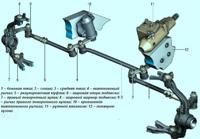
The ignition system uses a 4-pin ignition coil, which is a block of two 2-pin ignition coils
The ignition system has no moving parts and therefore requires no maintenance or adjustments, except for the spark plugs.
The current in the primary windings of the ignition coils is controlled by the controller, which uses information about the engine operating mode received from the sensors of the engine management system.
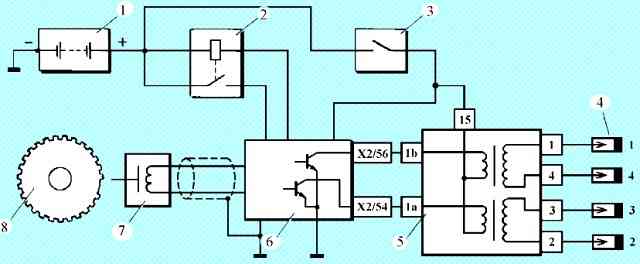
To switch the primary windings of the ignition coils, the controller uses two powerful transistor valves (Fig. 1).
The ignition system uses a spark distribution method called the "blank spark" method.
Engine cylinders are combined in pairs 1-4 and 2-3, and sparking occurs simultaneously in two cylinders: in the cylinder in which the compression stroke ends (working spark), and in the cylinder in which the exhaust stroke occurs (idle spark) .

Due to the constant direction of current in the primary and secondary windings, the sparking current of one candle always flows from the central electrode to the side, and the second - from the side to the central one.

A four-pin ignition coil (Fig. 3) has the following circuits:
Primary power circuit
The voltage of the vehicle's on-board network is supplied from the ignition switch to terminal "15" of the ignition coil.
Cylinder 1 and 4 ignition coil primary circuit, terminal "1b"
The controller switches to ground the primary circuit of the ignition coil, which supplies high voltage to the spark plugs of cylinders 1, 4.
Cylinder 2 and 3 ignition coil primary circuit, contact "1a"
The controller switches to ground the circuit of the primary winding of the ignition coil, which outputs high voltage to the spark plugs of cylinders 2, 3.
The ignition coil is non-separable, it is replaced in case of failure.

Spark plugs - A17 DVRM or their analogues with an interference suppression resistor (resistance 4-10 kOhm) and a copper core.
The gap between the electrodes is 1.0–1.1 mm.
Engine knock suppression
The ECM adjusts the ignition timing to prevent engine damage from sustained detonation.
The system has a knock sensor to detect knock

The controller analyzes the signal from this sensor and, upon detection of detonation, which is characterized by an increase in the amplitude of engine vibrations in a certain frequency range, corrects the ignition timing according to a special algorithm.
The adjustment of the ignition timing to dampen detonation is carried out individually for the cylinders, i.e. it determines which cylinder is detonating and reduces the ignition timing for that cylinder only.
In the event of a malfunction of the knock sensor, the corresponding malfunction code is entered into the memory of the controller and the malfunction indicator turns on.
In addition, the controller sets a lower ignition timing in certain engine operating modes, which excludes the occurrence of detonation.