Any deviations from the norm on the car (noises, knocks, loss of controllability, etc.) need to determine the source of the malfunction and the method of elimination
- Possible reason
Remedy
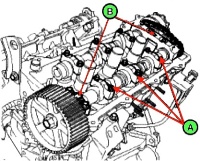
Characteristic high-pitched metallic knock from under the engine valve cover:
- Violation of valve clearances
Adjust valve clearance
- Broken (increased wear) bearings (bearing bearings) of camshafts
Replace or repair timing elements
- Violation in the operation of hydraulic lifters
Replace
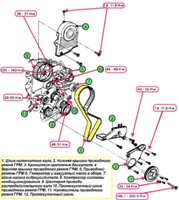
Clunking/hissing noise from under front engine cover (engine front):
- Reduced tension of the timing chain (gas distribution mechanism)
Tighten the chain
- Wear of camshaft drive sprockets
replace
- Increased wear of the timing chain
replace
A dull short knock from the bottom of the engine when starting it (two hits):
- Wear of thrust bearings (half rings) of the crankshaft
replace
Knock (clicks) when the ignition key is moved to the "Start" position:
Clicks while the key is in the "Start" position are due to a malfunction of the starter retaining winding
In an emergency, you can use a screwdriver with an insulating handle to short-circuit the starter holding winding.
rattling (clattering) metallic noise coming from fuel injectors (for diesel engines)
This sound may emit black smoke from the exhaust pipe
- Violation of the injectors, and / or the entire fuel system of the engine.
When dross forms on the injector nozzles, fuel leakage is possible, which may cause a loss of power and black smoke from the exhaust pipe.
Service the fuel system
Squeak, screech, whistle from the front of the engine:
- Wear or decrease in tension of auxiliary equipment drive belts
Tighten or replace belts
Steam from engine compartment:
- Engine overheating due to malfunctions in the cooling system
Stop and let the engine cool down. Perhaps the reason is the very high ambient temperature
Check cooling system fuses and fan failure
Loss of engine power due to overheating
The coolant temperature gauge is in the red zone:
- Insufficient heat removal, as a result of clogging of the radiator cells of the cooling system with foreign objects (road debris, leaves)
Clean the radiator using a special brush
- Breakdown of the cooling fan or wiring problems
Check the technical condition and replace
- Mechanical damage to the radiator
- replace
- Coolant leakage through loose pipe connections or damage to the radiator, cylinder block or block head
Find the leak and fix the problem
- Insufficient coolant level in the system
- add liquid to the required level
Smoke from engine compartment (after engine repair):
After repairing the engine, engine oil often gets on the block and cylinder head, if it is not removed by wiping it with a clean rag, then after turning on and as the engine warms up, smoke will start to come out from under the hood, this is due to oil burnout.
Usually not dangerous, but it's still best to turn off the engine and clean the block and block head with a clean rag.
Make sure that the cylinder head and block are free of engine oil after repair, clean if necessary using a rag and solvent
Slamming in the intake manifold:
- Shift of the ignition timing towards the earlier
This malfunction can lead to serious damage to the intake system and the connecting rod and piston group.
- Make repairs
Difficulty engaging or shifting gears
(for vehicles with manual transmission):
- The clutch leads, that is, the clutch does not completely disengage when the pedal is fully depressed.
At the same time, when switching, a characteristic blow of synchronizers is heard
Adjust clutch pedal stroke
Replace clutch disc
- Malfunction of the gear shift cable
Replace shift cable
- Loose fit or wear of the blocking rings and synchronizer cones
Troubleshoot or replace parts
- Weakening of synchronizer springs
Replace synchronizer springs
- Wrong grade oil filled
Fill in the required brand of oil
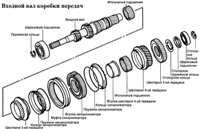
A dull, clicking, short-term knock coming from the gearbox when shifting
(vehicles with manual transmission)
In this case, the knock disappears when the clutch is released twice:
- Increased wear of the synchronizer (s) of the gearbox
- replace
Thunder noise when shifting gears
- (manual and automatic transmission) coming from the central tunnel.
Usually two or three hits:
- Increased wear of the propeller shaft crosses (typical for all-wheel drive and rear-wheel drive vehicles)
- Replace
- Cardan shaft imbalance
Balance
Metal "crunch" and knock when turning the car:
At the same time, the car "breaks" off the trajectory.
- Violation of the main gear differential.
Note:
Basically, this is jamming of the satellites due to wear or misalignment.
Make repairs
Characteristic metallic "crunch" and beating of balls when turning
- (4WD or FWD vehicles):
Dirt getting into the CV joint (constant velocity joint) due to a torn anther
- Replace CV joint
Avoid starting off and increased loads at the start when the wheels are fully turned out (front-wheel drive vehicles), as this can damage the CV joints.
Whistling when pressing the clutch pedal:
- Lack of lubrication or wear of the clutch release bearing
Replace release bearing
Deaf short-term knock when depressing the clutch pedal:
- Gearbox input shaft bearing wear (manual gearbox)
- Replace
- Violation of the gap adjustment in the gearing of the main gear
Disassemble, check the technical condition and adjust
"Buzzing" sound from the side of the final drive (mainly under load):
- Insufficient or no gear oil in the final drive housing
Add or fill in the required amount of gear oil
If there was no gear oil, it is necessary to identify the cause of the leak and check the technical condition of the main gear, in case of increased wear, replace it with a new one
Clutch slip resulting in:
- - the car does not respond to an increase in engine speed, inappropriate car speed.
- - lack of power when driving uphill
In this case, the characteristic smell of the friction material may appear.
- Inappropriate pedal play
Worn or damaged pressure spring
- Clogged clutch hydraulic system
Troubleshoot
- - Excessive wear on the surface of the clutch disc
- - Glazing of the surface of the clutch disc or oil on the surface
- - Damage to the clutch pressure plate or flywheel
- Replace
Spontaneous disengagement of gears:
- Depreciation of the shift forks or breakage of the springs of the clamps in mating
Replace plug or retainer
- Increased clearance of the synchronizer clutch on the hub
Replace hub and synchronizer clutch
Clutch drag/vibration:
- Oil getting on the surface of the clutch disc or cauterization
Check clutch disc
- Malfunction of the clutch pressure plate
Replace clutch basket
- Diaphragm spring damage
Replace clutch basket
- Damage or wear of the damper springs of the clutch disc
Replace clutch disc
- Loose fastening to the engine
- troubleshoot
Deaf metal knock at the top of the shock absorber strut (shock absorber)
- when hitting road bumps or obstacles:
Shock absorber strut support (upper shock absorber mount) broken
Not to be confused with suspension breakdown when hitting a road obstacle
Replace the shock absorber support and check the technical condition of the shock absorber
Rim and wheel hub overheating:
- Misalignment during installation or increased wear of the wheel hub bearing
Replace, adjust
Increased wear on the tie rod end ball joint:
Replace the tie rod end to determine wear:
Hang out the wheel to be checked, place a support under the lower suspension arm.
Grab the wheel at the front and back and rock it horizontally.
If a knock occurs, the ball joint is excessively worn and needs to be replaced
- Increased wear of the ball joint of the lower suspension arm
- Replace
To determine wear:
Hang out the wheel to be checked, place a support under the lower suspension arm.
Grab the wheel at the top and bottom and swing be in the vertical plane.
If there is a knock, ask the assistant to press the brake pedal and repeat the movement of the wheel.
If the noise persists after depressing the brake pedal, the ball joint is excessively worn and needs to be replaced.
Knock coming from car suspension:
- Wheel bearing wear
- Replace
To determine wear:
- - Hang the wheel to be checked, place a support under the lower suspension arm.
- - Grab the wheel at the top and bottom and swing it vertically.
- - If there is a knock, ask the assistant to press the brake pedal and repeat the movement of the wheel.
- - If the knock disappears after pressing the brake pedal, then the wheel bearing needs to be replaced
- - Anti-roll bar wear
- replace
- Wear of the bushings of the anti-roll bar (often manifests itself when turning the car)
- replace
Vibrations on the steering wheel with increasing speed:
- - Vibrations are possible due to poor quality road surface
- - Runout of the steered wheels, as a result of imbalance (with a subsequent increase in speed, shocks are heard in the suspension, car jerks are possible)
Can cause very serious damage to the chassis and steering of the vehicle
Balance the wheels, if necessary, check the technical condition of the chassis as a whole. Check steering wheel alignment
- The fastening elements of the running gear and / or steering have loosened
Self-locking nuts/bolts or slotted nuts are used to fasten the undercarriage and steering components, followed by cotter pins, be especially careful that the nuts are properly cottered when installing.
- - Dirt or ice buildup on wheels and/or wheel arches.
- - Wheel bolts/nuts loosened.
Tighten all running gear components to the required tightening torque
Noise during operation of the hydraulic power steering:
- Air entering the system
Make sure no air gets in through loose connections.
Perform the procedure for removing air from the system, for this:
Put the vehicle in the straight ahead direction.
Open the hood and cap of the expansion tank of the power steering pump.
Start the engine and turn the steering wheel from one extreme position to another to remove air from the system.
Air is removed if there are no air bubbles in the pump reservoir when turning the steering wheel
- Increased wear of the working surfaces of the pump of the power steering system
- replace
- Low fluid level
Fix leaks
- Leakage of the working fluid due to a violation of the tightness of the connections and / or leakage through the seals
- Replace
Swinging car when driving on uneven road surface:
- Leakage of working fluid from the shock absorber (s), as a result of the loss of damping capacity of the shock absorber
- Replace
Moving the car away from straight ahead:
- Violation of the angles of the steered wheels
Adjust installation angles
- Uneven tire wear
See "Types of tire wear"
- Violations in the installation of the steering wheel
Make adjustments
- Sticking brake pads on one side of the car
You can check by hanging each wheel in turn and turning by hand. The wheel should rotate freely, without jamming.
In this case, smoke may appear from the brake mechanism (burning of dust and friction material)
- Violation of the geometric parameters of the suspension elements (levers, steering knuckle, rods)
Check the geometric parameters on a special stand.
If necessary, replace defective parts
- Violations in the operation of passive safety systems ABS, ESP (exchange stability system), ASR (traction control)
Read fault codes using a special scanner.
Repair if necessary
Loss of braking efficiency
(Increased brake pressure required):
- Damage or malfunction of the vacuum brake booster
- Replace
- Excessive wear of the friction linings of the brake pads
Note:
Also, braking may be accompanied by a metallic creak.
- Replace
- Misalignment of the brake pads (violation during installation)
- Replace
- Violation of seal details of one of the hydraulic brake circuits
This will cause the brake pedal to drop about half of its travel
Find the place of depressurization and make repairs
- Freezing of individual elements of the brake mechanism in the winter period of operation
At low speed, press the brake pedal several times to warm up the brakes
The brake pedal failed, the car practically does not slow down:
This is a very dangerous situation, as a traffic accident may result.
The reason is the airiness of the brake system.
Note:
In an emergency while driving, if this situation occurs, you must alternately press the brake pedal several times and, if necessary, carefully use the parking brake
Before each ride, check the technical condition of the brake system (see above) in order to find and fix the problem early. Bleed the brake system.
- Leakage of brake fluid from the hydraulic brake
Find and repair the leak
Extraneous noises of body elements:
- Loose fasteners
Retighten to the correct torque
- Insufficient clearance between body elements
If possible, spread the components apart by loosening and tightening their fasteners to the required torque.
Insulate the components with suitable materials, such as polyurethane pads, foam pads, felt tape or polyurethane tape