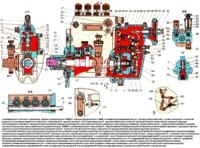
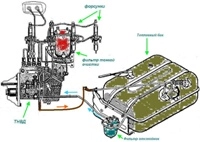
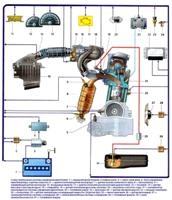
Let's consider the malfunctions that may occur during engine operation:
- - The crankshaft is not turned by the starter;
- - Strong noise during starter operation;
- - The crankshaft is turned by the starter, but the engine does not start;
- - The engine is unstable or stalls at idle;
- - The engine does not develop full power, the car does not have sufficient throttle response. Jerks and dips when driving a car;
- - Pops in the intake pipe;
- - Shots in the silencer;
- - Increased fuel consumption;
- - Increased oil consumption (more than 500 g per 1000 km);
- - Detonation (high-pitched metallic knocks that occur, as a rule, when the engine is running under load, especially at low speeds, for example, “pull-in” acceleration, etc. and disappear when the load is reduced);
- - Insufficient oil pressure (low oil pressure indicator is on);
- - The engine is overheating (the arrow of the coolant temperature gauge is in the red zone of the scale);
- - The electric fan of the engine cooling system is constantly running (even on a cold engine);
- - The engine takes a long time to warm up to operating temperature;
- - Coolant level drop in the expansion tank;
- - Extraneous noises and knocks in the engine;
- - Strong engine vibration;
- - Increased content of harmful substances in exhaust gases;
- Engine control system malfunction indicator lights up when the engine is running.
Possible malfunctions - diagnostics - methods of elimination
The crankshaft does not turn with the starter:
The battery is discharged (The voltage at the battery terminals with the consumers turned off is below 12 V. When the starter is turned on, a crack may be heard from under the hood)
- Charge the battery; if it doesn't charge, replace it. The engine can be started by "lighting up" from the battery of another car;
Reducing the capacity of the battery (The voltage at the battery terminals when the consumers are off is more than 12 V, but when the starter is turned on, it drops below 6-8 V. At the same time, crackling may be heard from under the hood)
- Charge the battery with a low current (no more than 1 A); if the capacity is still insufficient, replace the battery. the engine can be started by "lighting up" from the battery of another car
Oxidation of the battery terminals and wire terminals, their loose fit (When the starter is turned on, the voltage in the on-board network drops much more than at the battery terminals. At the same time, crackling can be heard from under the hood)
- Tighten the terminals, clean the contact surfaces, lubricate them with technical vaseline;
Jammed engine or attachments (Check engine crankshaft, coolant pump, alternator pulley)
- Repair the engine, generator, replace the coolant pump;
Damaged starter drive gear or flywheel teeth (Inspection after removing the starter)
- Repair or replace the starter, replace the flywheel;
Faulty starter activation circuit: faulty starter relay, damaged wires, ignition switch contacts do not close (When the ignition key is turned to position "2", the starter traction relay does not work (no click under the hood). Check if +12 is supplied B to the control contact of the traction relay)
- Replace the faulty ones: starter relay, wires, ignition switch contact group;
The starter traction relay is faulty: short circuit or open circuit in the retracting winding, sticking of the relay armature (armature skew, surface contamination, corrosion, etc.) (When the key is turned to the “II” position, the traction relay does not work (there is no click under the hood ), but +12 V is supplied to the control contact of the traction relay. Remove the relay, check its operation)
- Replace the faulty traction relay;
The contacts of the traction relay or wires are oxidized, poor ground contact (When the starter is turned on, a click is heard under the hood, but the starter armature does not rotate. Check the resistance of the battery → starter circuit with an ohmmeter, including the ground wire. If the circuits are OK, remove the starter and check the operation of the traction relay, it is powered directly from the battery)
- Tighten the wire ends, crimp the terminals. Replace the defective traction relay;
Open or short circuit in the holding winding of the starter traction relay (When the starter is turned on, a crack is heard from under the hood. The battery voltage is within normal limits. An open or short circuit in the holding winding of the starter traction relay is checked with an ohmmeter or by excessive heating)
- Replace the traction relay starter;
Burning of the starter collector, freezing of the brushes or their strong wear (The starter armature does not rotate or rotates slowly. First make sure that the traction relay is working, for which you can supply power to the starter contact bolt directly from the battery, bypassing the relay)
- At low speed, replace worn components or starter;
An open or short circuit in the starter armature winding (The starter armature does not rotate or rotates slowly. First make sure that the traction relay is working, for which you can supply power to the starter contact bolt, bypassing the relay. The winding is checked by an ohmmeter or by darkening of the insulation)
- Replace anchor or starter;
Slippage of the freewheel (When the starter is turned on, the armature rotates, the flywheel is stationary)
- Replace clutch or starter
Strong noise during starter operation:
The starter is skewed on the clutch housing, its fastening is loose or the cover on the drive side is broken (Inspection)
- Tighten the nuts securing the starter to the clutch housing, if the cover breaks, replace the starter;
Excessive wear on bearing bushings or journals on drive shaft and armature. Wear and damage to the gear teeth of the planetary gear (Inspection after disassembly of the starter)
- Replace planetary gear or starter;
The ring gear rotates on the flywheel (When the starter is turned on, the ring gear rotates, the flywheel and the crankshaft are stationary. A squealing, howl is heard from the clutch housing)
- Replace the flywheel;
Worn starter drive gear teeth or (more often) flywheel ring (Inspection after starter removal)
- Replace the drive gear, starter or flywheel;
The gear does not disengage from the flywheel: sticking of the drive lever, weakening or breakage of the freewheel clutch spring or starter traction relay, sticking of the clutch on the splines of the drive shaft or traction relay armature, malfunction of the ignition switch (ignition switch contacts do not open) (Check , whether voltage is removed from the control output of the starter relay when the ignition key is released, whether the key returns to position "I". The opening of the ignition switch contacts can be checked with an ohmmeter. If the voltage at the starter traction relay disappears when the ignition is turned off, remove and disassemble the starter for verification)
- Replace the starter traction relay or the starter assembly, the contact group of the ignition switch
The crankshaft is turned by the starter, but the engine does not start:
There is no fuel in the tank (According to the fuel gauge and fuel reserve indicator)
- add fuel;
The battery is discharged (The crankshaft turns the starter very slowly. The voltage at the battery terminals is below 12 V when consumers are turned off)
- Charge the battery: if it does not charge, replace it. the engine can be started by lighting it from the battery of another car;
Reducing the capacity of the battery (The crankshaft rotates very slowly. The voltage at the battery terminals with consumers turned off is more than 12 V, but when the starter is turned on, it drops to 6-8 V)
- Charge the battery with a low current (no more than 1 A); if the capacity is still insufficient, replace. The engine can be started by lighting from the battery of another car;
Oxidation of the wire terminals at the battery terminals, their loose fit (The crankshaft turns the starter very slowly. When the starter is turned on, the voltage in the on-board network drops much more than at the battery terminals)
- Tighten the terminals, clean the contact surfaces, lubricate them with technical vaseline;
Unreliable connection of the electrical circuits of the engine control and power systems (Check the connection of the electrical connectors of the wiring harnesses, the reliability of the contacts in the wire lugs)
- troubleshoot the connections in the connectors;
The crankshaft is turned by the starter very slowly
Increased resistance to rotation of the engine crankshaft: scuffs on the shafts, bearing shells, parts of the cylinder-piston group; shaft deformation; frozen engine oil; alternator, coolant pump jammed (If the weather is cold, and the day before the engine was running stably and without extraneous noise, the most likely cause of increased resistance to rotation is frozen oil. In this case, try starting the engine with a different battery. After starting, do not allow the engine to run at high speeds and watch the low oil pressure indicator: if it lights up, immediately stop the engine for 1-2 minutes so that the thickened oil has time to drain into the sump.If extraneous noises are heard when starting or running the engine, check the free rotation of the coolant pump and generator pulleys
- Use engine oil according to climatic conditions. When postor If there is noise in the area of the block or cylinder head, have the engine repaired. Replace alternator, coolant pump
Failure in the ignition system (Check spark plugs. If there is no spark, this may be due to malfunctions of devices and low voltage circuits (controller, primary winding of the ignition coil) or high voltage (secondary winding of the ignition coil, high voltage wires))
- Check the circuits and devices of the ignition system. Replace defective device and wires. Ensure contact in electrical circuits;
The high voltage wires are connected to the ignition coil in the wrong order; disconnected wire (Inspection)
- Connect the wires in accordance with the markings on the ignition coils;
Timing belt broken or belt teeth sheared (Inspection after removing the front timing cover)
- Replace the timing belt;
defective spark plugs (Check spark plugs)
- Replace candles;
The valve timing is broken (Check that the marks on the crankshaft and camshaft pulleys match)
- Set the correct relative position of the shafts (by marks);
The controller, its circuits or the crankshaft position sensor (less often the coolant temperature sensor) are faulty (Check that +12 V is supplied to the controller, the crankshaft position sensor circuit, the sensor itself is not damaged. If the temperature sensor is faulty, the controller may not work correctly calculate the composition of the fuel mixture)
- Replace faulty controller, sensors, wires;
The idle speed controller or its circuits are faulty (When starting the engine, lightly press the gas pedal with the throttle slightly open. If the engine starts, but stalls when the pedal is released, the idle speed controller is faulty)
- Replace the faulty regulator;
Fuse blown or main control relay defective (Check fuse and main control relay)
- Eliminate the cause of the blown fuse. Replace fuse or faulty relay;
Engine runs erratically or stalls at idle
Unreliable connection of the electrical circuits of the engine control and power systems (Check the connection of the electrical connectors of the wiring harnesses, the reliability of the contacts in the wire lugs)
- Troubleshoot the connections in the connectors;
The gap between the electrodes of the candles is not correct (The gap of 1.0-1.1 mm is checked with a round probe)
- Set the desired gap or replace the candles;
A lot of carbon deposits on the electrodes of the spark plugs; soot particles getting into the gap between the electrodes (Inspection)
- Check and, if necessary, replace the candles;
Spark plugs are faulty: current leakage through cracks in the insulator or thermal cone soot, poor contact in the central electrode (The absence of external damage and sparking between the electrodes on the turned out candle does not allow us to conclude that it is working)
- Replace candles;
Damage to the insulation of high-voltage devices and circuits (Use an ohmmeter to check for an open or “breakdown” (short to ground) of the ignition coil winding, high-voltage wires)
- Replace the damaged ignition coil, high voltage wires;
The valve timing is broken (Check that the marks on the crankshaft and camshaft pulleys match)
- Set the correct relative position of the shafts (by marks);
Low compression in the engine cylinders (less than 11 bar): wear or damage to valves, valve guides and seats, sticking or breakage of piston rings (Check compression)
- Replace defective parts;
Faulty: phase sensor, throttle position sensor, injectors open or shorted windings, atomizers heavily contaminated (Check the phase sensor, throttle position sensor, injectors. Check if +12 V is supplied to the controller, the operation of the injectors, electrical circuits and sensor)
- Replace faulty sensors, wires, injectors. Dirty nozzles can be washed on a special stand;
Idle speed control or its circuits are faulty (substitute a known-good one)
- Replace the faulty regulator;
Intake of extraneous air into the intake tract (Inspect the joints, check the fit of the hoses, fittings, tightness of the clamps. At the time of starting, turn off the vacuum brake booster by plugging the receiver fitting)
- Torn gaskets, parts with deformed flanges, replace a faulty vacuum booster;
Fuel pressure regulator defective (Check the pressure in the fuel system with a pressure gauge (at least 3.6 bar))
- Replace the faulty regulator;
The adsorber is faulty, leaks in the connections of the hoses of the pipes of the fuel vapor recovery system (Check the adsorber for damage, the correct installation of the purge solenoid valve and its connections)
- For change the faulty adsorber, hoses and tubes. Eliminate leaky connections;
Throttle valve or actuator stuck. Under these conditions, the controller does not control the engine idling (Check for ease of movement of the damper)
- Adjust the drive, throttle position. Replace throttle assembly;
The control oxygen concentration sensor is faulty (the indicator is on. You can evaluate the performance of the oxygen concentration sensor and the reliability of the connections of its electrical circuits using diagnostic equipment)
- Repair damaged electrical circuits. Replace the defective sensor;
Camshaft lobes wear (Inspection after partial engine disassembly)
- Replace the camshaft;
Clearances in the valve drive are not adjusted (Check the clearances)
- Adjust the clearances in the valve drive;
Faulty speed sensor (After stopping the car, the engine runs unevenly, but soon the idle speed stabilizes)
- Replace sensor
The engine does not develop full power, not enough throttle response
Jerks and dips when driving a car
Clogged air filter element (Check the condition of the air filter element)
- Blow out or replace the air filter element;
Increased resistance to movement of gases in the exhaust system (Inspect the exhaust system for dented and damaged pipes, check the condition of the catalytic manifold)
- Replace damaged elements of the exhaust system;
Sucking of extraneous air into the intake tract (Inspect the joints, check the fit of the hoses, fittings, tightness of the clamps. Turn off the vacuum brake booster for a short time by plugging the receiver fitting. Caution. The force on the brake pedal will increase significantly.)
- Replace gaskets, parts with deformed flanges, faulty vacuum booster;
Incomplete throttle opening (Determined visually with the engine stopped)
- Adjust the throttle actuator;
The valve timing is broken (Check that the marks on the crankshaft and camshaft pulleys match)
- Set the correct relative position of the shafts (by marks);
Low compression in the engine cylinders (less than 11 bar): wear or damage to the valves, their guide bushings and seats. piston rings stuck or broken (Check compression)
- Replace defective parts;
The gaps between the electrodes of the spark plugs are not correct (Check the gaps)
- By bending the side electrode, set the desired gap or replace the candles;
Heavy soot on the electrodes of the spark plugs; soot particles getting into the gap between the electrodes (Inspection)
- Check and, if necessary, replace the candles;
Damage to the insulation of high-voltage devices and circuits (Use an ohmmeter to check for an open or “Breakdown (short to ground) of the ignition coil winding, high-voltage wires)
- Replace damaged ignition coil, high voltage wires;
There is not enough fuel in the tank (According to the level indicator and the fuel reserve indicator)
- add fuel;
Clogged fuel filter, frozen water that got into the power system, deformed fuel lines (Check the pressure in the fuel system (at least 3.6 bar))
- Replace the fuel filter. In winter, put the car in a warm garage, blow out the fuel lines. Replace defective hoses and tubes;
The fuel pump does not create the necessary pressure in the system (Check the pressure in the fuel rail, make sure the strainer of the fuel module is clean)
- Clean the mesh filter of the fuel module. Faulty fuel pump, replace pressure regulator;
Bad contact in the fuel pump power circuit (including ground wires) or its relay is faulty (Checked with an ohmmeter)
- Strip the contacts, crimp the lugs of the wires, replace the faulty relay, wires;
The injectors or their circuits are faulty (the indicator is on. Check the windings of the injectors and their circuits with an ohmmeter (no open circuit or short circuit))
- Replace faulty injectors, ensure contact in electrical circuits;
The crankshaft position sensor is installed incorrectly (Check the gap between the sensor and the teeth of the crankshaft drive disk (0.5-1.5 mm))
- Clean the sensor rod from metal particles. Replace the damaged sensor;
The phase sensor or its circuits are faulty (the indicator is on. Check the sensor with a tester)
- Restore the contact in the electrical circuits, replace the faulty phase sensor;
Mass air flow sensor or its circuits are faulty (Mass air flow sensor can be assessed using diagnostic equipment)
- Restore the contact in the electrical circuits, replace the faulty sensor;
One or both oxygen concentration sensors are faulty (The signaling device is on. You can evaluate the performance of oxygen concentration sensors and the reliability of the connections of their electrical circuits using diagnostic equipment)
- Repair damaged electrical circuits. Replace the defective sensor;
The controller or its circuits are faulty (the warning light may be on, to check the controller, replace it with a known good one)
- Replace the faulty controller;
Valve drive clearance not adjusted (Check valve drive clearance)
- Adjust the clearances in the valve drive;
Strong wear of the camshaft lobes (Inspection after partial engine disassembly)
- Replace the worn camshaft;
Settlement or broken valve springs (Engine Dismantling Inspection)
- Repair the engine;
Throttle position sensor or circuit is faulty (Warning light is on. Check throttle position sensor)
- Restore the contact in the electrical circuits, replace the faulty sensor;
The coolant temperature sensor (engine management system) or its circuit is faulty (Check the resistance of the sensor at various temperatures with a tester)
- Restore the contact in the electrical circuits, replace the faulty sensor
Pops in the intake pipe
Clearances in the valve drive are not adjusted (Check the clearances)
- Adjust gaps;
Intake valves sticking in guide bushings: gum deposits on valve stem or bushing surfaces, sedimentation or broken valve springs (Inspection when disassembling the engine)
- Repair the engine;
The valve timing is broken (Check that the marks on the crankshaft and camshaft pulleys match)
- Set the correct relative position of the crankshaft and camshaft (by marks)
Shots in silencer
Valve drive clearance not adjusted (Check valve drive clearance)
- Adjust the clearances in the valve drive;
Exhaust valves sticking in bushings: increased wear of the valve stem or bushing, sediment or broken valve springs (Inspection when disassembling the engine)
- Repair the engine;
The valve timing is broken (Check that the marks on the crankshaft and camshaft pulleys match)
- Set the correct relative position of the shafts (by marks);
Spark plugs are faulty: current leakage through cracks in the insulator or carbon deposits on the thermal cone, poor contact of the central electrode (Spark plugs are checked on a special stand. The absence of external damage and sparking between the electrodes on an inverted spark plug does not allow us to conclude that it is working)
- Replace candles;
Damage to the insulation of high-voltage devices and circuits - interruptions in sparking (Use an ohmmeter to check for an open or "breakdown" (short to ground) of the ignition coil winding, high-voltage wires)
- Replace the faulty ignition coil, damaged high-voltage wires (when disconnecting the wire, pull its tip). In severe operating conditions, it is advisable to replace the wires every 3-5 years
Increased fuel consumption
Clogged air filter element (Check the condition of the air filter element)
- Blow out or replace the air filter element;
Leaks in the power supply system (Smell of gasoline, fuel leaks)
- Tighten the fuel line connections. Check fit of fittings; when the fit is loose, replace the corresponding nodes;
Spark plugs are faulty: current leakage through cracks in the insulator or carbon deposits on the thermal cone, poor contact of the central electrode (Spark plugs are checked on a special stand. The absence of external damage and sparking between the electrodes on an inverted spark plug does not allow us to conclude that it is working)
- Replace candles;
Failure of the throttle actuator (Check the stroke of the "gas" pedal, the gap in the actuator (pedal free play), make sure that the cable and pedal are not jammed)
- Replace defective parts, lubricate the cable with engine oil;
Idle speed regulator or its circuits are faulty (Warning lamp lights up. Replace with a known good one)
- Replace the faulty regulator;
The throttle valve does not close completely (A gap between the throttle valve and the body walls is visible through the light)
- Replace the throttle assembly;
Increased pressure in the fuel line due to a malfunction of the pressure regulator (Check the pressure in the fuel system with a pressure gauge (no more than 4.0 bar))
- Replace the faulty regulator;
Leaking nozzles (Check nozzles)
- Replace faulty injectors;
The coolant temperature sensor or its circuit is faulty (Warning lamp is on. Check the resistance of the sensor with an ohmmeter when different temperatures)
- Restore the contact in the electrical circuits, replace the faulty sensor;
One or both oxygen concentration sensors are faulty (the indicator is on. You can evaluate the performance of the oxygen concentration sensors and the reliability of the connections of their electrical circuits using diagnostic equipment)
- Repair damaged electrical circuits, replace the faulty sensor;
The controller or its circuits are faulty (substitute a known-good controller to check)
- Replace the faulty controller, repair damaged electrical circuits;
Low compression in the engine cylinders (less than 11 bar): wear or damage to the valves, their guide bushings and seats. piston rings stuck or broken (Check compression)
- Adjust the clearances in the valve drive. Replace defective parts;
Throttle position sensor, MAF sensor or their circuits are faulty (Warning light is on. Check the sensors and their circuits)
- Restore the contact in the electrical circuits, replace the faulty sensor(s);
Increased resistance to movement of gases in the exhaust system (Inspect the exhaust system for dented and damaged pipes, check the condition of the catalytic manifold)
- Replace damaged elements of the exhaust system
Increased oil consumption (more than 500 g per 1000 km)
Oil leakage through: crankshaft and camshaft seals; gaskets for the oil pan, cylinder head, oil pump housing; oil pressure sensor; oil filter o-ring (Wash the engine, then after a short run inspect for possible leaks)
- Tighten the fastening elements of the cylinder head, cylinder head cover, oil pan, replace worn seals and gaskets;
Wear, loss of elasticity of oil seals (valve seals). Wear of valve stems, guide bushings (Inspection of parts)
- Replace worn parts;
Wear breakage or coking (loss of mobility) of the piston rings. Wear of pistons, cylinders (Inspection and measurement of parts after engine disassembly)
- Replace worn pistons and rings. Boring and honing cylinders;
Using the wrong viscosity oil
- Change the oil;
Crankcase ventilation system clogged (Inspection)
- Clean the ventilation system
Knocking (high-pitched metallic knocks that usually occur when the engine is under load, especially at low speeds)
Unacceptably low octane number of gasoline
- Refuel the car with fuel recommended by the manufacturer;
Engine overheating (According to the coolant temperature indicator)
- Eliminate the cause of overheating (see "engine overheating" below);
A lot of carbon deposits in the combustion chamber, on the bottoms of the pistons, valve plates (Inspection after removing the cylinder head)
- Eliminate the cause of carbon deposits (see "Increased fuel consumption", "Increased oil consumption"). Use oils of the recommended viscosity and, if possible, with a low ash content
Candles with the wrong glow value are used
- Use candles recommended by the manufacturer
Insufficient oil pressure (low oil pressure warning light on)
Low oil in the engine (According to the oil level indicator)
- add oil;
Using the wrong viscosity oil
- Change the oil;
Clogged oil pickup screen (Inspection)
- Clear the grid;
Faulty oil filter (Replace filter with known good one)
- Replace the faulty oil filter;
Oil pump relief valve skewed, clogged, or valve spring weakened (Inspection)
- Clean the valve. Replace the faulty valve or pump;
Wear of the oil pump gears (Determined by measuring parts after disassembling the oil pump)
- Replace the oil pump;
Excessive clearance between bearing shells and crankshaft journals (Determined by measuring parts after engine disassembly)
- Replace worn liners. If necessary, replace or repair the crankshaft;
The insufficient oil pressure sensor is faulty (We unscrew the insufficient oil pressure sensor from the hole in the cylinder head and install a known-good sensor instead. If the indicator goes out, the turned-out sensor is faulty)
- Replace the faulty low oil pressure sensor
The engine is overheating (the needle of the coolant temperature gauge is in the red zone of the scale)
Faulty temperature sensor or gauge (Check the gauge and gauge with a tester)
- Faulty sensor, pointer - replace;
Defective ones thermostat (Check the thermostat)
- Replace the faulty thermostat;
Insufficient amount of coolant (Liquid level is below the “MIN” mark on the expansion tank)
- Eliminate leaks, add coolant;
A lot of scale in the cooling system
- Flush the cooling system with a descaling agent. Do not use hard water in the cooling system. Dilute concentrated antifreeze only with distilled water
Radiator cells dirty (Inspection)
- Rinse the radiator with a jet of water under pressure;
Coolant pump defective (Remove pump and inspect assembly)
- Replace the pump assembly;
The cooling fan does not turn on (Check the switching circuits of the electric fan)
- Restore contact in electrical circuits. Faulty fuse, relay, electric motor, temperature sensor, controller - replace;
Unacceptably low octane number of gasoline
- Refuel the car with fuel recommended by the manufacturer;
A lot of carbon deposits in the combustion chamber, on the bottoms of the pistons, valve plates (Inspection after removing the engine cylinder head)
- Eliminate the cause of carbon formation (see "Increased fuel consumption", "Increased oil consumption". Use oil of the recommended viscosity and, if possible, with a low ash content
Breakthrough of exhaust gases into the cooling system through a damaged cylinder head gasket (Expansion tank smells of exhaust gases and bubbles emerge)
- Replace the cylinder head gasket. Check for flatness of the cylinder head
The electric fan of the engine cooling system is constantly running (even on a cold engine)
An open in the coolant temperature sensor or its circuit (The sensor indicator is on and the circuits are checked with an ohmmeter)
- Replace the faulty sensor;
The contacts of the relay for turning on the electric fan do not open (Check with a tester)
- Replace the faulty relay;
The controller or its circuits are faulty (Check the controller or substitute with a known good one)
- Replace failed controller
The engine takes a long time to warm up to operating temperature
Thermostat is faulty (Check if the thermostat is working)
- Replace the faulty thermostat;
Low air temperature (below -15 °С)
- Insulate the engine: install shields in front of the radiator, but do not cover more than half of its area
Coolant level drop in expansion tank
Damage to the radiator, expansion tank, hoses, loosening of their fit on the nozzles (Inspection. The tightness of radiators (engine and heater) is checked in a bath of water with compressed air at a pressure of 1 bar)
- Replace damaged parts;
Fluid leaking through the coolant pump seal (Inspection)
- Replace the pump;
Cylinder head gasket damaged, defective cylinder block or cylinder head (Oil level gauge has a whitish emulsion. Abundant white smoke from the muffler and oil stains on the surface of the coolant (in the expansion tank) may occur. Coolant leaks on the outer engine surface)
- Replace damaged parts. Do not use water in the cooling system, fill in coolant suitable for climatic conditions
Extraneous noises and knocks in the engine
Clearances in the valve drive are not adjusted (Check the clearances)
- Adjust gaps;
Settlement or broken valve springs (Engine Dismantling Inspection)
- Repair the engine;
The timing belt is worn out. Faulty drive tensioner (Inspection)
- Replace the belt. Replace the faulty timing chain tensioner;
Knock of crankshaft and camshaft, connecting rod and main bearings, pistons, piston pins, play, whether jamming in the bearings of the generator, coolant pump (Check)
- Repair or replacement of parts;
Lost elasticity or collapsed one or more supports of the power unit (Inspection)
- Replace the support;
Low pressure in the oil line at minimum idle speed, the pressure in the lubrication system of a warm engine must be at least 2.0 bar)
(Check the pressure in the lubrication system. You can measure the pressure by connecting a pressure gauge to the oil line by unscrewing the oil pressure sensor)
- Troubleshoot the lubrication system
Strong engine vibration
Uneven compression across the cylinders is more than 2 bar: gaps in the valve drive are not adjusted, wear or damage to valves, seats; wear, sticking or breakage of piston rings (Check the compression. Compression should be at least 11 bar)
- Adjust valve clearances . Replace defective parts;
Damage to the insulation of high-voltage devices and circuits - interruptions in sparking (Use an ohmmeter to check for an open or "breakdown" of the ignition coil winding and high-voltage wires)
- Replace the faulty ignition coil, damaged high-voltage wires. Under severe operating conditions (salt on the roads, frost alternating with thaws), it is advisable to replace the wires every 3-5 years;
The high voltage wires are connected to the ignition coil in the wrong order; one or more wires are disconnected (Inspection)
- Connect the wires in accordance with the markings on the ignition coil;
Defective spark plugs (Check spark plugs)
- Replace defective spark plugs
The gap between the electrodes of the candles does not correspond to the norm (The gap of 1.0-1.1 mm is checked with a round probe)
- By bending the side electrode, set the desired gap or replace the candles;
Heavy soot on the electrodes of the spark plugs; soot particles getting into the gap between the electrodes (Inspection. By soot, you can, as a rule, determine the performance of the spark plug and the condition of the engine)
- Clean the spark plugs with compressed air or mechanically. (Do not damage the insulator!). Identify and eliminate the cause of increased carbon formation in the combustion chamber, if necessary, replace the candles;
Open or short circuit in the injector windings or their circuits (Check the injector windings and their circuits with an ohmmeter)
- Replace faulty injectors, ensure contact in electrical circuits;
Nozzles are leaking (overflow) or their nozzles are dirty (Check the tightness and shape of the nozzle spray pattern)
- Dirty nozzles can be washed on a special stand Replace leaky and heavily contaminated nozzles;
Idle speed regulator or its electrical circuit is faulty (warning lamp may be lit. Replace the regulator with a known good one)
- Replace the faulty regulator;
The supports of the power unit have lost their elasticity or collapsed, their fastening has weakened (Inspection)
- Replace the supports, tighten the fasteners
Increased content of harmful substances in exhaust gases
Nozzles are leaking (overflow) or their nozzles are dirty (Check the tightness and shape of the nozzle spray pattern)
- Dirty nozzles can be washed on a special stand. Replace leaking and heavily soiled nozzles;
Insulation damage on high voltage appliances and circuits - intermittent sparking (to test high voltage wires and ignition coils, replace them with known good ones)
- Replace the faulty ignition coil, damaged high-voltage wires. Under severe operating conditions (salt on the roads, frost alternating with thaws), it is advisable to replace the wires every 3-5 years;
Defective spark plugs: current leakage through cracks in the insulator or carbon deposits on the thermal cone, poor contact of the center electrode (Check spark plugs)
- Replace defective spark plugs;
The phase sensor or its circuits are faulty (the signaling device is on. Check the health of the phase sensor with a tester)
- Restore the contact in the electrical circuits, replace the faulty sensor;
Faulty coolant temperature sensor (Check the resistance of the sensor with an ohmmeter at various temperatures)
- Replace the faulty sensor
Throttle position sensor or its circuits are faulty (Warning lamp is on. Check the throttle position sensor is working)
- Restore the contact in the electrical circuits, replace the faulty sensor;
One or both oxygen concentration sensors are faulty (The indicator is on. You can evaluate the performance of the oxygen concentration sensors and the reliability of the connections of their electrical circuits using diagnostic equipment.)
- Repair damaged electrical circuits. Replace defective sensor(s);
Mass air flow sensor and its circuits are faulty (warning lamp is on. You can check the health of the mass air flow sensor using diagnostic equipment)
- Restore contacts in electrical circuits. Replace the defective mass air flow sensor;
The controller or its circuits are faulty (substitute a known-good controller for testing)
- Restore contacts in electrical circuits. Replace the faulty controller;
Leakage of the exhaust gas system in the area between the collector and the pipe of the additional muffler (Inspection at medium crankshaft speed)
- Replace the defective gasket, tighten the threaded connections;
Faulty exhaust gas catalytic converter (Warning light is on. You can check the serviceability of the exhaust gas catalytic converter using diagnostic equipment)
- Replace the catalytic converter;
Increased pressure in the fuel lines due to a malfunction of the pressure regulator (Inspection p, checking the pressure in the fuel system with a manometer (no more than 4.0 bar) at idle)
- Replace the faulty regulator
The engine control system warning lamp lights up when the engine is running
The controller, sensors, injectors or their circuits are faulty. The malfunction may be temporary, then the signaling device may turn off by itself, without any intervention (See the previous sections of fault diagnosis. Complete diagnosis of the control system is carried out using specialized equipment)
- If most of the sensors fail (except for the crankshaft position sensor), you can drive to the place of repair on your own. Replace faulty controller, sensors, injectors, wires;
Separate sensors, injectors were disconnected (possibly for testing), after which the ignition was turned on (the engine was started). At the same time, the corresponding fault code is recorded in the computer's memory, which is not erased even after the electrical connections are restored
- Remove the negative wire terminal from the battery terminal for at least 10 seconds. In this case, all fault codes are erased from the controller's memory