Combined lubrication system: the most loaded parts are lubricated under pressure, and the rest - either by directed spraying, or by spraying oil flowing from the gaps between mating parts
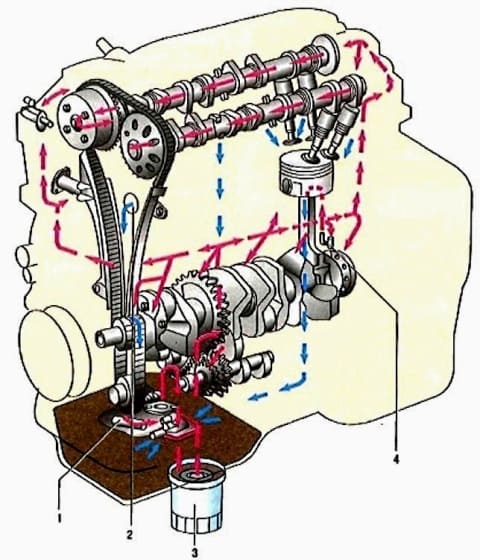
The lubrication system is pressurized by a gear oil pump) mounted externally at the front of the cylinder block and driven by a chain from the front end of the crankshaft. The pump is made with internal trochoidal gearing.
The pump sucks oil from the engine oil sump through an oil receiver with a strainer and through a full-flow oil filter 3 with a porous paper filter element delivers it to the main oil line located in the body of the cylinder block
The oil supply channels to the main bearings of the crankshaft depart from the main oil line
Oil is supplied to the connecting rod bearings through channels made in the body of the crankshaft.
A vertical channel for supplying oil to the camshaft bearings departs from the main oil line
In addition, from the main oil line of the engine, oil is supplied under pressure to oil nozzles 4 for cooling and lubricating the pistons, as well as to the chain tensioner and to the variable valve timing system.
To lubricate the camshaft bearings, oil from the vertical channel enters the central axial channels of the camshafts through radial holes in the outer bearings and is distributed through the channels to the rest of the bearings.
The camshaft cams are lubricated with oil coming from the central axial channels through the radial holes in the cams.
Excess oil is drained from the block head into the oil sump through drain channel 2.
A heat exchanger connected to the engine cooling system is installed between the engine crankcase and the oil filter to cool the oil.
Possible malfunctions of the oil system and solutions
Insufficient oil pressure in a warm engine
- using the wrong brand of oil
Change oil with recommended oil
- dilution or foaming of the oil due to the penetration of fuel or coolant into the oil sump
Remove causes of fuel or coolant intrusion. Change oil
- pollution of the working cavity or wear of the oil pump
Flush or repair the oil pump
- clogged oil filter
Change the oil filter
- loosening or clogging of the oil receiver
Fix the oil receiver, wash its filter
- increased clearance between the main or connecting rod bearing shells and the crankshaft journals
Sandthose necks and replace the liners
- cracks, pores in the walls of the oil channels of the cylinder block or clogging of the oil lines
Repair the cylinder block. If it is impossible to eliminate the defect, replace the block
- loose installation of oil channel plugs or their absence
Re-tighten plugs, install missing plugs
Increased oil consumption
- oil leakage through the engine seals
Tighten fasteners or replace gaskets and seals
- the crankcase ventilation system is clogged
Flush system parts crankcase ventilation
- wear of piston rings or engine cylinders
Rebore cylinders and replace pistons and rings
- breakage of piston rings
Replace rings
- coking of oil scraper rings or grooves in piston grooves
Clean rings and grooves from carbon deposits, change engine oil
- wear or damage to valve stem seals
Replace valve stem seals
- increased wear of valve stems or guide bushings
Replace valves, rebuild cylinder head