU is not repairable, so if it fails, it must be replaced.
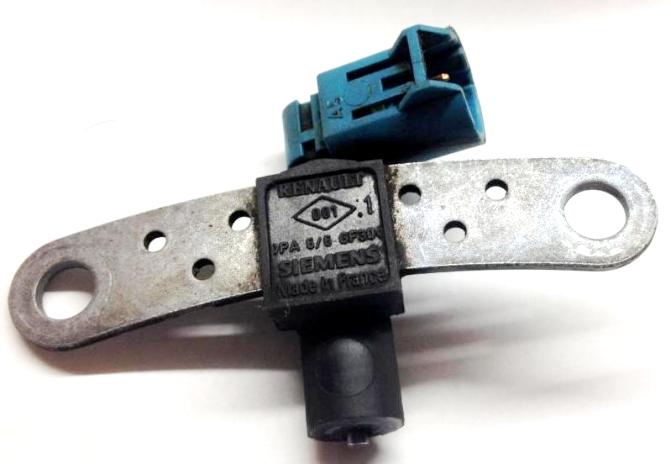
The crankshaft position sensor is designed to synchronize the operation of the electronic engine control unit with the angular position of the crankshaft.
The action of the sensor is based on the Hall effect.
The sensor is installed in the front of the clutch housing above the master ring on the flywheel.
The driving ring is a gear wheel.
As the crankshaft rotates, the flywheel teeth change the sensor's magnetic field, inducing AC voltage pulses.
The control unit determines the crankshaft speed using the sensor signals and sends pulses to the injectors.
If the sensor fails, the engine cannot be started.
The inductive type camshaft position (phase) sensor is installed at the rear of the cylinder head.
As the intake camshaft rotates, the protrusions on its front journal change the magnetic field of the sensor, inducing AC voltage pulses.
Sensor signals are used by the ECU to organize phased fuel injection in accordance with the order ohm of the operation of the cylinders, as well as to control the change in the valve timing depending on the operating mode of the engine.
If a malfunction occurs in the camshaft position sensor circuit, the electronic unit memorizes its code and turns on the warning light.
The coolant temperature sensor is installed in the water distributor housing of the engine cooling system.
The sensing element of the sensor is a thermistor, the electrical resistance of which changes inversely with temperature.
At a low coolant temperature (-20 °C), the resistance of the thermistor is about 15 kOhm, when the temperature rises to +80 °C, the resistance decreases to 320 Ohm.
The electronic unit supplies the temperature sensor circuit with a constant "reference voltage.
The voltage of the sensor signal reaches its maximum value on a cold engine and decreases as it warms up.
The electronic unit determines the engine temperature from the voltage value and takes it into account when calculating the injection and ignition control parameters.
If the sensor fails or there are violations in its connection circuit, the ECU sets the fault code and remembers it.
An additional thermistor is also installed in the sensor housing to control the coolant temperature gauge in the instrument cluster.
The throttle position sensor is mounted on the throttle body and is connected to the throttle valve axis.
The sensor is a potentiometer, one end of which is supplied with a "plus supply voltage (5 V), and the other end is connected to the ground."
The third output of the potentiometer (from the slider) is the output signal to the electronic control unit.
When the throttle valve is turned (from the action on the control pedal), the voltage at the output of the sensor changes.
It is below 0.5V when throttle is closed.
When the damper opens, the voltage at the sensor output rises; when the damper is fully open, it should be more than 4 V.
By monitoring the output voltage of the sensor, the ECU adjusts the fuel supply depending on the throttle opening angle (i.e. at the request of the driver).
The throttle position sensor does not require adjustment, since the control unit perceives idling (i.e. full throttle closing) as a zero mark
The oxygen concentration control sensor is used in the feedback injection system and is installed on the exhaust manifold.
Information about the presence of oxygen in the exhaust gases is used to correct the calculations of the duration of the injection pulses.
The oxygen contained in the exhaust gases reacts with the sensor, creating a potential difference at the sensor output.
It varies from approximately 0.1V (high oxygen - lean) to 1V (low oxygen - rich).
By monitoring the output voltage of the oxygen concentration sensor, the controller determines which command to adjust the composition of the working mixture to apply to the injectors.
If the mixture is lean (low potential difference at the sensor output), then the controller gives a command to enrich the mixture; if the mixture is rich (high potential difference) - to deplete the mixture.
The diagnostic oxygen sensor works on the same principle as the control sensor.
The signal generated by the diagnostic oxygen sensor indicates the presence of oxygen in the exhaust gases after the converter.
If the converter is working properly, the readings of the diagnostic sensor will differ significantly from the readings of the control sensor.
The knock sensor is attached to the side of the cylinder block in the area between the 2nd and 3rd cylinders and detects abnormal vibrations (knock) in the engine.
The sensing element of the knock sensor is a piezoelectric plate.
During detonation, voltage pulses are generated at the output of the sensor, which increase with increasing intensity of detonation impacts.
The electronic unit, based on the signal from the sensor, regulates the ignition timing flashing to eliminate detonation flashes of fuel.
In the process, the ECU also uses the vehicle speed data received from the speed sensor.
The absolute pressure sensor in the receiver converts the degree of vacuum in the receiver into a change in electrical voltage, according to the value of which the ECU sets the parameters of the engine. the sensor is installed on the receiver.
The output voltage of the sensor changes according to the pressure in the intake pipe - from 4.0 V (at wide open throttle) to 0.79 V (at closed throttle).
When the engine is not running, the control unit determines the atmospheric pressure from the sensor voltage and adapts the injection control parameters to the specific altitude.
Atmospheric pressure values stored in the memory are periodically updated when the vehicle is in steady motion and during full throttle opening.
The solenoid valve for the variable valve timing system on the engine is installed in the engine cylinder head.
The valve regulates the oil pressure supplied to the timing actuator mounted on the forward end of the intake camshaft.
The system performs optimal tuning of the valve timing, changing them over the entire range of engine frequency and load, which increases power and torque at any speed.
When the engine is stopped, oil pressure causes the control valve spool to move to the position corresponding to the latest valve timing.
The control valve is triggered by a signal from the engine control unit and supplies oil either to the lag chamber or to the advance chamber with a continuous change in the valve timing, respectively, either in the direction of their advance or in the direction of delay.
The diagnostic connector is used to display fault codes detected during the operation of the engine management system from the computer memory.
It is located in the car interior in the recess of the floor tunnel lining and is closed with a lid. The following main parameters of the engine operation are read through this connector:
- - fuel correction system operation mode;
- - calculated load on the engine;
- - coolant temperature;
- - fuel pressure in the fuel system;
- - air pressure in the intake pipe;
- - engine speed;
- - vehicle speed (in motion - with a portable scanning device connected);
- - ignition advance angle;
- - intake air temperature;
- - air flow;
- - throttle position;
- - data from oxygen sensors.
Electronic control unit
A 128-channel ECU of the brand SAGEM and type "S3000" with flash PROM controls the injection and ignition systems.
Multipoint sequential injection system.
Communication with other ECUs:
- - Block of protection and switching
- - UCH
- - automatic transmission computer
Electronic immobilizer system
The anti-theft immobilizer function is provided by the UCH and the injection computer.
Before the owner makes a control action (card operations + button press), the injection computer and the UCH exchange identification frames via the multiplex network and, based on the information contained in them, grant or not authorize the engine to start.
If more than 5 failed identification attempts are made in a row, the injection computer enters protection mode (anti-scan mode) and stops trying to identify the UCH.
The injection computer exits this mode only after the following operations have been carried out in the following sequence:
- - the ignition will remain on for at least 60 seconds, then
- - message delivery will stop and if
- - the duration of the self-feeding phase of the injection computer will be observed (the duration of self-feeding depends on the engine temperature).
After that, only one identification attempt is given. If it fails again, then you need to repeat all the above operations from the beginning.
Impact detection
If the impact information is stored in the memory of the injection computer, transfer the card in the reader device to the 1st detent for 10 seconds, then set it to the 2nd detent again so that the engine can be started.
Then clear the fault memory.
Camshaft Phase Control
The injection computer controls the camshaft dephaser, the type of which depends on the engine:
K4J engine
The camshaft phase control is missing.
F4R engine
The intake camshaft phaser is controlled by a two-position solenoid valve, which is commanded by the injection computer.
K4M engine
Intake camshaft phaser continuously changing phase
The valve timing from 0 to 43° in terms of the angle of rotation of the crankshaft is controlled by a solenoid valve, to the input of which a control signal is supplied from the injection system computer, which changes according to the CCO law (degree of cyclic opening).
When carrying out welding work on the vehicle, disconnect the wire blocks from the injection computer.
Turn on warning lights
The S 3000 injection system illuminates three warning lights and issues warning messages depending on the severity of the detected faults, which provides information to the owner and allows for correct diagnosis. The injection computer controls the warning lights and messages on the instrument panel.
These warning lamps come on during the starting phase of the engine and also come on if there is a malfunction in the injection system or the engine overheats.
Commands to turn on signal lamps are transmitted to the instrument panel via the multiplex network.
The principle of operation of signal lamps
During the engine start phase (pressing the engine start button), the "OBD" (On-Board Diagnostic System) warning light comes on for approximately 3 secondsand then goes out.
In the event of a malfunction in the injection system (severity 1), the message "injection a controler (check the injection system)" is displayed, accompanied by the "service" warning light
This indicates a reduction in safety and the need to use the engine in a "sparing" mode.
The owner should fix the problem as soon as possible.
Check and repair if necessary:
- - Motorized Throttle Body
- - accelerator pedal position sensor
- - absolute pressure sensor
- - ECU
- - actuator power circuits
- - computer power circuits
In the event of a serious injection system malfunction (2nd severity), the red engine icon with the word "stop" will illuminate (only with a dot matrix display) and the message "surchauffe moteur (engine overheating)" will be displayed, accompanied by a warning light "stop" and a beep.
In this case, stop driving immediately.
When a malfunction is detected that causes the exhaust gas toxicity threshold to be exceeded, the orange OBD warning light with an engine icon lights up:
- - flashing lightif there is a malfunction that can lead to the destruction of the catalytic converter (misfire leading to its destruction), in this case, stop driving immediately.
- - constant lightin case of non-compliance with toxicity standards (misfire mixture leading to increased emissions, catalytic converter malfunction, oxygen sensor malfunction, oxygen sensor signal mismatch and adsorber malfunction).
Faulty odometer
The parameter allows you to register the vehicle mileage while one of the injection system malfunction warning lamps is on: Malfunction Level 1 warning lamp (yellow), coolant temperature warning lamp or OBD warning lamp.
The counter can be reset using a diagnostic tool.
Fallbacks
Motorized Throttle Body
In standby mode, the motorized throttle body can be in 6 different states.
Status 0
Throttle opening degree less than in "Standby" position.
Throttle control is terminated and the throttle is automatically set to "Standby".
The operation of the trajectory stabilization system, the distance control to the vehicle in front, the speed limiter and automatic transmission is prohibited.
State 1
The throttle opening degree is no longer controlled.
Crank speed th shaft is limited by stopping the injection.
State 2
Reserve mode consists in setting a certain position of the accelerator pedal (the accelerator pedal remains in a certain position in accordance with the selected gear).
Status 3
Reserve mode is to limit the degree of throttle opening.
Maximum throttle opening is maintained so that the speed does not exceed 90 km/h.
Status 4
The ECU no longer processes requests to change the torque coming from the trajectory stabilization system, the distance control to the vehicle in front, the cruise control-limiter and the automatic transmission.
This standby mode is activated when there is a malfunction of the computer or a malfunction of the absolute pressure sensor or the boost pressure sensor.
The operation of the trajectory stabilization system, the distance control to the vehicle in front, the speed limiter is prohibited.
The automatic transmission is in "backup mode".
Status 5
The boost pressure control valve is not working.
Camshaft Phase Control
In standby mode, the camshaft dephaser can be in two states:
State 1
This fallback mode is used for all faults affecting the phaser position measurement.
The phase regulator is set to the lowest position, and the measured position of the camshaft angle is forced to 0.
Malfunction in the signal circuit of the crankshaft position sensor.
Diagnosis of the correspondence of the crankshaft position sensor signal / camshaft position sensor signal.
State 2
This standby mode is used for all faults that affect the operation of the phase regulator (gear pulley and solenoid valve).
The phase regulator is set to its lowest position.
Diagnosis of electrical circuits of the solenoid valve.
Diagnosis of the position of the phase regulator.
Fault codes for the gasoline engine injection system
Diagnostic Tool Fault - Corresponding DTC - Diagnostic Tool Name
- DF001 - 0115 - Coolant temperature sensor circuit
- DF002 - 0110 - Air temperature sensor circuit
- DF005 - 0335 - Engine Speed Sensor Circuit
- DF008 - 0225 - Fuel Pedal Position Sensor G-1 Circuit
- DF009 - 2120 - Gap 2 Pedal Position Sensor Circuit
- DF011 – 0641 - No. 1 sensor supply voltage
- DF012 – 0651 - No. 2 sensors supply voltage
- DF026 - 0201 - No. 1 injector control circuit
- DF027 - 0202 - No. 2 injector control circuit
- DF028 - 0203 - No. 3 injector control circuit
- DF029 - 0204 - No. 4 injector control circuit
- DF037 - 0513 - Electronic immobilizer system
- DF038 - 0606 - ECU
- DF046 - 0560 - Battery voltage
- DF049 - 0530 - Refrigerant pressure sensor circuit
- DF059 - 0301 - No. 1 Cylinder Misfire
- DF060 - 0302 - Cylinder 2 Misfire
- DF061 - 0303 - No. 3 Cylinder Misfire
- DF062 - 0304 - No. 4 Cylinder Misfire
- DF065 – 0300 - Mixture misfires
- DF072 - 0351 - Cylinder 1 Ignition Coil Circuit
- DF073 - 0352 - Cylinder 2 Ignition Coil Circuit
- DF074 - 0353 - Cylinder 3 Ignition Coil Circuit
- DF075 - 0354 - Cylinder 4 Ignition Coil Circuit
- DF078 - 2101 - Power Throttle Control Circuit
- DF079 - 0638 - Power Throttle Follower System
- DF080 - 0010 - Camshaft dephaser solenoid valve circuit
- DF081 - 0443 - Canister purge solenoid valve circuit
- DF082 - 0135 - Upstream oxygen sensor heating circuit
- DF083 - 0141 - Downstream oxygen sensor heating circuit
- DF084 - 0685 - Actuator relay control circuit
- DF085 - 0627 - Fuel Pump Relay Control Circuit
- DF088 - 0325 - Knock Sensor Circuit
- DF089 - 0105 - Absolute Pressure Sensor Circuit
- DF091 - 0500 - Vehicle speed information
- DF092 - 0130 - Upstream oxygen sensor circuit
- DF093 - 0136 - Downstream oxygen sensor circuit
- DF095 - 0120 - Throttle Body Sensor 1 Circuit
- DF096 - 0220 - Throttle Sensor Gutter 2 Circuit
- DF097 - 0340 - Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit
- DF099 - C101 - Communication with automatic transmission control unit or manual transmission control unit with automatic control via multiplex network
- DF100 - C155 - Multiplex communication with instrument panel
- DF101 - C122 - Multiplex with trajectory stabilization system
- DF105 - 0585 - Speed limiter switch circuit
- DF106 - 0575 - Cruise control-limiter switches on the steering wheel
- DF109 - 0313 - Mixture misfires at minimum fuel level
- DF110 - 0420 - Catalytic Converter
- DF125 – 0315 - Torque Meter Programming
- DF126 – 1604 - Interior heating element
- DF127 - 0703 - Brake light switch circuit 1
- DF128 - 0571 - Brake light switch circuit 2