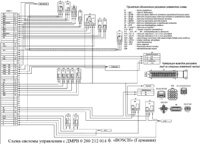
The electronic unit, processing the data received from the sensors of the system, controls the operation of two ignition coils, applying low voltage pulses to them
Sparking occurs simultaneously in two cylinders: the first and fourth or the second and third.
The ignition coil is a transformer that converts low voltage pulses from the control unit into the primary winding into high voltage in the secondary winding.
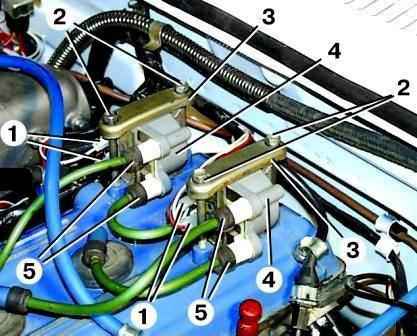
Coils - two-terminal models 3012.3705 or 406.3705.
Their malfunctions are most often explained by overheating or interturn short circuit, due to work with unacceptably large gaps at spark plugs or at the junctions of high-voltage wires.
Checking and replacing ignition coils
Turn off the ignition and disconnect the "negative" terminal of the battery.

Disconnect the two pads from the connectors of the primary winding of the ignition coil.

Disconnect the high-voltage wires from the connectors of the secondary winding of the ignition coil.

We connect an ohmmeter to the terminals of the primary winding of the coil and measure its resistance.

For a working coil, the resistance of the primary winding should be in the range of 0.4-0.5 Ohm.
To get the exact measurement value, by shorting the voltmeter probes, we measure the resistance of the device wires.

We connect an ohmmeter to the high-voltage terminals and measure the resistance of the secondary winding of the coil.
For a serviceable coil, the resistance of the secondary winding should be in the range of 5-7 kOhm.
It is possible to more accurately check the health of the coil only on a special stand.
A good coil should develop a secondary voltage of at least 24 kV, a spark energy of 50 mJ, with a duration of 1.5 ms, with an input signal frequency of 50 Hz.
Replace a faulty ignition coil.

Having disconnected the wires, use the “12” key to unscrew the two bolts securing the coil to the block head cover

And remove the coil.
Install the coil and connect the wires to it in reverse order