Welding tailgate hinges
Remove components and parts that prevent straightening, welding and painting work

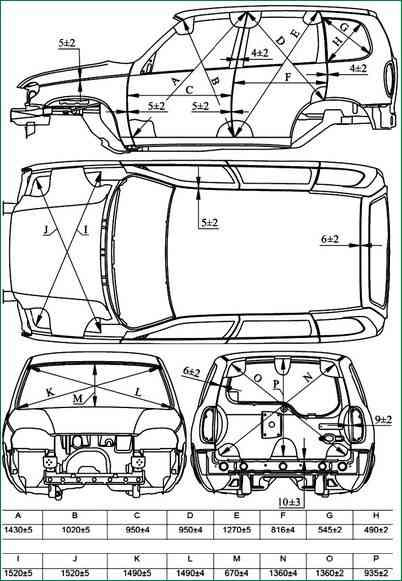
Assemble the upper 1 (Fig. 1) and lower 2 hinges together with the hinge connector 4 on the left pillar of the tailgate opening and fasten without tightening the bolts 3.
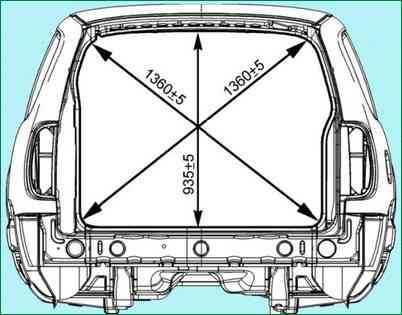
Install the tailgate assembly on the body in place and use the wedges to adjust the gaps and protrusion / recession in accordance with fig. 2.
Perform the operation with an assistant.
Fit the movable (welded) hinge links to the plane of the end of the door in place through the niche of the rear light and tighten the bolts 3.
Punch in the center of the holes in the movable links of both hinges on the end of the door points for drilling holes and mark the position of the movable links with a scriber.
Drill two holes with a diameter of 8.2 mm in the end of the door according to the marking with a core.
Fix the movable hinge links to the door with M8 bolts, nuts and washers.
Carefully, supporting from below, hang the door on the body, fasten the connector and check the tailgate for ease of opening / closing (make sure that the hinge axes are aligned).
Disconnect connector 3, and remove the hinged door assembly from the body without disturbing the position of the moving links on the door pillar.
Install connector 3 on the door.
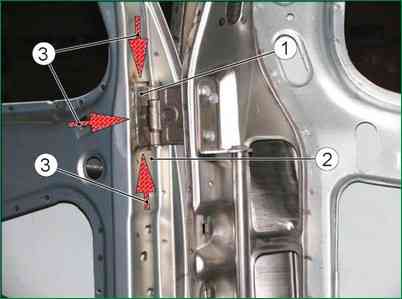
Make sure that the movable links are in the correct position on the end of the door (according to the marks made by the scriber) and weld the links of the movable hinges to the end of the door with a continuous seam with a 3-3.5 mm leg, as shown in fig. 8-142.
Clean up the welds and prepare the repaired area of the door for painting.
Mount the door to the bodywork with the final gap, protrusion/recession fit and adjust the door for ease of opening/closing.
Paint the door and hinges and install the removed components and parts.
Welding side door hinges
Remove components and parts from the car that prevent straightening, welding and painting work on the body
Remove the door from the body.
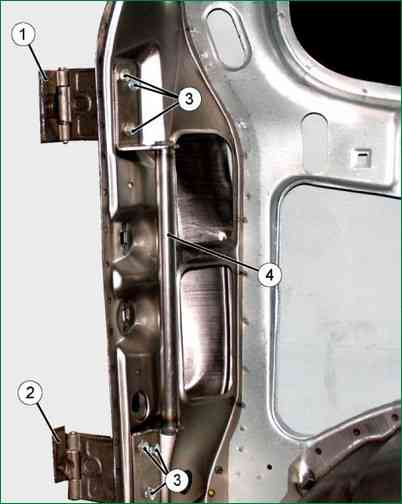
Remove the remains of the damaged hinge link 1 with a cutting machine and clean to the metal the place where the new hinge was welded on the pillar 2 of the body.
Install the side door with hinges in place on the body and, holding it in the closed position, align it along the opening and along the gaps, in accordance with fig. 2, using technological wedges. Perform the operation with an assistant.
While pressing fixed link 1 of the hinge against post 2 (with door 3 closed), tack the hinge to the post at three points around the perimeter of the hinge. Perform the operation with an assistant.
Carefully, while supporting the door from below, check the door for ease of opening / closing (make sure that the hinge axes are aligned and that the gaps of the door with mating parts comply with the requirements of Fig. 2). Perform the operation with an assistant.
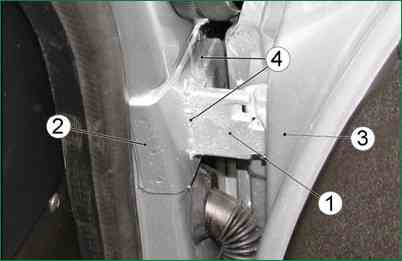
Remove the door and weld the fixed hinge link along the perimeter to the body pillar with a solid seam 4 with a 3-3.5 mm leg, as shown in fig. 4.
Clean up the welds and prepare the repaired body area for painting and anti-corrosion treatment.
Mount the door to the bodywork with the final opening, protrusion/recession fit and adjust the door for ease of opening and closing.
Paint the damaged areas of the paintwork of the door and pillar and carry out an anti-corrosion processing of the welding seam of the fixed link of the hinge and the hidden cavities of the rack.
Install the removed components and parts of the car.
Welding the studs for fastening the threshold lining
Degrease the sill of the sidewall of the right or left body with white spirit or other degreaser available in the company.
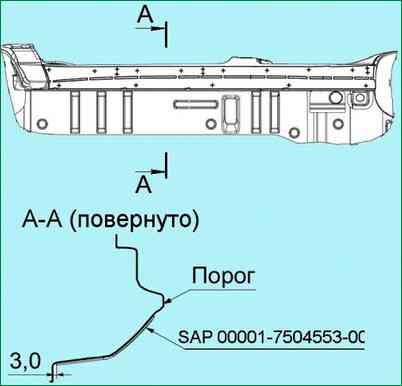
Prepare and apply the tool SAP 00001-7504553-00-00 (fig. 5) according to the instructions for use, on the threshold of the body and align it with the lower flange as shown in fig. 4.
Fix the fixture to the body with adhesive tape, ensuring a snug fit to the surface of the body.
Attention: It is not allowed to use a device with defects that affect the accuracy of marking.
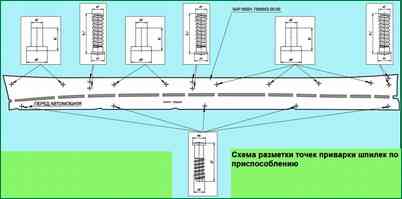
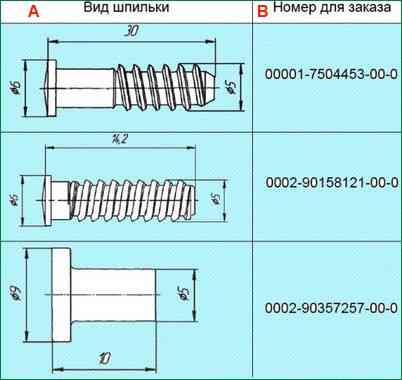
Weld the studs (Table 1) perpendicular to the plane of the threshold according to the marking with three welding points approximately 120 degrees around the circumference of the stud support pad according to the diagram, fig. 6.
Geometric base points of the body
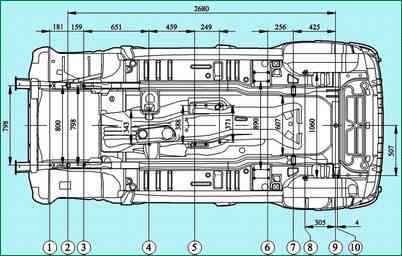
Engine and suspension mounting points: 1; 3 - attachment points of the front suspension; 2 - base holes with a diameter of 20 mm; 4 - attachment points of the rear support of the power unit; 5 - six attachment points of the transfer case; 6 - attachment points of the lower rear suspension arms; 7 - axes of fastening of the upper arms of the rear suspension; 8 - attachment points for rear shock absorbers; 9 - base hole with a diameter of 20 mm; 10 - attachment point of the rear suspension cross bar
Basic attachment points for transmission units
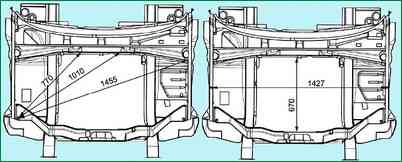
Front body
Rear body
Galvanized metal
For parts operating in a corrosive environment (the lower part of the car), the manufacturer uses one or two-sided galvanized metal.
The share of galvanized parts on the body of a Chevrolet-Niva car is more than 50 percent (by weight).
The following parts are galvanized on the Chevrolet-Niva body:
- 2123 - 5101024/025 floor panel front right/left;
- 2123 – 5101034 middle floor panel;
- 2123 - 5101042 rear floor panel;
- 2123 – 5101056/057 right/left floor threshold connector;
- 2123 – 5101068/069 right/left floor sill box connector;
- 2123 - 5401092/093 side panel inner right/left;
- 2123 – 5401102/103 sidewall lining lower right/left;
- 2123 - 8403024/025 front fender reinforcement rear right/left;
- 2123 - 8403264/265 front fender mudguard right/left;
- 2123 – 8404046/047 rear wing extension right/left;
- 2123 - 5401060/061 body side panel right/left;
- 2123 – 6101014/015 front door panel outer right/left;
- 2123 - 6101024/025 front door panel inner right/left;
- 2123 – 6201014/015 rear door panel outer right/left;
- 2123 - 6201024/025 rear door panel inner right/left;
- 2123 - 6301014 outer tailgate panel;
- 2123 - 6301024 inner tailgate panel;
- 2123 - 8403014/015 fender front right/left;
- 2123 - 8404014/015 rear fender right/left.
Galvanized sheets require different repair methods than conventional steel panels:
When welding galvanized panels in shielding gases, the welding point is more porous than when welding ordinary steel panels. Increase the number of welding points by 10%.
When burned in the welding zone, zinc releases harmful gas. Use personal protective equipment.
Before applying filler to galvanized steel panels, carefully sand the smooth galvanized surface (remove the shine) to increase the adhesion of the putty to the galvanized metal.
Use only epoxy-based body putty when working on galvanized steel panels.
Editing a damaged body
In operation, some cars are damaged as a result of traffic accidents, while the integrity and geometry of the front surfaces, frame and base of the body are violated.
When repairing such vehicles, it is necessary to restore the geometry of the attachment points of units and assemblies on the base of the body.
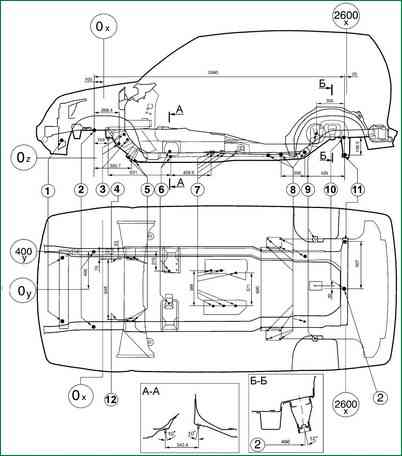
The main reference dimensions of the points of attachment of components and assemblies of the car: 1 - holes for installing a radiator; 2 - base holes 0 20 mm; 3 - fastening of the steering mechanism; 4 - mating plane of the pendulum arm bracket; 5 - stabilizer mounts; 6 - fastenings of the rear support of the power unit; 7 - fastening of the transfer case; 8 - fastening of the rear suspension arms; 9 - rear shock absorber mounts; 10 - base hole; 11- fastening of the transverse rod; 12 - mating plane of the steering mechanism.
The main reference dimensions for checking the base of the body are shown in the figure.
Body damage can vary in complexity.
Therefore, the repair rules in each individual case should be the most suitable for these damages, while it is necessary to use the possibilities of straightening damaged panels to the maximum.
If possible, it is necessary to avoid replacing welded parts so as not to violate the factory complex of anti-corrosion protection of the body.
When performing body repairs, it is recommended to remove components and parts that prevent straightening, welding and painting work in order to facilitate the measurement, control and installation of hydraulic and screw jacks to eliminate distortions and damage to the body.
The protrusion of front surfaces and removable parts relative to adjacent panels is eliminated by fitting and adjusting them.
Repair of deformed surfaces of parts
Repair of damaged body parts is carried out by drawing, straightening, straightening with metal shrinkage, cutting out areas that cannot be repaired, making repair inserts from rejected body parts or sheet metal and shaping them into the shape of a restored part.
The deformed places of the panels are straightened, as a rule, manually using a special tool (hammers, levers, various mandrels) and fixtures.
Heat straightening is used for upsetting (pulling) highly stretched panel surfaces.
To prevent deterioration of the mechanical properties of the metal, the panels are heated to 600-650°C (cherry red color). The diameter of the heated spot should be no more than 10–15 mm.
Straighten panels with metal shrinkage as follows:
- with a carbon electrode of a semi-automatic welding machine or a gas torch, heat the points of metal from the periphery to the center of the defective area and, with blows of a wooden mallet or hammer, upset the heated places on the reverse side of the upset part, using a support or anvil;
- repeat the operations of heating and depositing the metal until the required panel surface is obtained.
Irregularities in the panels can be smoothed out using polyester putties, thermoplastics, cold curing epoxy putties and soldering.
Polyester fillers like "Chempropol-P" or PE-0085 form reliable joints with panels cleaned to metal.
The temperature in the working room should not be below 18°C.
The prepared polyester putty must be used in no more than 10 minutes. It finally hardens 60 minutes after application.
The thickness of the putty layer on the treated surface of the panel should not exceed 2 mm.
Thermoplastic is available in powder form.
The elastic properties necessary for applying it to the metal surface of the panel, it acquires at a temperature of 150–160 ° C.
The surface to be filled must be thoroughly cleaned of rust, scale, old paint and other contaminants.
Thermoplastic has better adhesion to rough metal surfaces.
To apply thermoplastic, the area to be leveled is heated to 170–180°C and the first layer of powder is applied, which is rolled with a metal roller.
Then a second layer is applied and so on until the unevenness is filled.
Each layer is rolled until a monolithic layer of plastic mass is obtained. After curing, the thermoplastic is processed with a straightening saw.
Solders such as POSSu 18-2 or POSSu 25-2 are used to level areas previously filled with solder, build up the edges of parts and eliminate gaps.
In case of significant damage to body parts, they are replaced with new ones using electric arc welding in a shielding gas environment.