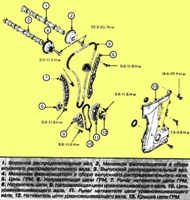
Specifications for automatic transmissions F4A42–1, F4A42–2
Description F4A42–1 / F4A42–2

Torque converter type: 3 elements, 1-stage, 2-phase
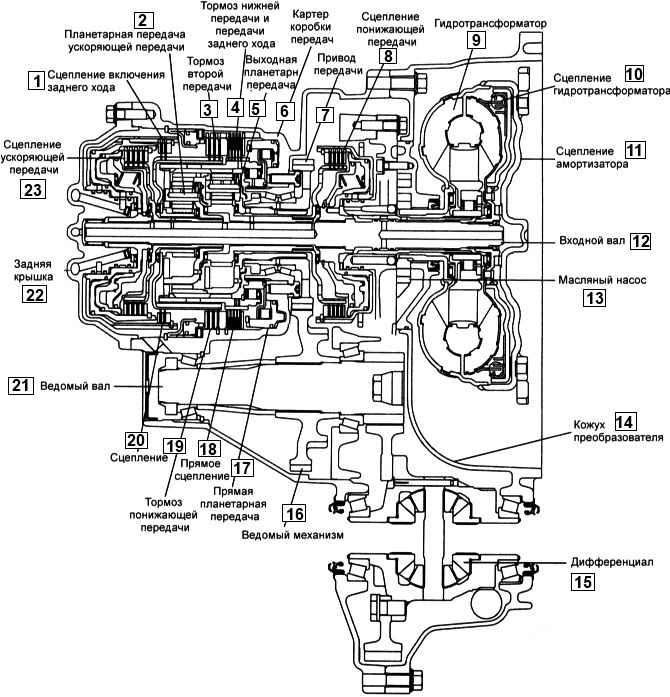
Gear type: 4 forward and 1 reverse
Gear ratio:
- - 1st gear 2.842 / 2.842
- - 2nd gear 1.529 / 1.529
- - 3rd gear 1,000 / 1,000
- - 4th gear 0.712 / 0.712
- - Reverse Gear 2.480 / 2.480
- Final gear: 4.042 / 3.770
Adjustment data
Name - Default value
Preload of driven shaft, mm: 0.01–0.09
Axial clearance of the band brake, mm: 0–0.16
Axial clearance of the band brake of low gear and reverse gear, mm: 1.35–1.81 (F4A42–1) / 1.65–2.11 (F4A42–2)
Axial clearance of the second gear band brake, mm: 0.79–1.25
Axial clearance of the downshift sun gear, mm: 0.25–0.45
Axial clearance of the input shaft, mm: 0.045–0.105
Differential preload, mm: 0.70–1.45
Axial clearance of the underdrive clutch, mm: 1.6–1.8
Axial clearance of shift return spring and overdrive, mm: 0–0.09
Axial clutch clearance of overdrive, mm: 1.6–1.8
Axial clearance of the reverse gear clutch, mm: 1.5–1.7
Gap between differential box and gear, mm: 0.025–0.105
Tightening torques, Nm
Bracket for wiring harness 20-26
Control cable mounting bracket 20–26
Eyebolt 27–33
Oil cooler pipe 10–12
Oil filter 11-13
Input shaft speed sensor 10-12
Output shaft speed sensor 10-12
Control lever 18–25
Transmission range switch 10-12
Vehicle speed sensor 4-6
Valve body cover 8–10
Valve body bolt 10–12
Oil temperature sensor 10–12
Shaft retainer 5–7
Rear cover 20-26
Torque converter housing 42-54
Oil pump
Output shaft locknut 160-180
Output shaft bearing holder 20–26
Oil drain plug 29–34
Differential gear 130–140
Valve body 10–12
Solenoid valve holder 5–7
Lubricants
Genuine Diamond ATF SP–II M Gear Oil
Oil volume, l: 8.5
Sealants
Elements - Sealant
Rear cover - Hyundai Sealant TB1281 B or equivalent
Torque Converter Housing - Hyundai Sealant TB1281 B or equivalent
Valve body cover - Hyundai Sealant TB1281 B or equivalent
Possible malfunctions of an automatic transmission
Fault
- possible causes of the malfunction
No connection with HI - SCAN
If there is no communication with the HI - SCAN, the electrical circuit may be faulty or the TCM is not functioning
- - Damage to the electrical circuit
- - Connector damage
- - TCM corruption
Unable to start the engine
The engine cannot be started when the selector lever is in position N or P.
In such cases, the cause may be a malfunction of the engine control system, torque converter or oil pump.
- - Damage to the engine management system
- - Torque converter damage
- - Oil pump damage
No forward movement
If there is no forward movement when the selector lever is moved from N to D, 3, 2 or L while the engine is idling, the cause may be an abnormal pressure in the pipeline or damage to the reduction gear or valve body.
- - Abnormal pressure in the pipeline
- - Downshift solenoid valve failure
- - Downshift clutch failure
- - Valve body damage
No reverse movement
If there is no reverse movement when the selector lever is moved from N to R while the engine is idling, the cause may be abnormal pressure in the reverse clutch, low and reverse brake, or valve body.
- - Abnormal pressure in reverse clutch
- - Abnormal low pressure in low and reverse brake
- - Low and Reverse Clutch Damage
- - Valve body damage
No forward or backward movement
If there is no forward or reverse movement when the selector lever is moved from N to any position while the engine is idling, the cause may be abnormal pressure in the pipeline, damage to the gearbox, oil pump or valve body.
Abnormal pressure in the pipeline
- - Gearbox damage
- - Oil pump damage
- - Valve body damage
Stop the engine at the beginning of the movement
If the engine stops when the selector lever is moved from N to D or R while the engine is idling, the cause may be damage to the engine management system, clutch damper solenoid valve, valve body, or torque converter
- - Damage to the engine management system
- - Damage to the clutch damper solenoid valve
- - Valve body damage
- - Torque converter damage
Jerking or slow response when moving the selector lever from N to D
If there is a jerk or lag of more than 2 seconds when the selector lever is moved from N to D while the engine is idling, the cause may be damage to the downshift, downshift pressure or clutch, valve body, or position switch
- - Abnormal downshift pressure
- - Abnormal low pressure in low and reverse brake
- - Downshift solenoid valve failure
- - Valve body damage
- - Position switch damage
Jerking or slow response when moving the selector lever from N to R
If there is a jerk or delay of more than 2 seconds when the selector lever is moved from N to R while the engine is idling, the cause may be abnormal reverse clutch pressure or back pressure in the brake system, reverse clutch, brake low gear and reverse gear, valve body or position switch
- - Abnormal reverse clutch pressure
- - Abnormal low pressure in low and reverse brake
- - Low and reverse solenoid valve damage
- - Reverse clutch damage
- - Valve body damage
- - Position switch damage
Jerking or slow response when moving the selector lever from N to D, N or R
If there is a jerk or a delay of more than 2 seconds when the selector lever is moved from N to D or from N to R while the engine is idling, the cause may be abnormal line pressure or damage to the oil pump or valve body.
Jerks and skips
If there is jerky movement while moving the selector lever and shifting into a higher gear than the engine speed, the cause may be abnormal pressure in the pipeline or damage to the solenoid valve, oil pump, valve body, brake or clutch.
- - Abnormal pressure in the pipeline
- - Damage to each solenoid valve
- - Oil pump damage
- - Valve body damage
- - Damage to each brake or clutch
Move Position Changes
All positions
If all travel positions are displaced while driving, the cause may be damage to the output shaft speed sensor, TPS, or solenoid valve.
- - Throttle sensor damage
- - Damage to each solenoid valve
- - Abnormal pressure in the pipeline
- - Valve body damage
Some Provisions
If some movement positions are displaced during movement, the cause may be damage valve body
- - Valve body damage
- - Missing offset
No diagnostic codes
If there is no shift and no DTCs while driving, the cause may be damage to the transmission range switch or TCM
- - Transmission Range Switch Damage
- - Valve body damage
Crashes while driving
Weak acceleration
If the vehicle's acceleration is weak, even if forced downshifting occurs, the cause may be damage to the engine control system, brake or clutch.
- - Damage to the engine management system
- - Brake or clutch damage
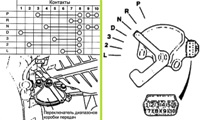
Transmission range switch
Probably caused by damage to the electrical circuit of the interlock switch, ignition switch or TCM
- Ignition lock damage
Vehicle speed sensor
- The reason may be damage to the electrical circuit of the vehicle speed sensor or TCM