If you need to repair the cylinder head of the engine installed on the car, remove it ("Replacing the cylinder head gasket")
In most cases, repair of the cylinder head consists of lapping or replacing valves and their guide bushings, replacing or grinding valve seats
Moreover, to perform work related to the repair of valve guides and seats, special tools and equipment are required, so these works must be performed in a specialized service.
In case of such malfunctions as a violation of the tightness of the channels of the jacket of the cooling system and warping of the mating surface to the cylinder block, the block head is replaced.
You will need: "10", "12", "17" wrenches, a spark plug wrench, a magnetized screwdriver (or tweezers) for removing valve spring cotters, a valve spring compressor tool.
Remove all spark plugs.
Remove the three mounting nuts and remove the exhaust manifold heat shield.
Remove the rest of the exhaust manifold mounting nuts and remove the manifold and the gasket installed underneath.
Remove the four upper bolts securing the intake pipe to the block head, unscrew the three lower nuts and remove the intake pipe together with the throttle assembly and the fuel rail (see "Replacing the intake pipe seal").
Remove the intake pipe gaskets.
Intake pipe gaskets must be replaced with new ones each time the joint is disassembled.
Remove the three mounting bolts and remove the thermostat.
Remove the valve rocker shaft with rocker arms and camshaft
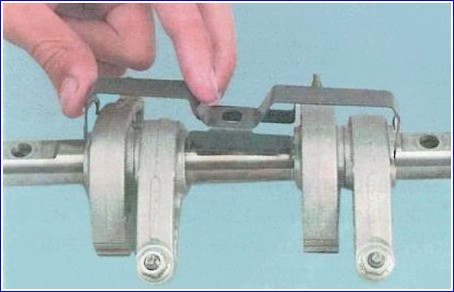
If necessary, remove the rocker and valve rocker retainers from the axle.

If you do not intend to replace the rocker arms, their axle and camshaft, do not remove the rocker arms from the axle in order to install them in their original places during assembly.

Inspect the rocker arms.
Replace the rocker arm if there is severe, clearly visible wear on the surface in contact with the camshaft cam.
Check the cleanliness of the lubrication hole to the camshaft cam.
Check the condition of the head of the adjusting bolt a and if it shows obvious signs of wear
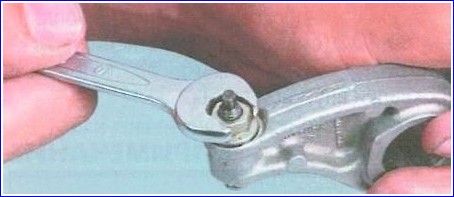
unscrew the locknut of the bolt and remove the bolt from the rocker

Install the valve spring compressor, compress the springs, remove the cotters, spring plates, springs (see "Replacing the valve stem seals") and remove the valves from the guide bushings.
After prolonged use, a mushroom-shaped burr may form on the upper end of the valve.
Remove this burr with a needle file before removing the valve from the valve guide.
It is strictly forbidden to knock the valve out of the guide sleeve with a hammer through the mandrel without removing the burr, as this will inevitably damage the inner surface of the sleeve.
Remove tar deposits from the top surface of the head and from the intake ports.
These deposits can be softened and washed away with kerosene or diesel fuel.
Clean the combustion chambers and exhaust passages from carbon deposits. Remove carbon deposits with a round metal brush installed in an electric drill chuck.
Pre-soak the soot with kerosene.
Be careful: avoid inhaling dust; formed during cleaning of combustion chambers. To prevent the formation of dust, periodically moisten the soot with kerosene,
Clean the inside surfaces of the thin cylinder valve guidesa brush made of copper wire clamped into an electric drill chuck.
Remove burnt gasket residue from the cylinder head contact surface.
It is forbidden to clean the mating surface of the head with metal brushes or emery cloth.
Use a hardwood or plastic spatula after softening the rest of the gasket with solvent.
After cleaning, inspect the head of the block to prevent its operation with damaged threaded holes, cracks (especially between valve seats and in exhaust passages), corrosion, inclusions of foreign materials, shells and fistulas.
It is forbidden to weld cracks, sinks and fistulas. Replace the defective head.
Using a metal ruler mounted on edge and a feeler gauge, check the flatness of the surface of the head to the block in the longitudinal and transverse directions, as well as diagonally.
If the gap between the edge of the ruler and the surface of the head is greater than 0.05 mm, replace the head
Clean the surfaces of the flanges of the head for installing the intake pipe and exhaust manifold from gasket residues and deposits.
Check for deformation of the flanges for the intake pipe and exhaust manifold, replace the deformed head.
Repair damaged threaded holes by threading with taps or installing a repair sleeve (screwdriver).
Determine valve guide wear by measuring the inside diameter of the valve guide bore and the valve stem diameter, and using the difference between these dimensions, determine the gap,
The wear limit for intake valves is 0.10 mm, for exhaust valves - 0.15 mm.
If the gap remains greater than the maximum allowable even when installing new valves, replace the guide bushings.
Have the guide bushings replaced by a specialist workshop that has the proper tools.
Check the condition of the valve seats. The seat faces must be free of wear, pitting, corrosion, and other defects.
Valve seats can be replaced at a specialist workshop.
Minor damage (minor risks, scratches, etc.) can be removed by lapping the valves
More significant defects in valve seats are eliminated by grinding.
Saddles must be ground in a specialized workshop, as this requires special tools and equipment.
If significant seat defects cannot be corrected by grinding, replace the seats. Remove carbon deposits from the valves and inspect them.
Deformation of the valve stem 1 and cracks on its plate 2 are not allowed.
Replace valve if damaged. Check whether the working bevel is too worn or damaged 3.
Grinding of the working chamfer of the valves is allowed (in repair shops with the appropriate equipment).
After grinding, the thickness of the cylindrical part of the plate must be at least 0.5 mm for intake valves and at least 1.0 mm for exhaust valves.
Minor scratches and scratches on the chamfer can be removed by lapping the valve against the seat.
Check the concentricity of the valve disc and seat; apply a thin coat of paint (e.g. Prussian blue) to the chamfer of the valve head, insert it into the guide sleeve and, pressing lightly against the seat, turn it.
By traces of paint on the bevel of the seat, you can judge the concentricity of the valve and seat.
Check the condition of the grooves 4 of the valve stem for crackers.
If there are traces of chipping of the edges of the grooves and wear of the cylindrical part, replace the valve.
Replace valve stem seals.
Inspect the valve springs. Cracks and reduction of elasticity of springs are not allowed.
Springs can be installed in one of two types.
The nominal length of the spring of the first type in a free state is (46.5±2) mm, the second type is (46.64±2) mm.
Length with fully compressed coils, respectively, 26.0 and 23.63 mm.
Springs, the length of which in the free state is less than the permissible, bent (the deviation of the spring axis from the vertical in the free state is more than 4 °) and with cracks, replace.
Check the condition of the spring plates. Replace the plates with significant wear on the support grooves for the springs.
Install all removed parts and components of the cylinder head in the reverse order of removal.
Always replace the gaskets of the cylinder head, intake pipe and exhaust manifold with new ones, since gaskets removed from the engine, even outwardly undamaged gaskets, may be heavily compressed and will not provide a tight seal.
















