Checking and adjusting wheel alignment angles are necessary to ensure good vehicle stability and controllability, as well as even tire wear during operation
Check and adjust wheel alignment angles on special stands in accordance with their operating instructions.
The discrepancy between the actual values measured on the vehicle and the control values indicated in the tables is due to wear or deformation of suspension parts or deformation of the body.
The values given in the table are valid for vehicles with a fully filled fuel tank and a load of 70 kg on the front seats.
After installing the car on the stand (immediately before checking the angles), “press” the car’s suspension, applying a force of 392-490 N (40-50 kgf) two or three times, directed from top to bottom, first to the rear bumper, and then to the front .
The wheels of the car must be located parallel to the longitudinal axis of the car.
When checking and adjusting the front wheel alignment angles, first check the caster angle, then the camber angle, and lastly, the wheel toe-in.
After adjusting the wheel alignment, program the torque sensor and steering wheel angle using the scan tool.
Table of wheel alignment angles
- The camber angle of the front wheels is 0.02′, the maximum difference for the left and right wheels is 0˚30′;
- Toe-in of front wheels 1.2 mm, maximum difference for left and right wheels 1.2 mm;
- The pitch angle of the front wheels is 5˚20′, the maximum difference for the left and right wheels is 0˚30′;
- The camber angle of the rear wheels is -1˚30′, the maximum difference for the left and right wheels is 0˚20′;
- Rear wheel toe-in 1.2 mm, maximum difference for left and right wheel 1.2 mm
Angle of longitudinal inclination of the axis of rotation
The pitch angle of the front wheel steering axis is formed by a vertical and a line passing through the middle of the upper support of the telescopic strut and the center of the ball joint sphere mounted on the lower arm of the front suspension.
Adjustment of the longitudinal inclination of the turning axis is not provided for by the vehicle design.
If the angle deviates from the nominal value, replace damaged and deformed parts.
Maximum value difference between right and left wheels = 30’
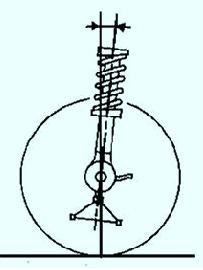
Values - Front suspension position, mm:
- 4°30’±30’ - W2-W1=94;
- 5°06’±30’ - W2-W1=75;
- 5°42’±30’ - W2-W1=62;
- 6°18’±30’ - W2-W1=46
Wheel camber
The camber angle of the front wheels is characterized by the deviation of the average plane of rotation of the wheel from the vertical.
Adjustment of the camber angle of the front wheels is not provided for by the design of the car.
Maximum value difference between right and left wheels = 30’
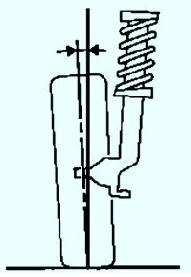
Values - Front suspension position, mm:
- 0°30’±30’ - R1-W1=118;
- -0°01’±30’ - R1-W1=125;
- -0°12’±30’ - R1-W1=146;
- -0°16’±30’ - R1-W1=158
Wheel alignment
Adjustable by rotating the steering linkage couplings
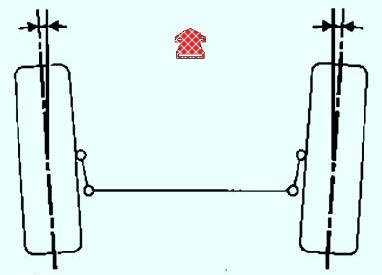
Values - Front suspension position, mm:
- For two wheels Reverse toe 0°10"±10" - Vehicle without load;
- For rims measuring 15"" - 1.1 mm±1.1 mm;
- For rims size 16" - 1.2 mm±1.2 mm;
- For rims size 17"" - 1.3 mm±1.3 mm





