The fuel vapor recovery system prevents fuel vapors from escaping into the atmosphere, which adversely affect the environment
The system uses the method of absorbing vapors with a carbon adsorber, which is installed on the fuel tank under the car (can be installed in the luggage compartment, depending on the configuration).
The purge solenoid valve, according to the signals from the engine control unit, switches the operating modes of the system.
Fuel vapors from the fuel tank are constantly discharged through the pipeline and accumulate in the adsorber filled with activated carbon (adsorbent).
When the engine is running, the adsorbent is regenerated (recovered) by purging the adsorber with fresh air entering the system under the action of vacuum transmitted through the pipeline from the receiver to the adsorber cavity when the purge valve is opened.
The control unit regulates the degree of adsorber purge depending on the engine operating mode by sending a signal to the valve with a variable pulse frequency.
Fuel vapors from the adsorber through the pipeline enter the engine receiver and burn in the cylinders.
Failures in the evaporative emission system can lead to unstable idling, engine shutdown, increased toxicity of exhaust gases and poor driving performance.
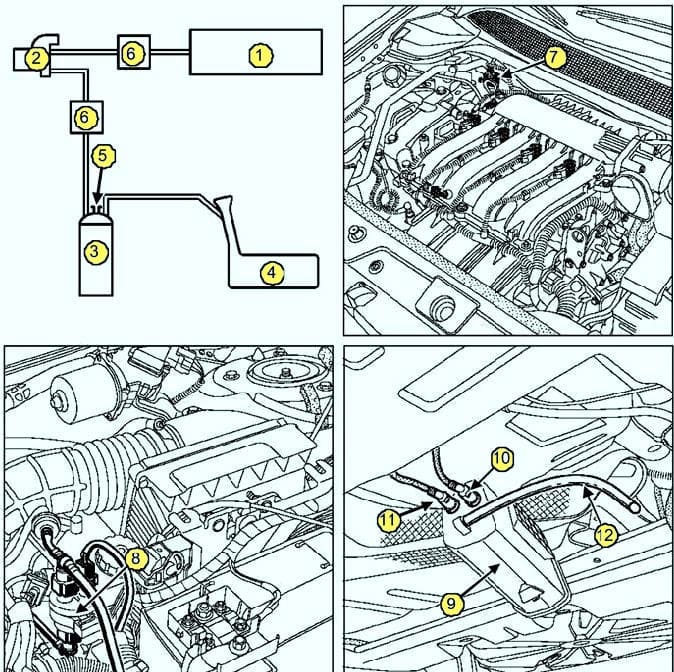
Fig. 1. Functional diagram and arrangement of elements of the toxicity reduction system: 1 - intake manifold; 2 - solenoid valve for adsorber purge; 3 - adsorber; 4 - fuel tank; 5 - hole of communication with the atmosphere; 6 - check valve (only on the F4R 776 engine); 7 - solenoid valve purge adsorber K4M; 8 - canister purge solenoid valve (F4R); 9 - adsorber; 10 - pipeline for supplying gasoline vapor from the fuel tank; 11 - pipeline for supplying gasoline vapors to the intake manifold; 12 - communication tube with adsorber atmosphere
Communication with the atmosphere of the fuel tank is carried out through the adsorber (fuel vapor trap).
Gasoline vapors are retained by the activated carbon contained in the adsorber.
Gasoline vapors from the adsorber enter the engine, where they burn out.
To do this, the absorber is connected to the intake manifold using a solenoid valve located on the mudguard cup.
The principle of operation of the solenoid valve is to change the flow area depending on the signal of the degree of cyclic opening coming from the injection computer.
The change in the flow area of the fuel vapor channel in the solenoid valve occurs due to the balance between the magnetic field created by the winding supply voltage and the force of the return spring, which ensures the closing of the solenoid valve.
Canister Purge Conditions
The control signal to the canister purge solenoid valve is supplied through contact C-E1 of the computer connector under the following conditions:
- - coolant temperature above 55°С;
- – air temperature above 10°С;
- – the engine is not in idle mode;
- – the specified load threshold has been reached;
- - throttle position sensor is not in the "idle" position.
When diagnosing with the "On-Board Diagnostic System", canister purge is not allowed.
Canister Purge Solenoid Valve Cycling Degree can be determined using a scan tool by reading parameter PR102 (Canister Purge Solenoid Valve Cycling Degree).
The solenoid valve is closed below 1.2%.
Removing and checking the adsorber

Squeeze the fasteners of the fuel vapor inlet hose

Disconnect the hose tip from the adsorber fitting

Squeeze the clamps of the tip of the fuel vapor outlet hose

Disconnect the hose tip from the adsorber fitting

Disconnect the atmospheric hose from the adsorber fitting

Pry off with a large screwdriver
Overcoming the elastic resistance of the clamps, remove the adsorber

Install the adsorber in reverse order

Checking the adsorber
Shut off the branch pipe of the pipeline coming from the fuel tank on the adsorber.
Connect the pressure gauge of the instrument (Mot. 1311-01) to the absorber atmosphere connection.
When the engine is idling, make sure that there is no vacuum in the canister atmosphere connection (and also that the value of the parameter "degree of cyclic opening of the canister purge solenoid valve remains minimum" X read on the device is less than or equal to 1.5%) .
If there is a vacuum, then with the ignition off, use a vacuum pump to create a vacuum of 500 mbar at the output of the solenoid valve.
The vacuum must not change by more than 10 mbar in 30 seconds.
If the pressure fluctuates, the solenoid valve is defective, replace it.
If the pressure does not change, under purge conditions, the vacuum should increase (at the same time, the parameter value on the screen of the diagnostic tool should increase).
Under this condition, an electrical fault occurs, so the circuit must be checked.
Removing the canister purge solenoid valve
Disconnect the negative battery terminal

We press the retainer of the purge valve wire block

Remove the block

Squeeze the clamps of the purge outlet hose

Disconnect the hose tip from the valve fitting

Remove the valve from the bracket
Squeeze the clamps of the inlet hose tip

Disconnect the hose tip from the valve fitting


Install the canister solenoid valve in reverse order